10% Tariff Baseline: Trump's Condition For Trade Deals
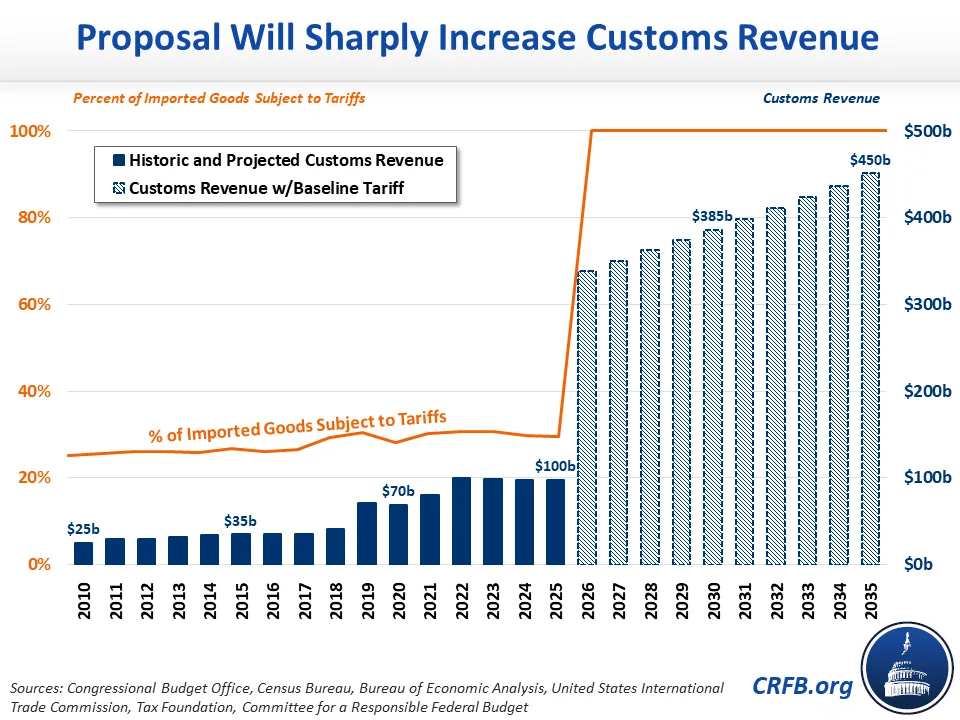
Table of Contents
The 10% Tariff Baseline: A Foundation for Negotiation
The 10% tariff baseline served as a central negotiating tactic for the Trump administration. It wasn't simply a random number; it was a deliberate strategy designed to exert leverage in trade negotiations and reshape the US's relationship with its trading partners. The rationale behind this approach was multifaceted, encompassing both protectionist aims and a desire to renegotiate existing trade agreements perceived as unfavorable to the United States.
-
Leverage: The threat of imposing, or actually imposing, a 10% tariff across a broad range of imported goods provided significant leverage in negotiations. Trading partners faced the prospect of substantial economic repercussions if they didn't concede to US demands. This tactic aimed to force concessions on issues ranging from intellectual property rights to market access.
-
Protectionism: Proponents argued the 10% tariff baseline was necessary to protect American industries from unfair competition and to level the playing field. The underlying assumption was that many US industries were facing undue pressure from imports due to lower production costs or unfair trade practices in other countries.
-
Renegotiation: The administration used the 10% tariff baseline as a catalyst to renegotiate existing trade agreements, such as NAFTA (renegotiated as USMCA). The threat of tariffs was used to pressure other countries into accepting revised terms more favorable to the United States.
Impact on Specific Trade Deals (Examples)
The 10% tariff baseline played a significant role in shaping several key trade negotiations during the Trump administration. The impact varied depending on the specific circumstances and the willingness of the trading partner to compromise.
-
Case study 1: Negotiations with China: The trade war with China involved the imposition of tariffs on hundreds of billions of dollars worth of Chinese goods. While the initial tariffs were not uniformly 10%, the threat of further increases, up to and potentially exceeding the 10% baseline, was a constant pressure point in negotiations. These negotiations eventually led to the "Phase One" trade deal, but the overall impact on the relationship remains complex and heavily debated.
-
Case study 2: Negotiations with Mexico and Canada (USMCA): The renegotiation of NAFTA involved significant discussions regarding tariffs. While a uniform 10% baseline wasn't explicitly applied, the threat of tariffs loomed large, prompting concessions from both Mexico and Canada on issues such as labor standards and intellectual property protections within the resulting USMCA agreement.
-
Analysis: The effectiveness of the 10% baseline in achieving specific trade goals is debatable. While it undoubtedly influenced negotiations, the long-term consequences and the net economic benefit to the US remain subjects of ongoing analysis and controversy among economists. Some argue that it led to beneficial concessions, while others highlight the significant costs associated with trade wars and retaliatory tariffs.
Economic Consequences of the 10% Tariff Baseline
The economic consequences of the 10% tariff baseline were far-reaching, affecting both the US and its trading partners.
-
Increased prices for consumers: Tariffs increased the cost of imported goods, leading to higher prices for consumers. This impact was felt particularly acutely in sectors heavily reliant on imports.
-
Impacts on US businesses reliant on imports: Many US businesses rely on imported components or raw materials. Increased import tariffs led to higher production costs for these businesses, potentially reducing their competitiveness and profitability.
-
Retaliatory tariffs imposed by other countries: The imposition of US tariffs often triggered retaliatory measures from other countries, leading to a tit-for-tat escalation of trade tensions. This resulted in higher costs for US exporters and disruptions to global supply chains.
-
Disruptions to global supply chains: The unpredictable nature of tariff policy disrupted global supply chains, making it more difficult for businesses to plan and operate effectively.
Criticisms and Alternatives to the 10% Tariff Baseline
The 10% tariff baseline faced considerable criticism from economists, businesses, and other stakeholders.
-
Arguments against protectionist trade policies: Many economists argued that protectionist trade policies like the 10% tariff baseline are ultimately harmful to economic growth. They argued that free trade promotes efficiency, innovation, and consumer welfare.
-
Potential for negative economic consequences: The imposition of tariffs can lead to higher prices, reduced consumer choice, and decreased economic competitiveness. The potential for retaliatory tariffs exacerbates these negative consequences.
-
Alternative strategies for securing fair trade practices: Critics suggested alternative strategies to achieve fair trade practices, such as focusing on diplomatic negotiations, strengthening international trade rules, and addressing specific instances of unfair trade practices through targeted measures rather than broad-based tariffs.
-
Focus on multilateral trade agreements: Instead of unilateral tariff actions, many advocated for a greater emphasis on multilateral trade agreements and international cooperation to address global trade imbalances and promote fair competition.
Conclusion
The 10% tariff baseline served as a prominent feature of the Trump administration's trade policy, aiming to leverage tariffs as a tool to renegotiate trade deals and protect American industries. While it undoubtedly influenced negotiations and led to some changes in trade agreements, its overall impact remains a subject of ongoing debate. The economic consequences, including increased prices for consumers, disruptions to supply chains, and retaliatory tariffs, were substantial. Critics argued that the 10% tariff baseline was a protectionist measure with significant negative economic consequences and suggested alternative approaches to achieving fair trade. Understanding the 10% tariff baseline and its implications remains crucial for navigating the complexities of international trade. Further research into the long-term effects of this policy, and a critical examination of alternative trade strategies, are needed to inform future negotiations and foster a more balanced global trade system. Learn more about the impact of 10% tariff baseline policies on global trade by exploring related resources and engaging in informed discussions.

Featured Posts
-
 Dijon Concertation Adoptee Pour La Troisieme Ligne De Tram
May 10, 2025
Dijon Concertation Adoptee Pour La Troisieme Ligne De Tram
May 10, 2025 -
 Watch Pam Bondis Statements On Killing American Citizens Explained
May 10, 2025
Watch Pam Bondis Statements On Killing American Citizens Explained
May 10, 2025 -
 Palantir Technology Stock Buy Before May 5th Wall Streets View
May 10, 2025
Palantir Technology Stock Buy Before May 5th Wall Streets View
May 10, 2025 -
 Sensex And Nifty Today Market Analysis And Key Highlights
May 10, 2025
Sensex And Nifty Today Market Analysis And Key Highlights
May 10, 2025 -
 New Program Offers Technical Skills Training To Transgender People In Punjab
May 10, 2025
New Program Offers Technical Skills Training To Transgender People In Punjab
May 10, 2025
