5% Of Manufacturers Prioritize Cybersecurity: A 41% Point Investment Surge

Table of Contents
In today's interconnected world, manufacturing plants are prime targets for cybercriminals. Sophisticated attacks targeting industrial control systems (ICS) and operational technology (OT) are on the rise, causing significant disruptions and financial losses. Yet, a recent study reveals a startling truth: only 5% of manufacturers prioritize cybersecurity. This alarming statistic underscores a critical vulnerability within the manufacturing sector, highlighting the urgent need for improved cybersecurity in manufacturing. While a 41% point surge in investment has been observed, the question remains: is it enough? This article will explore the alarming lack of cybersecurity prioritization in the manufacturing sector, the significant investment gap, and the crucial steps manufacturers must take to improve their defenses.
2. Main Points:
2.1. The Alarmingly Low Cybersecurity Adoption Rate in Manufacturing
H3: Why are so few manufacturers prioritizing cybersecurity?
The low adoption rate of robust cybersecurity measures in manufacturing stems from a confluence of factors. Many manufacturers lack a comprehensive understanding of the multifaceted risks they face. This lack of awareness often leads to an underestimation of the potential financial and operational consequences of a cyberattack. A common misconception is that cybersecurity is an overly expensive and complex undertaking, particularly for companies with legacy systems. Furthermore, a shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals specializing in industrial control systems (ICS) and operational technology (OT) within the manufacturing sector exacerbates the problem.
- Real-world consequences:
- Production downtime leading to significant revenue loss.
- Data breaches resulting in hefty fines and reputational damage.
- Ransomware attacks crippling operations and demanding exorbitant payouts.
- Intellectual property theft jeopardizing competitive advantage.
H3: The vulnerability of manufacturing infrastructure:
Modern manufacturing relies on a complex interplay of legacy systems and cutting-edge technologies, creating a vast and vulnerable attack surface. Outdated equipment and systems often lack the security features necessary to withstand modern cyber threats. The integration of these legacy systems with newer technologies like IoT devices further complicates security management. Increased reliance on IoT devices, while offering efficiency gains, significantly expands the attack surface, introducing numerous potential entry points for malicious actors. Many manufacturers also lack robust access control and authentication mechanisms, leaving their systems vulnerable to unauthorized access.
2.2. The 41% Point Investment Surge: A Necessary but Insufficient Step
H3: Analyzing the increase in cybersecurity investment:
The observed 41% point surge in cybersecurity investment is largely driven by several factors. Increased awareness of the devastating consequences of cyberattacks, coupled with stricter government regulations and insurance mandates, is pushing manufacturers to prioritize their cybersecurity posture. However, simply increasing investment doesn't guarantee improved security. The effectiveness of these investments depends heavily on proper allocation and implementation.
H3: Where is the investment going?
Much of the increased investment is directed towards crucial cybersecurity solutions. This includes endpoint protection software, network security appliances like firewalls and intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and data loss prevention (DLP) tools. However, the allocation of funds is not always optimized. Some manufacturers may overspend on less critical areas while neglecting fundamental security practices.
- Examples of effective spending: Implementing a robust incident response plan, investing in employee cybersecurity awareness training.
- Examples of ineffective spending: Purchasing expensive security software without proper implementation or skilled personnel to manage it.
2.3. Essential Cybersecurity Measures for Manufacturers
H3: Building a robust cybersecurity strategy:
A comprehensive cybersecurity strategy for manufacturers requires a multi-layered approach. This includes:
- Risk assessment and vulnerability management: Regularly assess and mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
- Strong access control and authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) and robust access control mechanisms.
- Network security measures: Deploy firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and secure network segmentation.
- Endpoint protection: Utilize antivirus software, endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, and patch management processes.
- Data backup and recovery: Implement robust data backup and recovery solutions to minimize data loss in the event of a cyberattack.
- Employee training and awareness: Educate employees about phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and safe password practices.
- Incident response planning: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to effectively manage and mitigate cyberattacks.
H3: Leveraging emerging technologies:
Emerging technologies offer significant potential for enhancing cybersecurity in manufacturing.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML can be used for advanced threat detection and analysis.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology offers secure and transparent data management solutions.
- Cloud-based security solutions: Cloud-based security services can provide scalable and cost-effective security solutions.
3. Conclusion: Securing the Future of Manufacturing through Proactive Cybersecurity
The low adoption rate of cybersecurity measures, coupled with an increased but still insufficient investment, highlights a critical gap in the manufacturing sector's defenses. Proactive cybersecurity is no longer a luxury; it's a necessity for manufacturers to protect their operations, data, and reputation. Don't wait for a devastating cyberattack. Take control of your manufacturing plant's cybersecurity today. Invest in a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, including robust security measures and skilled personnel, and protect your business from the growing threat landscape. For further resources on implementing effective manufacturing cybersecurity, consult industry best practices and relevant cybersecurity standards.

Featured Posts
-
 La Protection Civile En Allemagne Faiblesses Passees Et Ambitions Futures
May 13, 2025
La Protection Civile En Allemagne Faiblesses Passees Et Ambitions Futures
May 13, 2025 -
 Kak Novye Standarty Po Fizike I Khimii Povliyayut Na Detskie Sady
May 13, 2025
Kak Novye Standarty Po Fizike I Khimii Povliyayut Na Detskie Sady
May 13, 2025 -
 Perang Melawan Judi Online Dan Penipuan Telekomunikasi Di Myanmar Strategi Dan Tantangan
May 13, 2025
Perang Melawan Judi Online Dan Penipuan Telekomunikasi Di Myanmar Strategi Dan Tantangan
May 13, 2025 -
 State Of The Union Protest Local Residents Voice Opposition
May 13, 2025
State Of The Union Protest Local Residents Voice Opposition
May 13, 2025 -
 Dodgers Shutout Cubs 3 0 Yamamotos Gem Edmans Homer
May 13, 2025
Dodgers Shutout Cubs 3 0 Yamamotos Gem Edmans Homer
May 13, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Reawakening Of Putins Arctic Naval Forces A Geopolitical Assessment
May 13, 2025
The Reawakening Of Putins Arctic Naval Forces A Geopolitical Assessment
May 13, 2025 -
 Crew Bounce Back 2 1 Victory Over Earthquakes
May 13, 2025
Crew Bounce Back 2 1 Victory Over Earthquakes
May 13, 2025 -
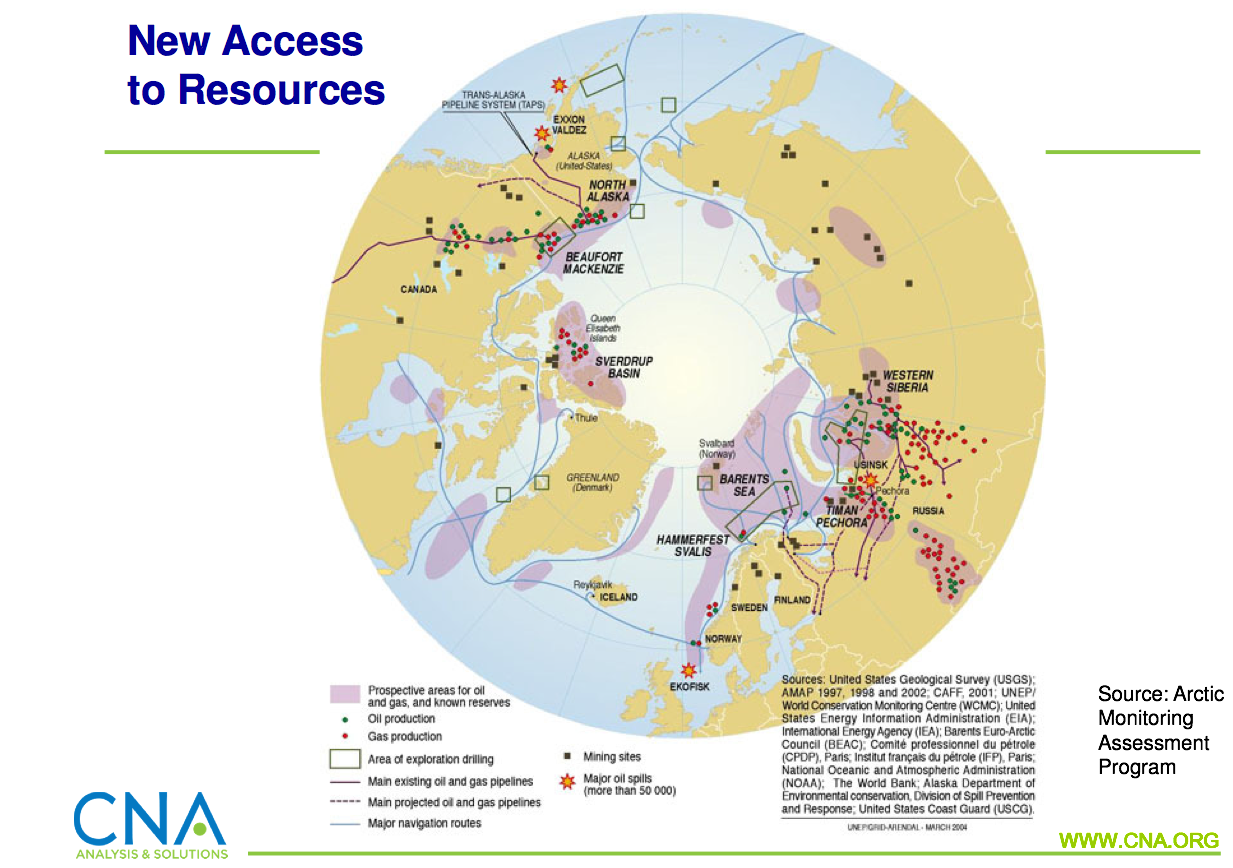 Putins Resurfaced Arctic Fleet Analyzing The Strategic Implications
May 13, 2025
Putins Resurfaced Arctic Fleet Analyzing The Strategic Implications
May 13, 2025 -
 Columbus Crew Defeat San Jose Earthquakes 2 1 After First Loss
May 13, 2025
Columbus Crew Defeat San Jose Earthquakes 2 1 After First Loss
May 13, 2025 -
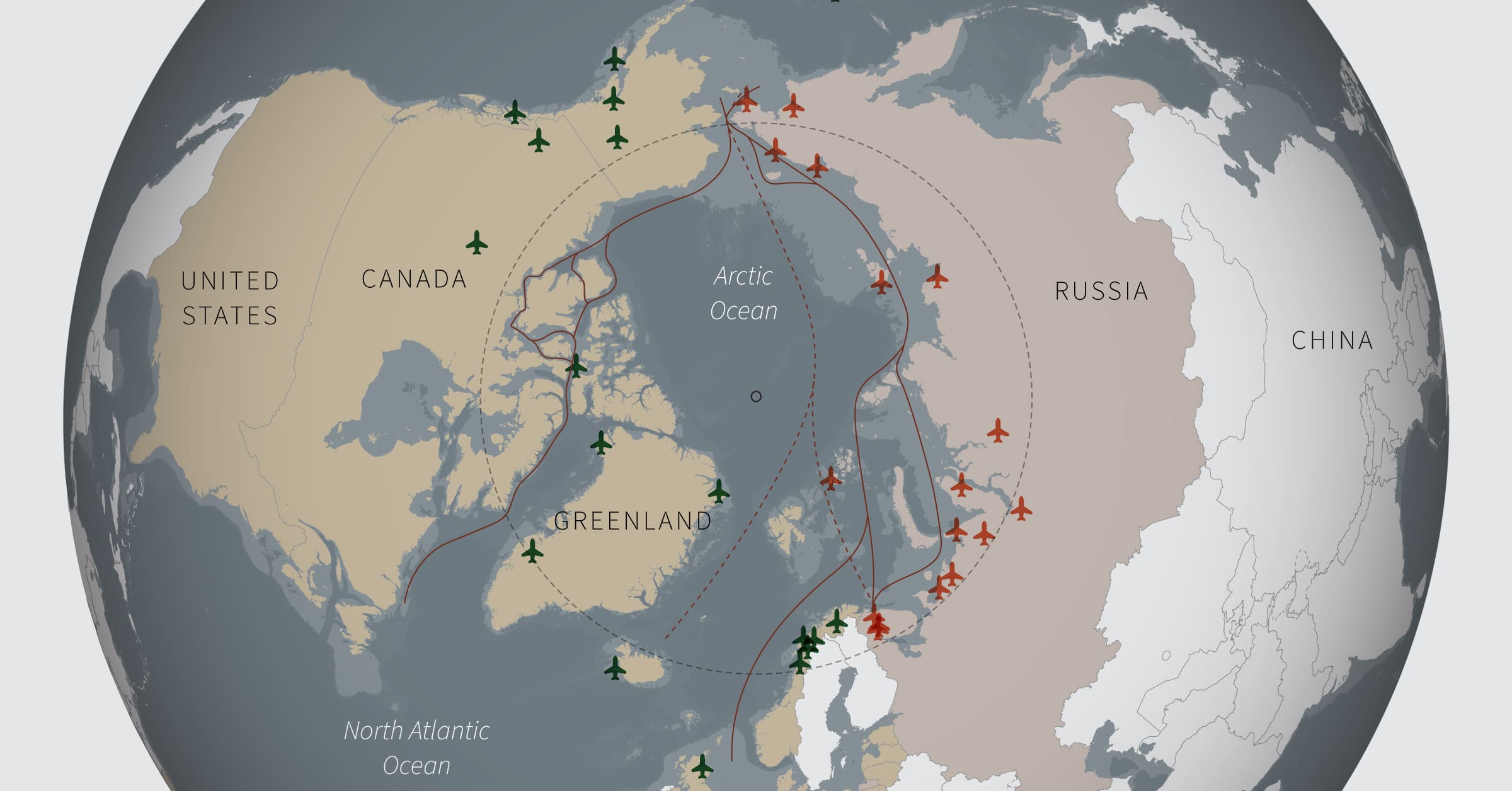 Russias Arctic Shadow Fleet Renewed Activity Sparks Global Concern
May 13, 2025
Russias Arctic Shadow Fleet Renewed Activity Sparks Global Concern
May 13, 2025
