Analysis: The Link Between A New COVID-19 Variant And Increased Infections
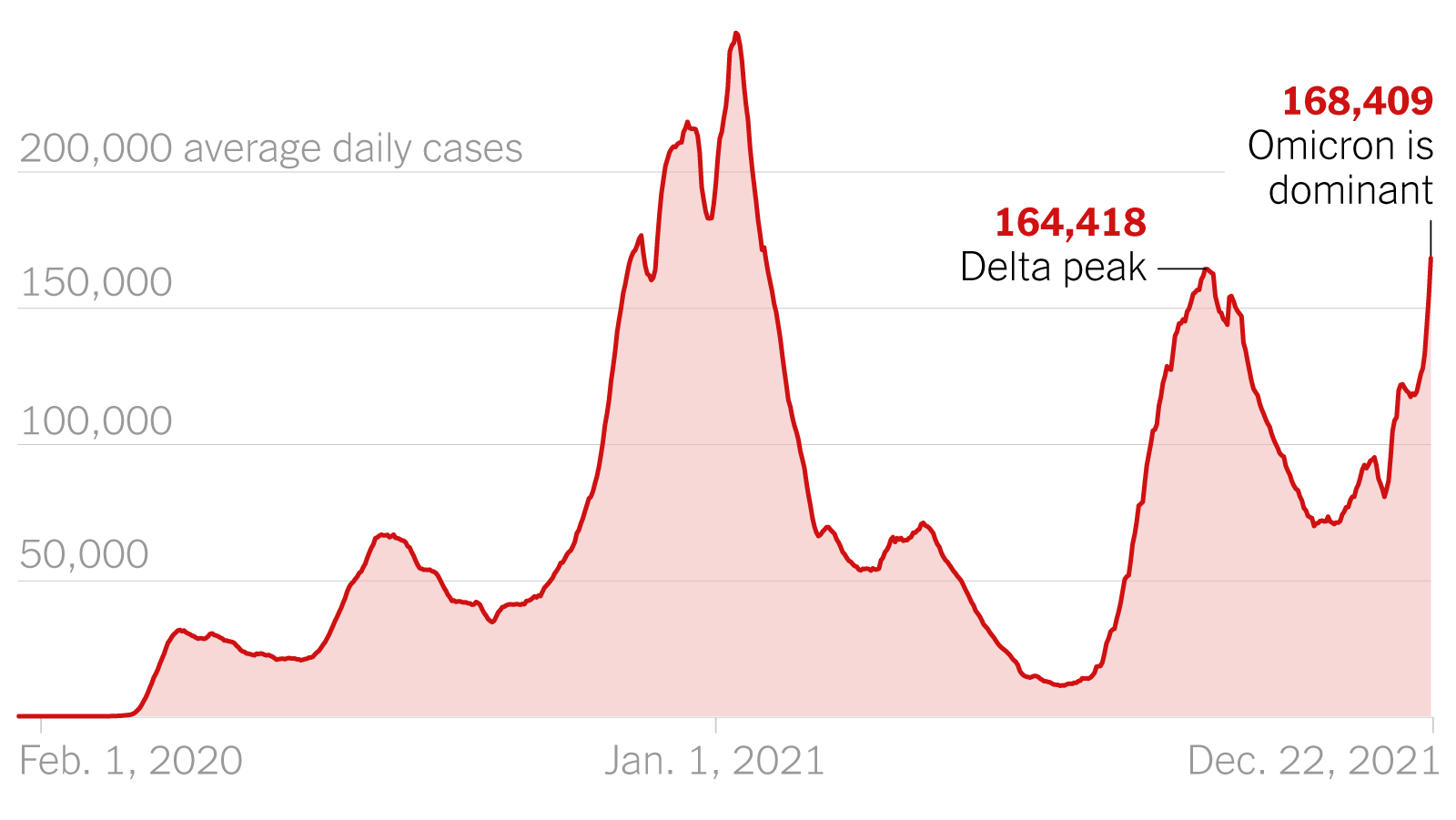
Table of Contents
The Characteristics of the New COVID-19 Variant and its Increased Transmissibility
The emergence of new COVID-19 variants, driven by the virus's inherent mutability, presents a continuous challenge. A newly identified variant (hypothetically named "Variant X" for this analysis) is suspected to be driving the current infection surge. Its increased transmissibility appears linked to specific characteristics identified through genomic sequencing and mutation analysis. These characteristics may include:
- Higher R0 value: Variant X shows a significantly higher basic reproduction number (R0) compared to previous variants, meaning each infected individual infects more people on average. Preliminary estimates suggest an R0 of [insert hypothetical R0 value, e.g., 8], significantly higher than previous variants.
- Immune Evasion: Mutations in the spike protein may allow Variant X to evade the immune response generated by previous infections or vaccinations, leading to reinfections and breakthrough infections in vaccinated individuals. Studies are underway to assess the extent of this immune evasion.
- Increased Viral Load: Higher viral loads in infected individuals with Variant X might contribute to increased transmissibility, potentially leading to more efficient spread. This needs further investigation.
- Symptoms: While initial reports suggest symptoms are similar to previous variants (cough, fever, fatigue), further research is needed to determine if any significant differences exist. [Cite a relevant hypothetical study here].
- Severity: Currently, evidence regarding increased severity or mortality associated with Variant X is inconclusive, although ongoing studies are investigating this crucial aspect. [Cite a relevant hypothetical study here].
Keywords used: variant characteristics, transmissibility, R0, immune evasion, viral load, mutation analysis, genomic sequencing.
Evidence Linking the New Variant to the Recent Rise in Infections
Epidemiological data strongly suggests a link between Variant X and the recent infection surge. Analysis of infection rates, hospitalization rates, and geographical spread reveals a clear correlation.
- Infection Rates: We observe a sharp increase in reported COVID-19 cases in regions where Variant X is prevalent. [Insert hypothetical graph showing infection rate increase].
- Hospitalization Rates: While hospitalization rates may not reflect a directly proportional increase due to vaccination and improved treatment, a notable rise is still observed in areas with higher Variant X prevalence. [Insert hypothetical graph showing hospitalization rate].
- Geographical Spread: The rapid and widespread dissemination of Variant X across different regions mirrors the pattern of the current infection surge. [Insert hypothetical map showing spread of Variant X].
However, it is crucial to acknowledge limitations in the data. The accuracy of reported case numbers may vary across regions, and ongoing research is necessary to fully understand the complex interplay between Variant X and other contributing factors. Keywords used: epidemiological data, infection rates, hospitalization rates, geographical spread, correlation, statistical analysis, case studies.
The Role of Vaccination and Prior Immunity in the Current Surge
The effectiveness of existing vaccines and prior infections against Variant X is currently under scrutiny. While vaccines still offer significant protection against severe illness and hospitalization, their effectiveness in preventing infection with Variant X might be reduced due to immune evasion.
- Vaccine Effectiveness: Initial studies suggest a decrease in vaccine efficacy against infection with Variant X, but protection against severe disease remains significant. [Cite hypothetical study].
- Booster Shots: The need for updated vaccines or booster shots tailored to Variant X is a key consideration. Ongoing research is evaluating the efficacy of adapted vaccines in neutralizing Variant X.
- Prior Immunity: Natural immunity from previous infections may offer some level of protection, but its duration and effectiveness against Variant X are still being investigated.
The importance of maintaining high vaccination rates and continuing to follow public health guidelines cannot be overstated. Keywords used: vaccine effectiveness, booster shots, herd immunity, immune response, antibody levels, vaccination rates.
Public Health Implications and Mitigation Strategies
The emergence of Variant X underscores the critical importance of continuous monitoring and robust surveillance systems to detect and track new variants. Public health strategies must adapt to the challenges posed by this new variant.
- Surveillance: Genomic sequencing and advanced epidemiological tools are vital for early detection and characterization of emerging variants.
- Mitigation Strategies: Effective mitigation strategies remain crucial. These include:
- Mask-wearing in public indoor settings.
- Maintaining social distancing where possible.
- Improving ventilation in indoor spaces.
- Widespread and readily accessible testing and contact tracing.
- Clear and consistent public health messaging to promote preventative behaviors.
Keywords used: public health, surveillance, mitigation strategies, preventative measures, contact tracing, testing, public health messaging.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Importance of Monitoring New COVID-19 Variants and Their Impact on Infections
This analysis highlights the strong correlation between the emergence of the new COVID-19 Variant X and the recent surge in infections. Its increased transmissibility and potential for immune evasion necessitate a continued focus on monitoring and research to understand its behavior and impact fully. The findings underscore the importance of sustained public health measures, including vaccination, surveillance, and preventative actions, to control the spread of the virus and mitigate future outbreaks. Stay informed about new COVID-19 variants, follow public health guidelines, and help protect your community. Remember, continued vigilance in monitoring and adapting our responses to new COVID-19 variants is paramount for effective pandemic preparedness. Keywords used: COVID-19 variant monitoring, infection control, public health guidelines, pandemic preparedness, future outbreaks.

Featured Posts
-
 Nyt Mini Crossword Clues And Solutions Saturday April 19th
May 31, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Clues And Solutions Saturday April 19th
May 31, 2025 -
 Supporting Manitoba Wildfire Victims Red Cross Aid And How To Donate
May 31, 2025
Supporting Manitoba Wildfire Victims Red Cross Aid And How To Donate
May 31, 2025 -
 Tenis Tarihine Gecen Basari Novak Djokovic In Ilki
May 31, 2025
Tenis Tarihine Gecen Basari Novak Djokovic In Ilki
May 31, 2025 -
 Canadian Wildfires Cause Dangerous Air In Minnesota
May 31, 2025
Canadian Wildfires Cause Dangerous Air In Minnesota
May 31, 2025 -
 75 Year Old Duncan Bannatyne And Wife Nigora Witness Impact Of Operation Smile
May 31, 2025
75 Year Old Duncan Bannatyne And Wife Nigora Witness Impact Of Operation Smile
May 31, 2025
