Bank Of Canada Interest Rate Cuts: The Impact Of Tariff-Related Job Losses
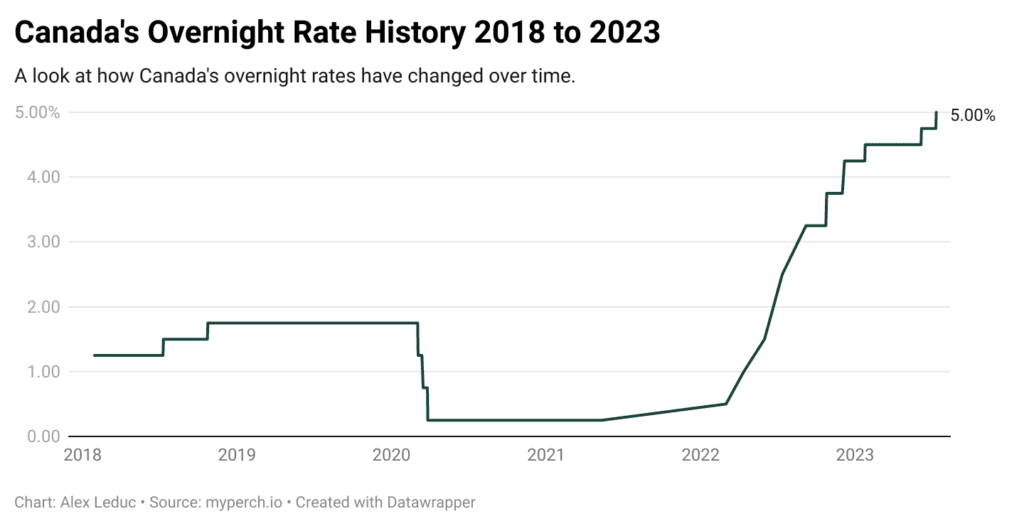
Table of Contents
Understanding the Impact of Tariffs on Employment
Tariffs, essentially taxes on imported goods, can have a profound and multifaceted impact on employment within a country. While proponents argue tariffs protect domestic industries, the reality is often more nuanced. Tariffs lead to job losses, primarily in sectors heavily reliant on imports or exports, such as manufacturing and agriculture. The ripple effect extends far beyond these directly affected industries. For instance, reduced activity in manufacturing can lead to decreased demand for transportation services, impacting logistics and trucking jobs.
- Increased prices of imported goods, leading to reduced consumer demand: Higher prices resulting from tariffs can decrease consumer purchasing power, forcing businesses to cut production and lay off workers.
- Reduced competitiveness of domestic businesses, leading to layoffs: Tariffs can make Canadian goods less competitive in global markets, leading to reduced exports and consequent job losses.
- Retaliatory tariffs from other countries, further harming exports and jobs: If other countries retaliate with their own tariffs on Canadian goods, the negative impact on employment is amplified.
Specific industries significantly impacted by tariffs and subsequent job losses include the Canadian auto industry, which relies heavily on cross-border trade, and the agricultural sector, particularly farmers exporting products to countries imposing retaliatory tariffs.
The Bank of Canada's Response to Economic Slowdown
The Bank of Canada's primary mandate is to maintain price stability and promote sustainable economic growth. To achieve these objectives, it utilizes various tools, most prominently interest rate adjustments. When the economy slows down, as it might following significant tariff-related job losses, the Bank of Canada often employs interest rate cuts to stimulate economic activity.
Interest rate cuts work by making borrowing cheaper for businesses and consumers. This increased affordability can lead to:
- Lower borrowing costs for businesses, encouraging investment and hiring: Reduced interest rates incentivize businesses to invest in expansion, modernization, and hiring new employees.
- Lower mortgage rates, stimulating housing markets and consumer spending: Lower mortgage rates can boost the housing market, which in turn, stimulates related industries and increases consumer spending.
- Increased consumer confidence leading to more spending and job creation: Lower interest rates can lead to greater consumer confidence, resulting in increased spending and subsequent job creation.
Analyzing the Correlation Between Interest Rate Cuts and Tariff-Related Job Losses
Analyzing the correlation between Bank of Canada interest rate cuts and tariff-related job losses requires careful consideration of various economic indicators. While interest rate cuts aim to stimulate the economy and potentially offset some job losses, their effectiveness is not guaranteed and depends on several factors. Data analysis may reveal a correlation, but proving causality is challenging. Other economic factors, such as global economic conditions and inflation, also influence the Bank of Canada's decisions. Furthermore, the impact of interest rate cuts might be delayed and not immediately visible in employment figures. Therefore, solely relying on interest rate cuts to address job losses resulting from tariffs is insufficient.
Potential Future Scenarios and Policy Recommendations
Several future scenarios are possible, depending on future tariff policies and the broader global economic environment. If protectionist policies persist, further job losses in export-oriented sectors are likely. Alternatively, a move toward freer trade could lead to economic recovery and job creation. To mitigate the negative effects of tariffs on employment, a multi-faceted approach is crucial.
Policy recommendations include:
- Diversification of the Canadian economy: Reducing reliance on specific sectors vulnerable to tariffs is essential.
- Investment in worker retraining and support programs: Government support for workers displaced by tariff-related job losses is vital for their reintegration into the workforce.
- Strategic partnerships and trade agreements: Strengthening international trade relationships can help mitigate the effects of protectionist measures.
The Canadian government can also explore targeted support for industries hit hardest by tariffs through subsidies or tax breaks.
Conclusion: The Interplay of Bank of Canada Interest Rate Cuts and Tariff Impacts
In conclusion, the relationship between Bank of Canada interest rate cuts and tariff-related job losses is complex and indirect. While interest rate cuts can stimulate economic activity and potentially mitigate some job losses, they are not a silver bullet. The effectiveness of interest rate cuts is influenced by various other economic factors, and a solely monetary policy-based approach is unlikely to fully address the problems stemming from tariff-related job losses. A multi-faceted approach combining monetary policy adjustments with targeted government interventions, including support programs and initiatives to diversify the economy, is essential. Stay informed about the Bank of Canada's monetary policy decisions and their impact on the Canadian economy – understanding the interplay of Bank of Canada interest rate cuts and tariff-related job losses is crucial for navigating the challenges ahead. For further reading on these complex economic issues, explore resources from the Bank of Canada and Statistics Canada.

Featured Posts
-
 Tzortz Kloynei Kai Antam Santler I Nea Komodia Jay Kelly
May 11, 2025
Tzortz Kloynei Kai Antam Santler I Nea Komodia Jay Kelly
May 11, 2025 -
 Johnson Familys Easter Greetings Include Adorable Son
May 11, 2025
Johnson Familys Easter Greetings Include Adorable Son
May 11, 2025 -
 Guardians Vs Yankees Series Injured List Update April 21 23
May 11, 2025
Guardians Vs Yankees Series Injured List Update April 21 23
May 11, 2025 -
 Ou Investir Mon Argent En 2024 Meilleurs Placements
May 11, 2025
Ou Investir Mon Argent En 2024 Meilleurs Placements
May 11, 2025 -
 Quand C Est L Heure C Est Mueller Analyse Du Match Bayern Inter Milan C1 Quarts
May 11, 2025
Quand C Est L Heure C Est Mueller Analyse Du Match Bayern Inter Milan C1 Quarts
May 11, 2025
