Bank Of Canada Interest Rate Outlook: Tariffs And Employment Weigh Heavily

Table of Contents
The Impact of Tariffs on the Canadian Economy and Interest Rates
Trade tariffs, both imposed on Canada and those imposed by Canada, create significant ripples throughout the economy. These tariffs directly affect import and export prices, impacting inflation and overall economic growth. A trade war, for example, introduces significant economic uncertainty.
-
Increased Cost of Goods: Tariffs increase the cost of imported goods, leading to inflationary pressures. This makes goods and services more expensive for consumers, potentially reducing purchasing power and slowing economic growth.
-
Sector-Specific Impacts: Industries heavily reliant on international trade, such as manufacturing and agriculture, are particularly vulnerable to tariff impacts. These sectors may experience reduced competitiveness and job losses.
-
Retaliatory Tariffs: The imposition of tariffs often leads to retaliatory measures from other countries, creating a cycle of escalating trade tensions and further economic uncertainty. This can significantly impact Canadian exports and exacerbate inflationary pressures.
-
Inflationary Pressures and Interest Rates: The Bank of Canada closely monitors inflation. Sustained inflationary pressures resulting from tariffs could prompt the central bank to raise interest rates to cool down the economy and prevent runaway inflation. This is a key element of the Bank of Canada's monetary policy.
Employment Data as a Key Indicator for Interest Rate Decisions
Employment data, including job creation and the unemployment rate, is a crucial factor informing the Bank of Canada's monetary policy decisions. These economic indicators provide valuable insights into the health of the labor market and the overall economy.
-
Strong Employment and Inflation: Robust job growth often indicates a strong economy, potentially leading to increased consumer spending and inflationary pressures. This might encourage the Bank of Canada to raise interest rates to manage inflation.
-
Weak Employment and Economic Stimulus: Conversely, weak employment data, such as a high unemployment rate, suggests a sluggish economy. In such scenarios, the Bank of Canada might opt for lower interest rates to stimulate economic activity and job creation.
-
Sectoral Differences: The composition of job growth across different sectors (e.g., manufacturing vs. services) also influences interest rate sensitivity. Strong growth in inflation-sensitive sectors may warrant a more aggressive interest rate response.
-
Key Economic Indicators: The unemployment rate, job growth figures, and labor market participation rates are all vital economic indicators that the Bank of Canada meticulously analyzes before making interest rate decisions.
Predicting the Bank of Canada's Next Move: Interest Rate Hike or Hold?
Predicting the Bank of Canada's next move regarding interest rates requires careful analysis of current economic data and forecasts. The interplay between tariffs, employment, and inflation creates a complex scenario.
-
Arguments for an Interest Rate Hike: Strong employment numbers coupled with rising inflation might push the Bank of Canada towards an interest rate hike to curb inflationary pressures and prevent overheating of the economy.
-
Arguments for a Hold: Persistent trade uncertainties caused by tariffs, combined with weak employment growth in certain sectors, could lead the Bank of Canada to maintain current interest rates to support economic growth.
-
Risks Associated with Each Decision: Raising interest rates too aggressively risks slowing economic growth and potentially increasing unemployment. Conversely, maintaining low interest rates for too long could fuel inflation.
-
Short-Term and Long-Term Factors: The Bank of Canada's decision will also consider short-term factors like global economic conditions and commodity prices, as well as long-term economic forecasts and potential risks to financial stability. The value of the Canadian dollar is another important factor. An interest rate forecast must weigh all these elements.
Conclusion: Understanding the Bank of Canada Interest Rate Outlook in a Changing Economic Climate
The Bank of Canada's interest rate decisions are intricately linked to the performance of the Canadian economy, with tariffs and employment data playing significant roles. The interplay between these factors makes predicting the Bank of Canada's next move challenging. While a balanced approach is needed, understanding the influence of tariffs and employment on inflation and economic growth is crucial for informed financial planning. To stay ahead of interest rate changes, we strongly recommend regularly monitoring key economic indicators and the Bank of Canada's announcements. Subscribe to reputable financial news sources and economic reports to stay informed about the Bank of Canada interest rate outlook and make sound financial decisions. Understanding interest rate changes and their impact on the Canadian economy is key to effective economic monitoring.

Featured Posts
-
 Captain America Brave New World Disney Premiere Everything We Know So Far
May 14, 2025
Captain America Brave New World Disney Premiere Everything We Know So Far
May 14, 2025 -
 Bellinghams Future Arsenal Or Manchester United
May 14, 2025
Bellinghams Future Arsenal Or Manchester United
May 14, 2025 -
 Transfer News Chelsea Favored To Sign Jobe Bellingham Over Man United
May 14, 2025
Transfer News Chelsea Favored To Sign Jobe Bellingham Over Man United
May 14, 2025 -
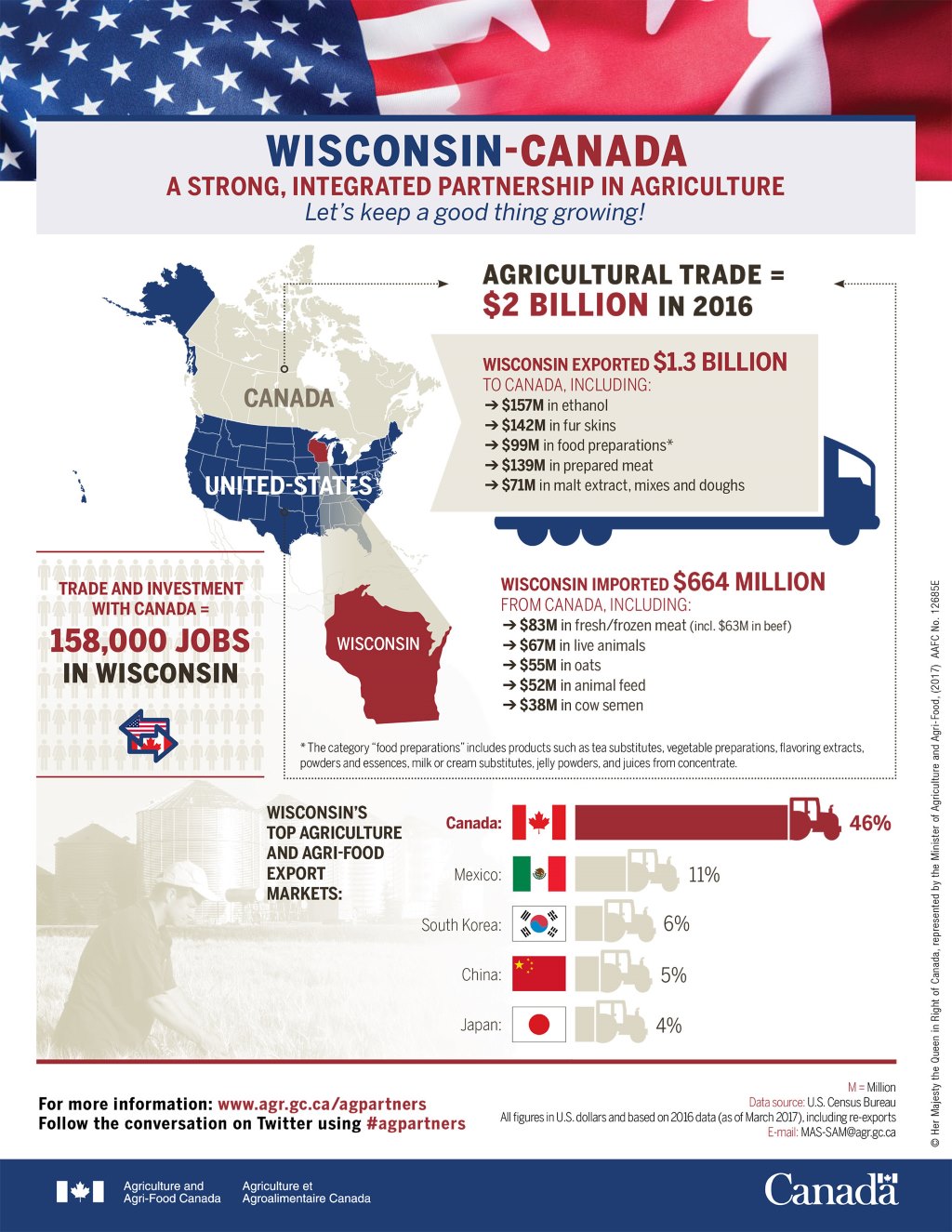 Moose Jaw Hopes Tariffs Will Attract Canadian And American Businesses
May 14, 2025
Moose Jaw Hopes Tariffs Will Attract Canadian And American Businesses
May 14, 2025 -
 Captain America Brave New Worlds Box Office Performance A Disappointing Debut
May 14, 2025
Captain America Brave New Worlds Box Office Performance A Disappointing Debut
May 14, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Traitors Zdrajcy Sezon 2 Odcinek 1 Analiza Konfliktow I Materialy Za Kulisy
May 14, 2025
The Traitors Zdrajcy Sezon 2 Odcinek 1 Analiza Konfliktow I Materialy Za Kulisy
May 14, 2025 -
 Zdrajcy 2 Odcinek 1 Spory Graczy Po Pierwszym Wyzwaniu I Materialy Dodatkowe
May 14, 2025
Zdrajcy 2 Odcinek 1 Spory Graczy Po Pierwszym Wyzwaniu I Materialy Dodatkowe
May 14, 2025 -
 The Traitors Sezon 2 Odcinek 1 Analiza Konfliktow Po Pierwszym Wyzwaniu
May 14, 2025
The Traitors Sezon 2 Odcinek 1 Analiza Konfliktow Po Pierwszym Wyzwaniu
May 14, 2025 -
 Zdrada 2 Odcinek 1 Konflikty Graczy Po Pierwszym Zadaniu Materialy Dodatkowe
May 14, 2025
Zdrada 2 Odcinek 1 Konflikty Graczy Po Pierwszym Zadaniu Materialy Dodatkowe
May 14, 2025 -
 Mlb Power Rankings Winners And Losers At The 30 Game Mark 2025
May 14, 2025
Mlb Power Rankings Winners And Losers At The 30 Game Mark 2025
May 14, 2025
