Bank Of Canada's Inflation Predicament: Navigating The Core Inflation Rise

Table of Contents
Understanding the Rise in Core Inflation
Core inflation, which excludes volatile items like food and energy, provides a clearer picture of underlying price pressures in the economy. A persistent rise in core inflation signals broader inflationary pressures and necessitates a more robust policy response. Unlike headline inflation, which can fluctuate significantly due to temporary shocks, core inflation reflects more persistent inflationary trends. The current rise in core inflation in Canada is a result of several interacting factors:
-
Supply chain disruptions: The lingering effects of the pandemic continue to constrain supply chains, leading to shortages and higher prices for various goods and services. These supply chain bottlenecks impact everything from manufacturing to transportation, fueling inflationary pressures.
-
Strong consumer demand and wage growth: Robust consumer spending, fueled by pent-up demand and government stimulus, has put upward pressure on prices. Simultaneously, strong wage growth, while positive for workers, contributes to inflationary pressures by increasing businesses' labor costs.
-
Housing costs: The Canadian housing market has experienced significant price increases in recent years, contributing substantially to core inflation. This housing inflation affects not only homebuyers but also renters, as rising housing costs translate to increased rental prices.
-
Global inflationary pressures: Canada is not immune to global inflationary trends. Rising commodity prices, particularly energy, and global supply chain disruptions have exerted upward pressure on prices within the Canadian economy. These core inflation drivers are interconnected and complex.
The Bank of Canada's Response to Rising Core Inflation
The Bank of Canada's primary tool for managing inflation is monetary policy, primarily through adjustments to its key interest rate. To combat rising core inflation, the Bank has implemented a series of interest rate hikes. These increases aim to cool down the economy by making borrowing more expensive, thus reducing consumer spending and investment.
-
Timeline of interest rate changes: The Bank has steadily increased its key interest rate over the past year, with a clear timeline of adjustments publicly available on their website.
-
Impact on borrowing costs: Higher interest rates translate to increased borrowing costs for individuals and businesses, impacting mortgage payments, business loans, and consumer credit.
-
Economic forecasts and growth projections: The Bank continuously monitors economic data and publishes forecasts, outlining its projections for economic growth and inflation. These forecasts inform its policy decisions.
-
Potential risks associated with different policy approaches: Aggressive interest rate hikes, while effective in curbing inflation, carry the risk of triggering an economic slowdown or even a recession. The Bank must carefully balance the need to control inflation with the need to avoid unnecessarily harming the economy. This careful balance of Bank of Canada policy is key.
Navigating the Challenges: Balancing Inflation Control and Economic Growth
The Bank of Canada faces the difficult task of navigating a trade-off between controlling inflation and maintaining sustainable economic growth. The challenge is compounded by the inherent difficulty in accurately inflation forecasting. Different economic scenarios present different potential implications:
-
Risks of over-tightening monetary policy: Raising interest rates too aggressively could lead to a sharp economic contraction, resulting in job losses and a significant recession.
-
Risks of under-tightening monetary policy: Failing to raise interest rates sufficiently could allow inflation to become entrenched, making it harder to control in the long run.
-
Potential for a "soft landing" vs. a recession: The Bank aims for a "soft landing," a scenario where inflation is brought under control without triggering a significant economic downturn. However, achieving this outcome is challenging and depends on various factors.
-
Importance of data analysis and forward guidance: The Bank relies heavily on data analysis and provides forward guidance to help manage expectations in the market. This transparency and commitment to data-driven decisions is vital.
Future Outlook and Potential Scenarios
Predicting the future path of inflation and the economy is inherently uncertain. However, several potential scenarios can be envisioned based on different policy choices and economic developments:
-
Scenario 1: Successful inflation control with minimal economic damage. The Bank successfully manages to bring inflation down to its target range with only a mild slowdown in economic growth.
-
Scenario 2: Persistent high inflation requiring further interest rate hikes. Inflation proves more stubborn than anticipated, necessitating further increases in interest rates, potentially increasing the risk of recession.
-
Scenario 3: Recession due to aggressive monetary policy. Aggressive interest rate hikes lead to a significant economic downturn, resulting in job losses and reduced economic activity. This scenario highlights the recession probability associated with aggressive monetary policy tools.
Conclusion: The Bank of Canada's Ongoing Inflation Predicament
The Bank of Canada faces a significant challenge in managing core inflation while simultaneously supporting sustainable economic growth. Understanding the complex interplay between inflation, interest rates, and economic growth is crucial in navigating this inflation predicament. The uncertainties and potential risks involved highlight the difficulty of making optimal policy decisions. To stay informed about the Bank of Canada's actions and their impact on the Canadian economy, regularly check the Bank's website and follow economic news related to core inflation and Bank of Canada policy. Further research into Bank of Canada inflation targets will enhance your understanding of this critical economic issue.

Featured Posts
-
 Understanding Core Weave Inc S Crwv Significant Stock Jump Last Week
May 22, 2025
Understanding Core Weave Inc S Crwv Significant Stock Jump Last Week
May 22, 2025 -
 Abn Amro Rapporteert Forse Groei In Occasionverkoop
May 22, 2025
Abn Amro Rapporteert Forse Groei In Occasionverkoop
May 22, 2025 -
 A Sneak Peek At The Next Gumball Chapter
May 22, 2025
A Sneak Peek At The Next Gumball Chapter
May 22, 2025 -
 New Piglets Gender Revealed An Update From Mummy Pig On Peppa Pig
May 22, 2025
New Piglets Gender Revealed An Update From Mummy Pig On Peppa Pig
May 22, 2025 -
 Prediksi Juara Liga Inggris 2024 2025 Peran Strategi Pelatih Liverpool
May 22, 2025
Prediksi Juara Liga Inggris 2024 2025 Peran Strategi Pelatih Liverpool
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
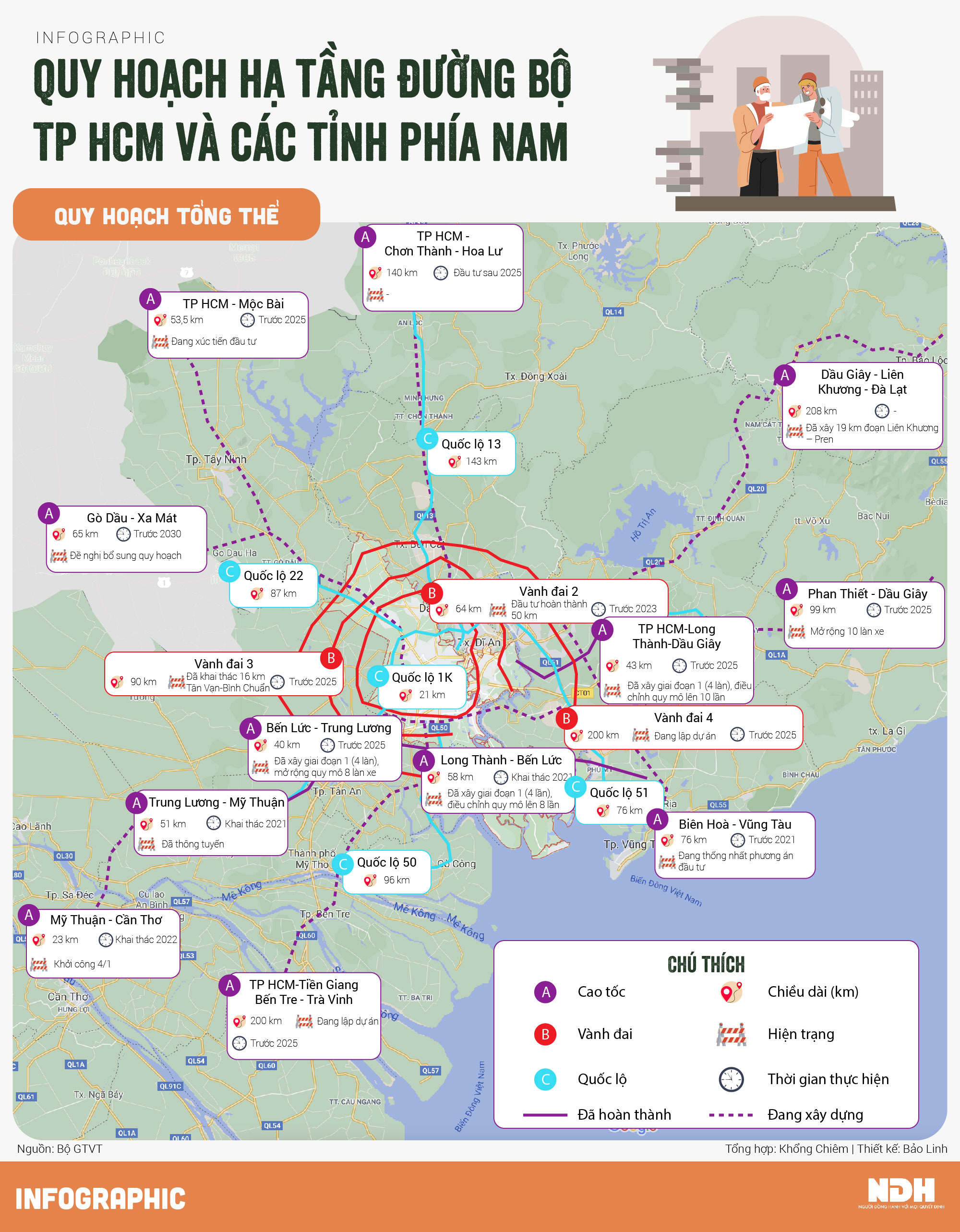 Du An Ha Tang Trong Diem Dong Luc Phat Trien Giao Thong Tp Hcm Binh Duong
May 22, 2025
Du An Ha Tang Trong Diem Dong Luc Phat Trien Giao Thong Tp Hcm Binh Duong
May 22, 2025 -
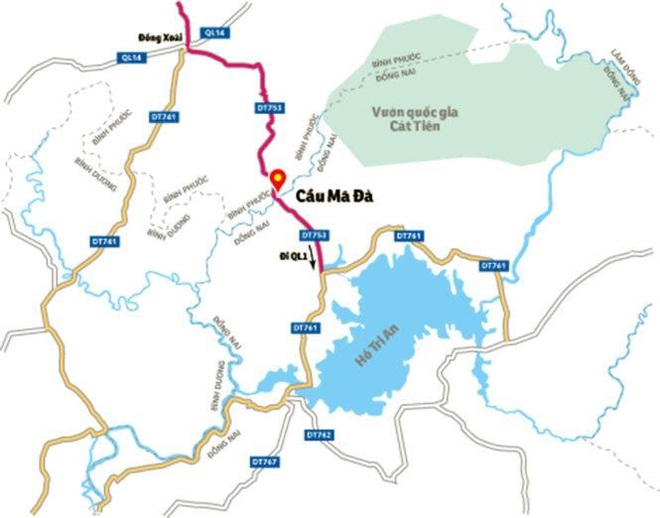 Danh Gia Tac Dong Kinh Te Xa Hoi Cua Du An Cau Ma Da Dong Nai
May 22, 2025
Danh Gia Tac Dong Kinh Te Xa Hoi Cua Du An Cau Ma Da Dong Nai
May 22, 2025 -
 Nhung Du An Ha Tang Thuc Day Giao Thong Tp Hcm Binh Duong
May 22, 2025
Nhung Du An Ha Tang Thuc Day Giao Thong Tp Hcm Binh Duong
May 22, 2025 -
 Cau Ma Da Du An Trong Diem Thuc Day Phat Trien Dong Nai
May 22, 2025
Cau Ma Da Du An Trong Diem Thuc Day Phat Trien Dong Nai
May 22, 2025 -
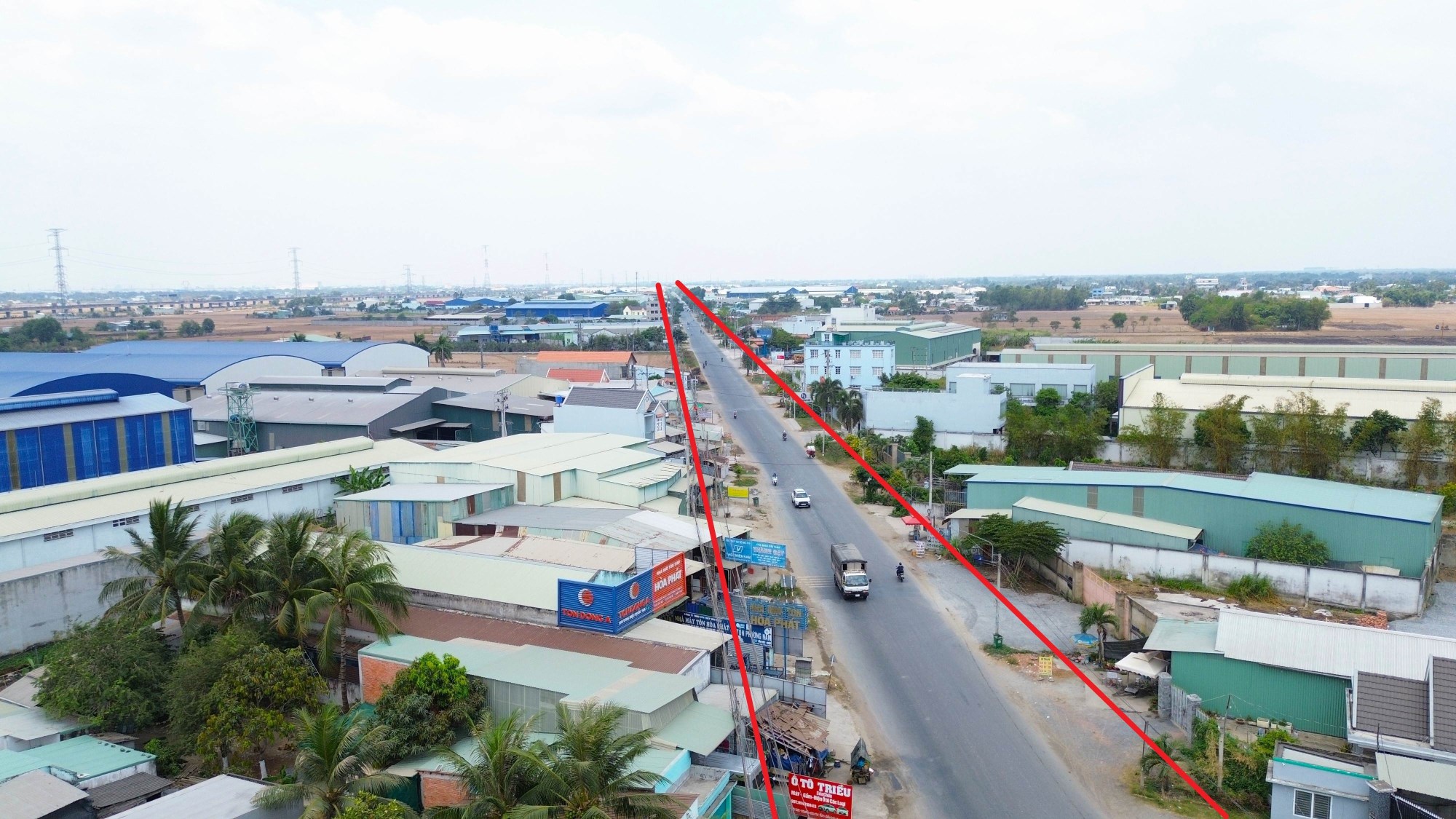 Thuc Day Phat Trien 7 Vi Tri Ket Noi Tp Hcm Long An Can Dau Tu
May 22, 2025
Thuc Day Phat Trien 7 Vi Tri Ket Noi Tp Hcm Long An Can Dau Tu
May 22, 2025
