Canada's Housing Crisis: The Impact Of Large Down Payments
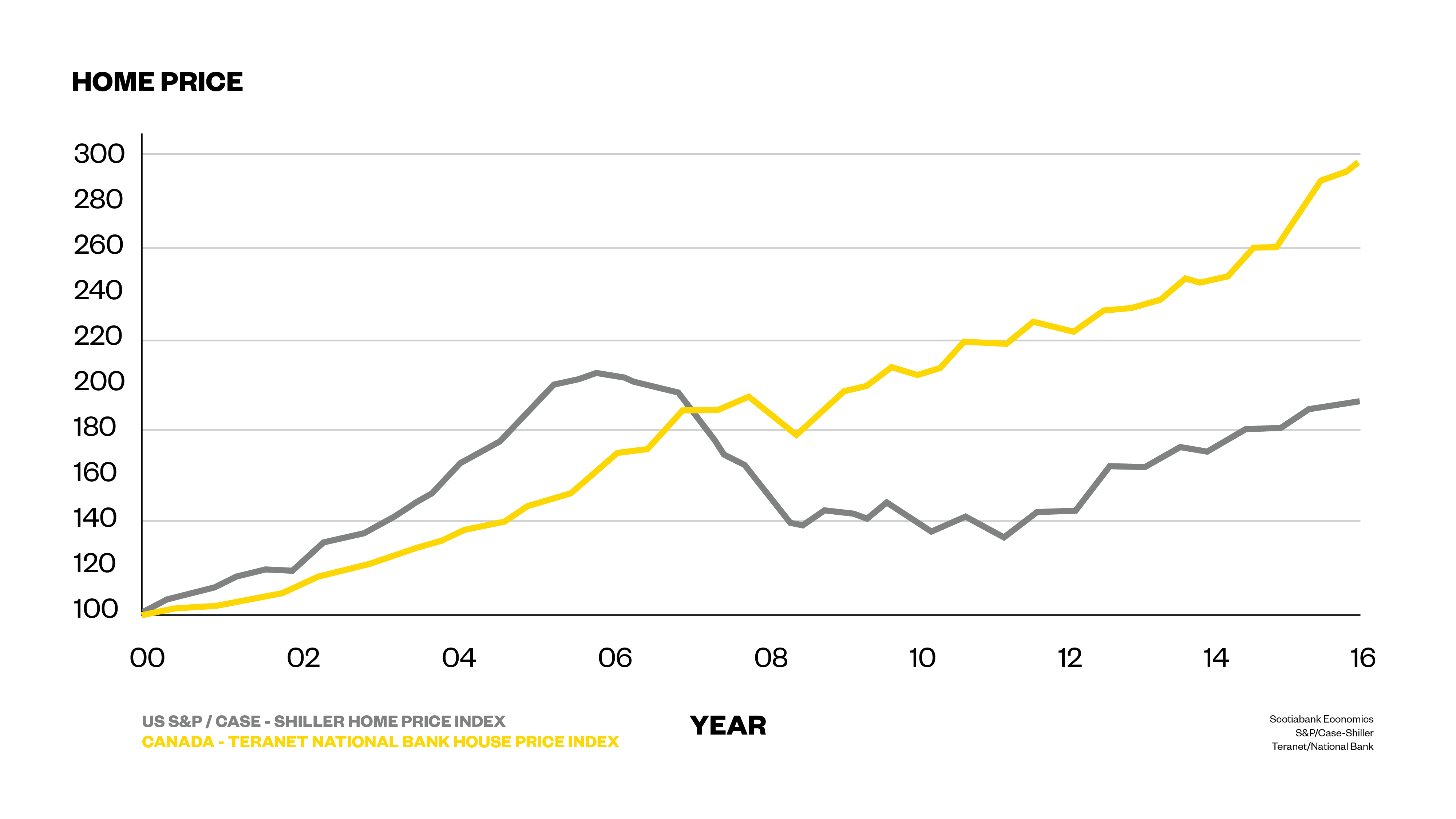
Table of Contents
The Impact of Rising House Prices on Down Payment Requirements
Escalating property values in major Canadian cities are the primary driver of increasingly large down payments. The relentless rise in house prices in urban centers like Toronto, Vancouver, and Montreal has created a significant barrier to entry for prospective homebuyers. What was once a manageable down payment is now often a monumental financial hurdle.
For example, purchasing a modest detached home in Toronto might require a down payment exceeding $200,000, while a comparable property in Vancouver could necessitate even more. In Montreal, while prices are generally lower, the required down payment still represents a substantial portion of many individuals' savings.
- Increased competition among buyers drives up prices: High demand and low inventory fuel bidding wars, pushing prices beyond what many can afford.
- Impact of low inventory on affordability: The scarcity of available homes intensifies competition, further exacerbating the price increases and subsequent down payment requirements.
- The effect of interest rates on mortgage affordability and overall cost: Rising interest rates increase the overall cost of borrowing, making it even harder for buyers to afford both the down payment and the mortgage payments.
The Financial Barrier to Homeownership for First-Time Buyers
Saving for a substantial down payment presents an immense challenge for first-time homebuyers, particularly younger generations. Millennials and Gen Z face a unique set of obstacles, including high student loan debt, stagnant wages, and the rising cost of living. These factors make accumulating the required funds for a down payment exceptionally difficult.
Many are forced to rely on financial assistance from family, highlighting the increasing prevalence of parental assistance in the home-buying process. While shared equity mortgages offer an alternative, these also come with their own limitations and complexities.
- Savings challenges for millennials and Gen Z: High levels of student loan debt and the increasing cost of living make saving for a down payment a long and arduous process.
- The role of student debt in hindering down payment savings: Significant student loan repayments often divert funds that could otherwise be used towards a down payment.
- The psychological impact of the high barrier to entry: The seemingly insurmountable challenge of saving for a large down payment can be demotivating and discouraging for potential homebuyers.
The Disproportionate Effect on Marginalized Communities
The demand for large down payments disproportionately affects racialized and low-income communities, further widening the existing socio-economic gap. Systemic inequalities in access to wealth and resources create significant barriers to saving for a down payment, perpetuating a cycle of disadvantage.
- Systemic barriers faced by Indigenous communities: Generational trauma, historical injustices, and limited access to resources contribute to significant disparities in homeownership rates.
- Access to financial literacy and resources: Lack of access to financial education and resources further limits the ability of marginalized communities to save effectively.
- The impact on intergenerational wealth transfer: The inability to accumulate wealth through homeownership hinders the ability to transfer wealth to future generations.
Policy Implications and Potential Solutions
Addressing Canada's housing affordability crisis requires bold policy interventions that focus on reducing the burden of large down payments. Several potential solutions warrant consideration:
- Review of existing government programs and their effectiveness: A critical assessment of current down payment assistance programs is necessary to identify areas for improvement and expansion.
- Proposals for new policies to support first-time homebuyers: Innovative policy solutions, such as tax incentives for first-time buyers or increased investment in affordable housing, could significantly impact affordability.
- Potential impact of changes to stress test requirements: Relaxing overly stringent stress test requirements could increase mortgage accessibility for some buyers, indirectly impacting the need for substantial down payments.
Conclusion: Navigating Canada's Housing Crisis: A Call for Action on Down Payments
Large down payments are a major contributor to Canada's housing crisis, creating a significant barrier to homeownership for many Canadians, particularly first-time buyers and marginalized communities. The challenges are multifaceted, stemming from rising house prices, systemic inequalities, and insufficient government support. Addressing this crisis demands immediate action.
We urge readers to learn more about existing government initiatives supporting homeownership, explore alternative financing options like shared equity mortgages, and advocate for policy changes that reduce the burden of large down payments. Finding affordable housing and down payment solutions is crucial to ensuring a more equitable and accessible housing market for all Canadians. Let's work together to create a future where the dream of homeownership in Canada is attainable for everyone.

Featured Posts
-
 Tougher Uk Immigration Rules English Language Proficiency Key To Residency
May 10, 2025
Tougher Uk Immigration Rules English Language Proficiency Key To Residency
May 10, 2025 -
 Analysis Trumps Trade War Costs Top 10 Billionaires 174 Billion
May 10, 2025
Analysis Trumps Trade War Costs Top 10 Billionaires 174 Billion
May 10, 2025 -
 A Non Binary Life Lost Examining The Death Of A Pioneer In America
May 10, 2025
A Non Binary Life Lost Examining The Death Of A Pioneer In America
May 10, 2025 -
 Fatal Stabbing Woman Charged With Racially Motivated Murder
May 10, 2025
Fatal Stabbing Woman Charged With Racially Motivated Murder
May 10, 2025 -
 Divine Mercy In 1889 A Look At Religious Diversity And Gods Grace
May 10, 2025
Divine Mercy In 1889 A Look At Religious Diversity And Gods Grace
May 10, 2025
