China's Steel Production Cuts: Impact On Iron Ore Prices And Global Markets
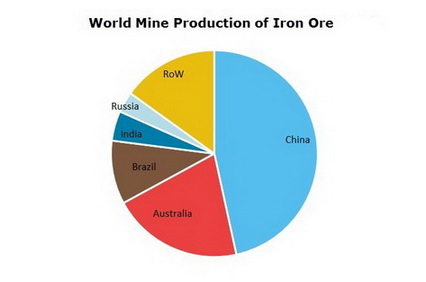
Table of Contents
The Reasons Behind China's Steel Production Cuts
China's decision to curb steel production stems from a confluence of factors, primarily environmental concerns and a slowing economy.
Environmental Regulations
China's increasingly stringent environmental regulations are a key driver of steel production cuts. The government is pushing aggressively towards carbon neutrality, leading to significant changes in the steel industry.
- Increased fines for non-compliance: Steel mills failing to meet stricter emission standards face substantial financial penalties, forcing them to invest heavily in cleaner technologies or risk closure.
- Stricter emission standards: New regulations mandate drastic reductions in pollutants like sulfur dioxide and particulate matter, requiring costly upgrades to existing facilities.
- Closure of inefficient plants: Many older, less efficient steel plants, which contribute disproportionately to pollution, have been ordered to shut down.
- Government targets for carbon neutrality: China's ambitious commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2060 necessitates a significant reduction in carbon emissions across all sectors, including steel production.
These regulations directly impact production capacity and output, forcing many steel mills to scale back operations or even cease production altogether. The cost of compliance is high, and many smaller players lack the resources to meet the new standards.
Reduced Demand Due to Slowing Economic Growth
China's economic growth has slowed in recent years, leading to a decrease in domestic steel demand. This reduced demand further contributes to the cuts in steel production.
- Decreased construction activity: A slowdown in the real estate sector and infrastructure projects has reduced demand for steel, a key component in construction.
- Lower infrastructure spending: Government spending on infrastructure, a significant driver of steel demand, has been moderated, reflecting a shift in economic priorities.
- Reduced consumption of steel-intensive products: Lower overall economic activity translates to decreased demand for various steel-intensive products, from automobiles to appliances.
The correlation between China's GDP growth and steel consumption is undeniable. As economic growth slows, so does the demand for steel, creating a feedback loop that pressures steel producers to reduce output.
Government Policies and Initiatives
In addition to environmental concerns and economic slowdown, targeted government policies have played a role in controlling steel production.
- Production quotas: The government has implemented production quotas for certain steel mills, limiting their output to specific levels.
- Capacity restrictions: Measures are in place to restrict the expansion of steel production capacity, preventing the addition of new facilities.
- Consolidation of the steel industry: Government policies encourage mergers and acquisitions, aiming to create larger, more efficient, and environmentally responsible steel companies.
These initiatives, while aimed at improving efficiency and environmental performance, can have unintended consequences, such as potential job losses and disruptions to the supply chain. The long-term effectiveness of these policies remains to be seen.
Impact on Global Iron Ore Prices
The reduction in China's steel production has had a significant impact on global iron ore prices, primarily through changes in supply and demand dynamics.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
Reduced Chinese steel production directly translates to lower demand for iron ore, the primary raw material used in steelmaking.
- Reduced demand for iron ore from China: China accounts for a massive share of global iron ore consumption; therefore, its reduced demand significantly affects the overall market.
- Impact on iron ore futures prices: Iron ore futures prices on exchanges like the Singapore Exchange have shown significant volatility reflecting the changing supply and demand dynamics.
- Price volatility in the short and long term: The impact on prices has been uneven, with short-term price fluctuations and longer-term uncertainty about future demand.
The elasticity of demand for iron ore is relatively low, meaning that even small changes in Chinese steel production can cause significant price fluctuations.
Major Iron Ore Producing Countries
The impact on major iron ore exporters is substantial, particularly Australia and Brazil, which supply a large portion of China's iron ore needs.
- Changes in export volumes: These countries have experienced a reduction in iron ore export volumes to China, impacting their trade balances and economic growth.
- Impact on their economies: The decreased demand from China puts downward pressure on iron ore prices, affecting the revenue and profitability of mining companies in these nations.
- Potential for price wars among producers: With reduced demand, there's a risk of increased competition and potential price wars among iron ore producers, leading to further price instability.
These countries are adapting by diversifying their export markets and exploring new technologies to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Alternative Uses for Iron Ore
While reduced demand from China is a primary concern, other sectors are potential sources of future demand.
- Examples of other sectors that consume iron ore: These include infrastructure projects in developing countries, renewable energy projects, and the automotive industry.
- Potential for growth in these sectors: Increased global investment in infrastructure and renewable energy could offset some of the decreased demand from China.
However, the potential for these sectors to fully compensate for the reduced Chinese demand remains uncertain, depending on various economic and political factors.
Wider Implications for Global Markets
The ripple effects of China's steel production cuts extend beyond iron ore prices, impacting various global markets.
Impact on Shipping and Logistics
The reduced demand for iron ore has significantly impacted the shipping industry.
- Reduced freight rates: Lower iron ore shipments have led to reduced demand for shipping services, putting downward pressure on freight rates.
- Impact on shipping companies: Shipping companies specializing in bulk commodities have experienced lower revenues and reduced profitability.
- Changes in shipping routes: Some shipping routes may see reduced traffic, affecting port operations and related logistics businesses.
The shipping industry is highly sensitive to changes in commodity trade, and the reduction in iron ore trade has had a noticeable impact.
Geopolitical Implications
Changes in iron ore production and trade have geopolitical implications, affecting international relations and power dynamics.
- Changes in trade relationships: The shift in iron ore demand has altered trade relationships between China and major exporting countries.
- Potential for trade disputes: Competition for market share among iron ore producers could lead to trade disputes and protectionist measures.
- Impact on global power dynamics: Changes in the iron ore market can influence global power dynamics, particularly concerning resource control and economic influence.
The interplay between economics and geopolitics is complex, and the changing iron ore market is no exception.
Impact on Steel Prices in Other Countries
China's production cuts have a ripple effect on steel prices globally.
- Changes in steel prices in other countries: Depending on the region and specific steel product, prices may rise or fall due to changes in global supply and demand.
- Competition between steel producers: Steel producers in other countries face altered competitive landscapes, with potential for increased or decreased market share.
- Implications for manufacturing industries: Changes in steel prices directly impact the cost of production for various manufacturing industries, affecting their profitability and competitiveness.
The interconnectedness of the global steel market means that changes in one region significantly impact other countries and industries.
Conclusion
China's steel production cuts have created a seismic shift in the global iron ore market. The reduced demand from China, driven by environmental policies and economic slowdown, has significantly impacted iron ore prices and triggered a cascade of consequences across the global supply chain, impacting shipping, geopolitics, and the economies of major iron ore producing countries. Understanding the nuances of these changes is crucial for businesses and policymakers alike. Staying informed about future developments in China's steel production and their impact on iron ore prices is essential for navigating this evolving global landscape. Further research and analysis into the long-term effects of these production cuts will be critical for strategic planning in the steel and iron ore industries.

Featured Posts
-
 Les Ecologistes Et Les Municipales 2026 A Dijon
May 09, 2025
Les Ecologistes Et Les Municipales 2026 A Dijon
May 09, 2025 -
 Franco Colapintos Deleted Drive To Survive Message What He Said
May 09, 2025
Franco Colapintos Deleted Drive To Survive Message What He Said
May 09, 2025 -
 String Of Car Break Ins Reported Across Elizabeth City Apartment Complexes
May 09, 2025
String Of Car Break Ins Reported Across Elizabeth City Apartment Complexes
May 09, 2025 -
 Nov Film Na Netflix Adaptatsiya Na Roman Na Stivn King
May 09, 2025
Nov Film Na Netflix Adaptatsiya Na Roman Na Stivn King
May 09, 2025 -
 Broadcoms Proposed V Mware Price Hike At And T Highlights A Staggering 1050 Increase
May 09, 2025
Broadcoms Proposed V Mware Price Hike At And T Highlights A Staggering 1050 Increase
May 09, 2025
