Combating Urban Heat In Indian Cities: The Role Of Advanced Materials
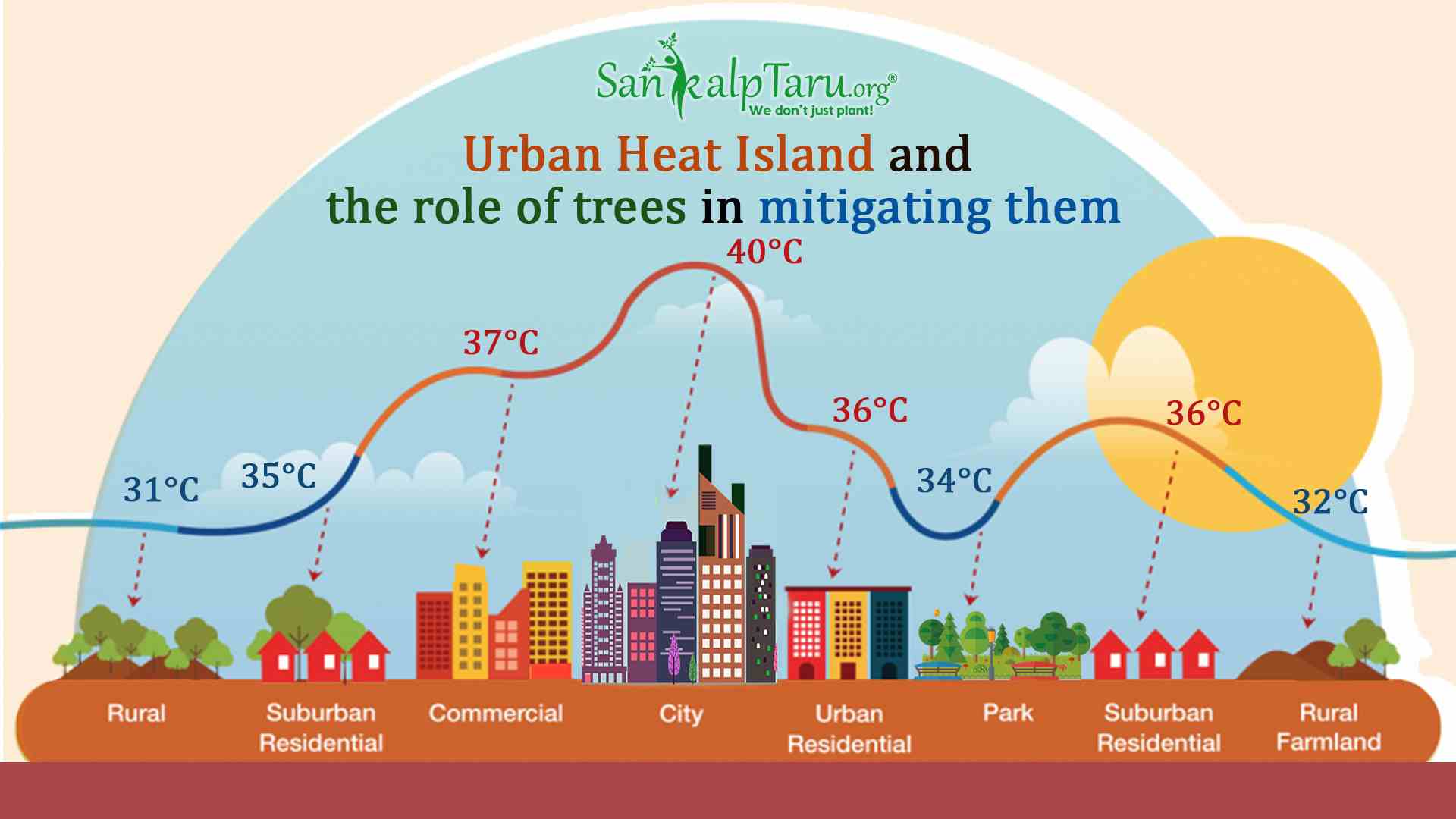
Table of Contents
Understanding the Urban Heat Island Effect in India
The urban heat island (UHI) effect is a phenomenon where urban areas experience higher temperatures than their surrounding rural counterparts. In the Indian context, several factors contribute to this effect. The rapid urbanization and densification of Indian cities, coupled with a lack of green spaces and the prevalence of dark-colored surfaces that absorb significant solar radiation, amplify the UHI effect. High population density further contributes to heat retention and increased heat generation from human activities and vehicular traffic.
The health consequences of UHI in India are severe. Prolonged exposure to extreme heat leads to heat strokes, respiratory problems, cardiovascular issues, and increased mortality, particularly among vulnerable populations like the elderly and children. Cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Kolkata are grappling with particularly intense UHI challenges, experiencing significantly higher temperatures than their surrounding regions during heat waves.
- Increased energy consumption: Higher temperatures necessitate increased use of air conditioning, leading to higher energy consumption and increased strain on the power grid.
- Negative impact on air quality: Increased temperatures can worsen air quality by enhancing the formation of ground-level ozone and other pollutants.
- Reduced comfort and productivity: Extreme heat reduces comfort levels, impacting productivity in both indoor and outdoor settings.
Advanced Materials for Cooler Cities: A Technological Solution
Advanced materials offer a promising technological solution for mitigating the UHI effect. These materials possess unique properties that enhance solar reflectance (albedo) and thermal emittance, effectively reducing surface temperatures and creating cooler urban environments.
- Cool pavements: Concrete pavements incorporating high-albedo materials reflect more sunlight, minimizing heat absorption and reducing surface temperatures. These materials are designed to stay cooler even under direct sunlight.
- Reflective roofing materials: White or light-colored roofing tiles and coatings significantly reduce the amount of solar radiation absorbed by buildings, keeping indoor spaces cooler and reducing the need for excessive air conditioning.
- Coatings with high thermal emissivity: Coatings applied to building surfaces enhance their ability to radiate heat away, thereby lowering surface temperatures.
- Phase-change materials: These materials absorb and release heat, buffering temperature fluctuations and contributing to thermal comfort. They are increasingly being integrated into building materials and infrastructure.
The effectiveness of these materials stems from their ability to modify the surface energy balance. High albedo materials reflect a greater proportion of incoming solar radiation, while high thermal emissivity materials efficiently radiate heat away from the surface. A lifecycle assessment, including considerations of material sourcing, manufacturing, and disposal, is crucial to ensure the environmental sustainability of these advanced materials.
Case Studies and Successful Implementations in India
While large-scale implementation is still nascent, several pilot projects in India demonstrate the potential of advanced materials in combating urban heat. For instance, some cities are experimenting with cool pavements in select areas, recording noticeable temperature reductions. Organizations and initiatives focusing on sustainable urban development are actively promoting the adoption of reflective roofing materials and high-emissivity coatings. These implementations are yielding quantifiable results, showing positive impacts on temperature reduction, energy savings, and public health. However, challenges remain, including the initial cost of these materials, their widespread availability, and the need for scalable implementation strategies.
- Examples of successful UHI mitigation projects: Specific projects, if available, should be cited here with links to relevant reports and publications.
- Quantifiable results: Data on temperature reduction, energy savings, and other positive impacts should be presented.
- Challenges and opportunities: Discussion of cost-effectiveness, scalability, and other implementation obstacles is crucial.
Future Directions and Policy Recommendations
Future research and development should focus on exploring innovative advanced materials and technologies for UHI mitigation. This includes smart materials that adapt to changing environmental conditions and bio-based materials with reduced environmental impact. Policy interventions are crucial to drive the widespread adoption of these materials.
- Government initiatives: Incentives, subsidies, and building codes mandating the use of cool materials can significantly accelerate adoption.
- Integration with green building standards: Incorporating the use of advanced materials into green building certification schemes can incentivize their use.
- Research and development priorities: Continued investment in research to develop and optimize the performance of advanced materials is crucial.
Integrating advanced materials with other urban design strategies, such as increasing green spaces and implementing urban forestry, is essential for a holistic approach to urban heat mitigation. A multi-pronged strategy incorporating both technological solutions and urban planning interventions is crucial for creating resilient and sustainable cities in India.
Conclusion: Combating Urban Heat with Advanced Materials in Indian Cities
The increasing severity of the urban heat island effect in Indian cities necessitates the urgent adoption of innovative solutions. Advanced materials, with their ability to reduce surface temperatures and enhance thermal comfort, play a critical role in mitigating this challenge. Adopting these materials offers significant benefits, including improved public health, reduced energy consumption, and enhanced urban livability. We urge government officials, urban planners, architects, material scientists, and researchers to actively explore and implement advanced materials to combat the rising urban heat challenge in India. Further research and development in this vital area are crucial for building more sustainable and resilient cities, ensuring a healthier and more comfortable future for all. Let's work together to create cooler, more sustainable Indian cities using advanced materials and smart urban planning.

Featured Posts
-
 Des Moines Crash Vehicle Ends Up On Its Side
May 30, 2025
Des Moines Crash Vehicle Ends Up On Its Side
May 30, 2025 -
 Las Carreras Sprint De Moto Gp Riesgo Excesivo Para La Recompensa
May 30, 2025
Las Carreras Sprint De Moto Gp Riesgo Excesivo Para La Recompensa
May 30, 2025 -
 Kawasaki W175 Cafe Motor Retro Klasik Yang Menawan
May 30, 2025
Kawasaki W175 Cafe Motor Retro Klasik Yang Menawan
May 30, 2025 -
 Improving Gene Editing The Promise Of A New Crispr Modification
May 30, 2025
Improving Gene Editing The Promise Of A New Crispr Modification
May 30, 2025 -
 Madrid Open Update Swiatek Wins De Minaur Eliminated
May 30, 2025
Madrid Open Update Swiatek Wins De Minaur Eliminated
May 30, 2025
