Commercial Aircraft And Engine Imports: The Threat Of Trump Tariffs
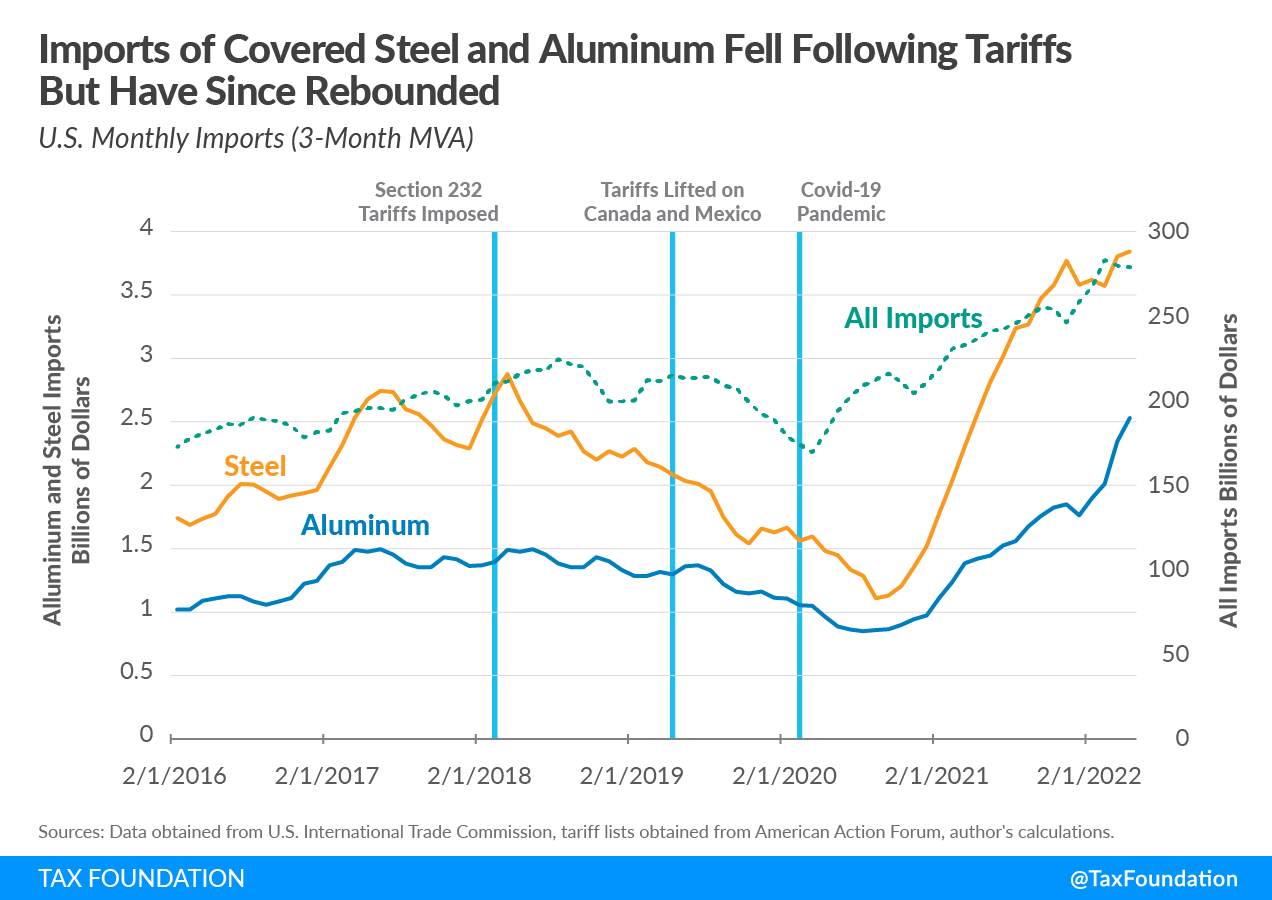
Table of Contents
The Impact of Trump Tariffs on Aircraft Manufacturers
The tariffs levied during the Trump administration directly impacted aircraft manufacturers, creating a ripple effect throughout the industry.
Increased Production Costs
Tariffs significantly increased the cost of imported parts, directly impacting manufacturing timelines and profitability. This increase wasn't simply a percentage added to the price; it fundamentally altered the economics of aircraft production.
- Engines: Tariffs on engine components, including sophisticated turbines and advanced materials, led to increased manufacturing costs.
- Avionics: The cost of importing advanced avionics systems, crucial for modern aircraft operation and safety, rose dramatically.
- Landing Gear: Even seemingly minor components like landing gear parts saw price increases, contributing to the overall cost escalation.
This increase in production costs reduced the competitiveness of US-based manufacturers in the global market, making it harder to compete with companies in countries without similar tariffs.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The tariffs disrupted established supply chains, creating significant challenges for aircraft manufacturers. The reliance on global supply networks was suddenly threatened by unpredictable import costs and delays.
- Delays: Customs procedures became more complex and time-consuming, leading to delays in receiving essential components.
- Shortages: Some components became scarce due to the difficulties and increased costs associated with importing them.
- Restructuring: Manufacturers were forced to explore alternative suppliers, a costly and time-consuming process that often compromised quality and efficiency.
The disruption of established supply chains led to production bottlenecks and increased lead times for new aircraft.
Job Security and Economic Impacts
The increased costs and supply chain disruptions ultimately threatened job security and had a negative impact on the broader economy.
- Job Losses: While precise figures are difficult to isolate, the increased costs and decreased competitiveness potentially led to job losses in the manufacturing sector.
- Economic Downturn: The challenges faced by aircraft manufacturers contributed to a broader economic slowdown within related industries, including those providing support services and materials.
- Ripple Effect: The impact extended beyond the immediate manufacturing sector, affecting suppliers, subcontractors, and the wider aerospace ecosystem.
The Effects on Airlines and Consumers
The increased costs faced by aircraft manufacturers directly translated into higher prices for airlines and, ultimately, higher ticket prices for consumers.
Higher Ticket Prices
The increased cost of purchasing new aircraft directly impacted airline profitability and pricing decisions.
- Aircraft Acquisition: Airlines faced higher costs for new planes, squeezing their profit margins.
- Fleet Renewal: The cost of maintaining and upgrading fleets also increased, impacting airlines' ability to invest in modernization and efficiency improvements.
- Fare Increases: Airlines passed a portion of the increased costs onto consumers in the form of higher ticket prices, thus impacting air travel accessibility.
This increase in airfare disproportionately affected budget travelers and reduced the affordability of air travel for many people.
Reduced Flight Frequency & Route Options
Faced with increased costs, airlines were forced to make difficult choices, including reducing flight frequencies or canceling less profitable routes.
- Route Cuts: Airlines reduced service on less profitable routes, limiting passenger connectivity and choice.
- Reduced Frequency: Some routes saw a decrease in the number of flights per day or week, impacting convenience and accessibility.
- Market Consolidation: The financial pressures caused by the tariffs potentially hastened market consolidation among airlines.
Maintenance and Repair Challenges
The tariffs created challenges in obtaining spare parts and conducting timely maintenance.
- Spare Part Delays: Delays in importing necessary spare parts led to increased maintenance costs and longer aircraft downtime.
- Increased Costs: The higher price of imported parts directly impacted maintenance budgets, further straining airline profitability.
- Safety Concerns: Delays in maintenance due to tariff-related import issues created potential safety concerns.
Long-Term Implications for the Global Aviation Industry
The Trump-era tariffs had far-reaching consequences that extend beyond the immediate impacts on manufacturers and airlines.
Geopolitical Repercussions
The tariffs exacerbated trade tensions between nations and negatively impacted international cooperation within the aviation sector.
- Trade Disputes: The tariffs led to retaliatory measures from other countries, escalating trade disputes.
- International Cooperation: The increased trade tensions undermined the collaborative efforts necessary for smooth international air travel.
- Global Instability: The resulting uncertainty added instability to the global aviation market.
Restructuring of Supply Chains
In response to the tariffs, companies began restructuring their supply chains to reduce their reliance on specific countries.
- Nearshoring and Reshoring: Many companies explored moving manufacturing closer to home or back to their home countries.
- Alternative Suppliers: Companies sought out alternative suppliers in different regions to mitigate risks associated with tariffs and geopolitical instability.
- Cost and Efficiency Implications: These changes in supply chain configuration had long-term cost and efficiency implications for the industry.
The Shift Towards Protectionism
The tariffs exemplified a shift towards protectionist trade policies, with broader implications for global economic stability.
- Similar Measures: Other industries also saw the implementation of protectionist measures, creating a cascade effect.
- Trade Conflicts: The increasing use of protectionist measures raised the potential for future trade conflicts, undermining global economic stability.
- Reduced Global Competition: Protectionist policies inherently limit global competition and can lead to higher prices and less innovation.
The Enduring Impact of Commercial Aircraft and Engine Imports and Tariffs
The Trump-era tariffs significantly impacted commercial aircraft and engine imports, leading to increased costs, supply chain disruptions, and broader economic consequences. The increased costs affected manufacturers, airlines, and ultimately, consumers. The disruption of established supply chains created instability and uncertainty, prompting companies to restructure their operations at significant expense. These events highlight the importance of stable and predictable trade policies for the global aviation industry. Further research and discussion are crucial to understanding the long-term effects of protectionist trade policies on the commercial aircraft and engine imports sector. We must advocate for fair and transparent trade practices to foster a healthy and globally competitive aviation industry. The future of commercial aircraft and engine imports relies on informed policy decisions.

Featured Posts
-
 10 Unforgettable Film Noir Movies You Need To See
May 10, 2025
10 Unforgettable Film Noir Movies You Need To See
May 10, 2025 -
 Snls Impression Of Harry Styles The Singers Disappointed Response
May 10, 2025
Snls Impression Of Harry Styles The Singers Disappointed Response
May 10, 2025 -
 Indian Stock Market Update Sensex Gains Niftys Positive Trend
May 10, 2025
Indian Stock Market Update Sensex Gains Niftys Positive Trend
May 10, 2025 -
 Materialists Nea Romantiki Komenti Me Dakota Johnson Pedro Pascal Kai Chris Evans
May 10, 2025
Materialists Nea Romantiki Komenti Me Dakota Johnson Pedro Pascal Kai Chris Evans
May 10, 2025 -
 Investigating Us Government Funding For Transgender Animal Research
May 10, 2025
Investigating Us Government Funding For Transgender Animal Research
May 10, 2025
