Competition Bureau's Case Against Google: Potential Constitutional Implications

Table of Contents
The Competition Bureau's Allegations Against Google
The Competition Bureau alleges that Google has engaged in a series of anti-competitive practices, abusing its dominant position in the digital market. These allegations constitute a significant challenge to Google's business model and raise concerns about the fairness of competition in the digital age. The core of the Competition Bureau's case rests on accusations of:
- Abuse of Dominance: The Bureau argues that Google leverages its market dominance in search and advertising to stifle competition, giving its own products and services an unfair advantage. This includes allegations of prioritizing its own services in search results, disadvantaging competitors.
- Anti-competitive Agreements: Allegations include claims that Google has entered into agreements that restrict competition and prevent rivals from accessing key markets. These agreements could involve preferential treatment of specific businesses in exchange for certain actions.
- Predatory Pricing: The Bureau might allege that Google uses predatory pricing strategies—selling services below cost to eliminate rivals—to maintain its market dominance.
The investigation into Google’s anti-competitive behaviour includes a review of extensive internal documents and evidence gathered through interviews. The Competition Bureau investigation aims to determine if Google’s actions violate Canada’s Competition Act, which prohibits anti-competitive practices that harm consumers. The accusations paint a picture of a digital monopoly leveraging its power to suppress competition and potentially harm innovation.
Constitutional Challenges to the Competition Bureau's Case
The Competition Bureau's case against Google triggers several profound constitutional questions. The potential implications for fundamental rights warrant careful scrutiny.
Freedom of Speech Concerns
One significant concern is whether the Competition Bureau's actions infringe on Google's freedom of speech. Regulating search results could be interpreted as censorship, restricting Google's ability to present information as it sees fit. The argument rests on the idea that a search algorithm is a form of expression, protected under freedom of speech principles. However, this must be balanced against the need to ensure fair competition and prevent monopolistic practices. Relevant case law regarding digital rights and the application of freedom of speech in the digital realm will play a crucial role in determining the outcome. The question of search neutrality—the idea that search results should be unbiased—is central to this debate.
Due Process Rights
Another critical constitutional aspect is whether Google’s due process rights are being adequately protected. This includes ensuring fairness throughout the investigation and any subsequent legal proceedings. Concerns may arise regarding:
- Access to evidence: Google must have fair and timely access to all relevant evidence presented by the Competition Bureau.
- Fair procedures: The investigative and judicial processes must be impartial and unbiased.
- Opportunity to be heard: Google must have a full opportunity to present its case and challenge the Competition Bureau’s allegations. Any infringement of these legal rights could lead to significant legal challenges. The issue of procedural fairness will be crucial in assessing the legality of the Bureau’s actions.
Property Rights and Intellectual Property
The case also raises questions about Google's property rights in its algorithms and technology. The Competition Bureau’s actions could be seen as infringing upon Google’s intellectual property. The argument focuses on whether regulation can dictate how Google uses its own algorithms and technology, potentially impacting its algorithm rights and stifling innovation. This requires a nuanced legal analysis that balances the need to regulate monopolies with the protection of innovation and property rights.
International Precedents and Comparative Law
Examining international antitrust law and similar cases in other jurisdictions is crucial to understanding the potential implications of the Competition Bureau’s case. The EU competition law has already seen several significant cases against Google, providing valuable precedents. A comparison of approaches to regulating global tech regulation reveals diverse strategies employed by different countries, highlighting the complexities of this global challenge. These international precedents offer valuable insights and can influence the legal arguments and the ultimate decision in the Canadian case.
Potential Outcomes and Their Constitutional Implications
The potential outcomes of the Competition Bureau's case against Google have significant implications for the future of tech regulation. Depending on the ruling, we could see:
- Structural remedies: These could involve forcing Google to divest certain assets or restructure its business to increase competition.
- Behavioral remedies: These might entail imposing restrictions on Google's practices, such as limitations on how it uses its data or presents search results.
- Financial penalties: Significant fines could be imposed as a deterrent to future anti-competitive behavior.
Each of these potential rulings carries different constitutional implications, potentially setting a constitutional precedent impacting the balance between regulation, innovation, and the protection of fundamental rights in digital markets. The long-term impact on competition and innovation will significantly depend on the final decision.
Conclusion: The Future of Competition and Constitutional Rights in the Digital Age
The Competition Bureau's case against Google is not merely an antitrust dispute; it is a significant test of the interplay between competition law and constitutional rights in the digital age. The key takeaways underscore the complex balancing act required to regulate powerful tech companies without infringing on fundamental freedoms of speech, due process, and property rights. This case will shape the future of antitrust rulings and how we approach tech regulation impact on fundamental rights. We must carefully consider the constitutional precedent that will be set, ensuring both fair competition and the protection of individual liberties in an increasingly digital world. To stay informed about this crucial legal battle and its potential ramifications, further research into the ongoing developments is crucial. Continue to follow updates on the "Competition Bureau's Case Against Google and its potential constitutional implications" to understand the shaping landscape of digital competition and constitutional rights.

Featured Posts
-
 Assemblee Nationale Frontieres Et Chaos La Strategie Du Rn Face A Lfi
May 30, 2025
Assemblee Nationale Frontieres Et Chaos La Strategie Du Rn Face A Lfi
May 30, 2025 -
 San Diego Weather Alert Fog Light Showers And Cooler Temperatures Predicted
May 30, 2025
San Diego Weather Alert Fog Light Showers And Cooler Temperatures Predicted
May 30, 2025 -
 Madden Nfl Rob Manfreds Mlb Ownership Troubles
May 30, 2025
Madden Nfl Rob Manfreds Mlb Ownership Troubles
May 30, 2025 -
 Kan Kasper Dolberg Score 35 Mal Pa En Saeson En Realistisk Vurdering
May 30, 2025
Kan Kasper Dolberg Score 35 Mal Pa En Saeson En Realistisk Vurdering
May 30, 2025 -
 Dolbergs Afloser Spaendende Kandidater I Kikkerten
May 30, 2025
Dolbergs Afloser Spaendende Kandidater I Kikkerten
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 New Covid 19 Variant Fueling Case Increase In Multiple Nations
May 31, 2025
New Covid 19 Variant Fueling Case Increase In Multiple Nations
May 31, 2025 -
 Health Impacts Of Canadian Wildfire Smoke On Minnesota
May 31, 2025
Health Impacts Of Canadian Wildfire Smoke On Minnesota
May 31, 2025 -
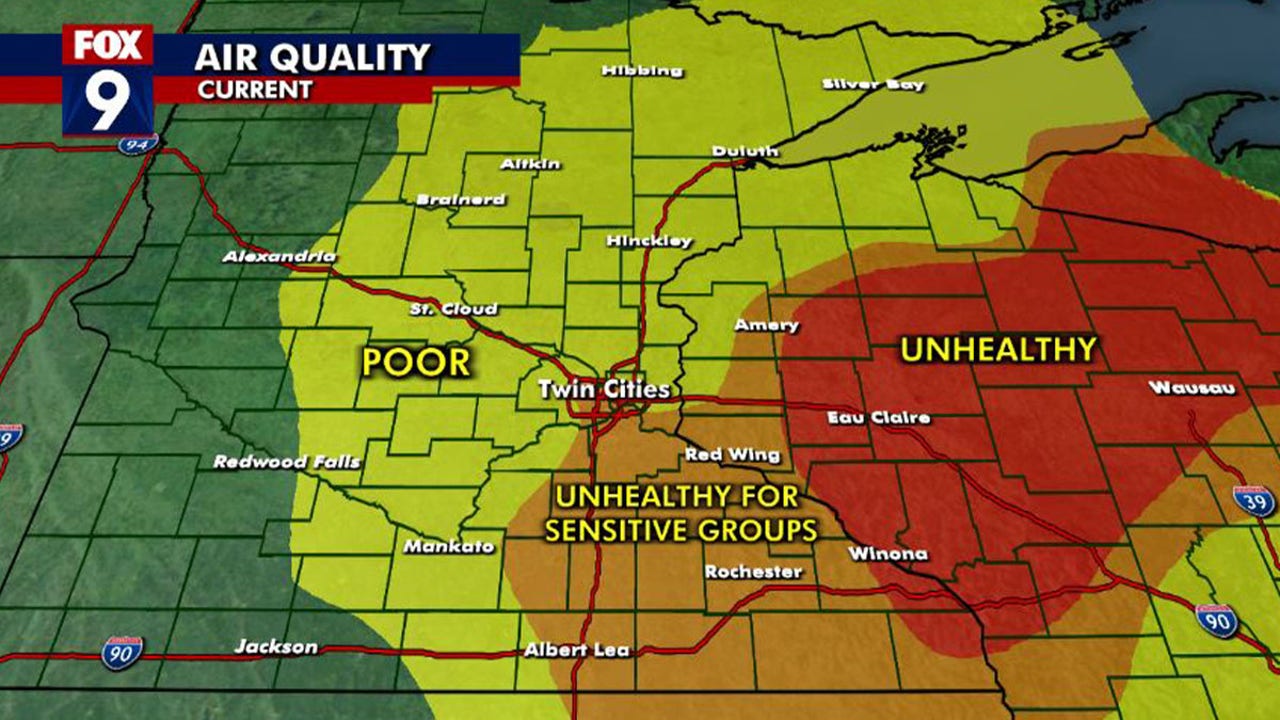 Dangerous Air Quality In Minnesota Due To Canadian Wildfires
May 31, 2025
Dangerous Air Quality In Minnesota Due To Canadian Wildfires
May 31, 2025 -
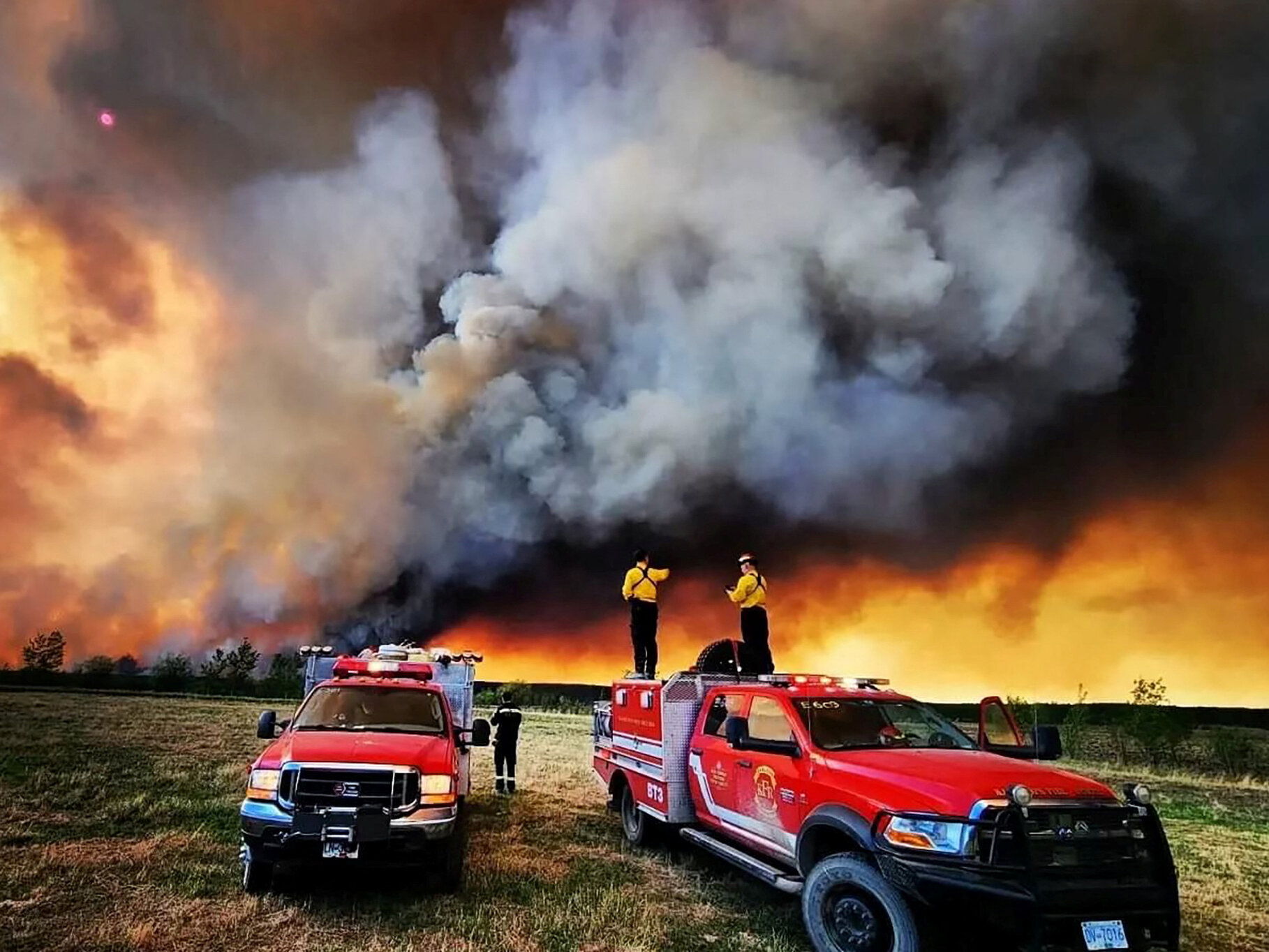 Canadian Wildfires Cause Dangerous Air In Minnesota
May 31, 2025
Canadian Wildfires Cause Dangerous Air In Minnesota
May 31, 2025 -
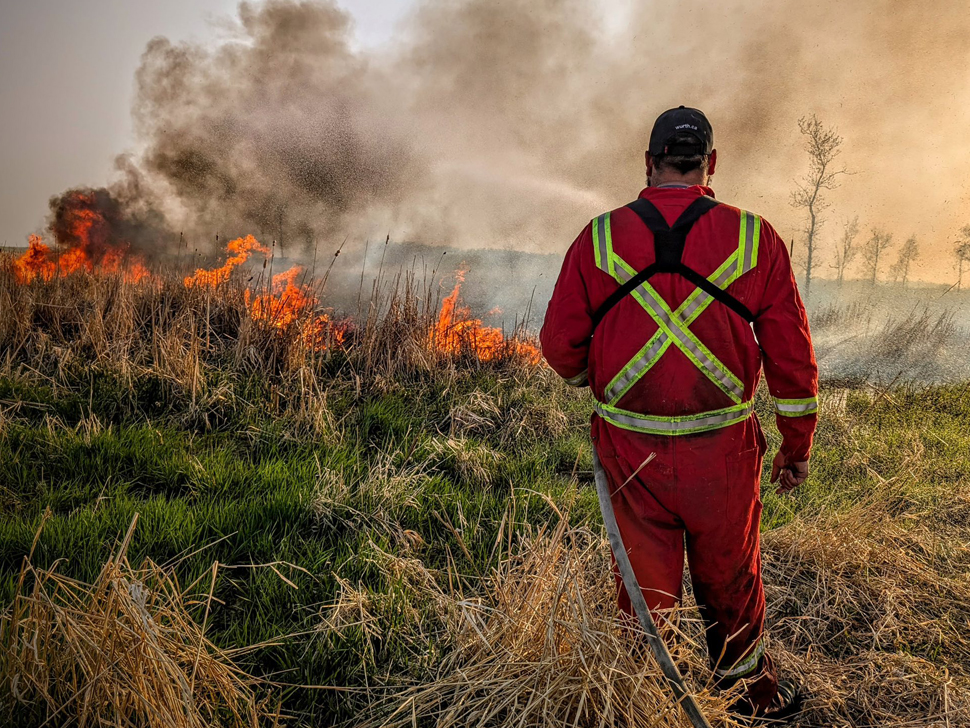 Eastern Manitoba Wildfires Rage Crews Struggle For Control
May 31, 2025
Eastern Manitoba Wildfires Rage Crews Struggle For Control
May 31, 2025
