Congo's Cobalt Export Ban: Impact On The Global Market And The Upcoming Quota Plan
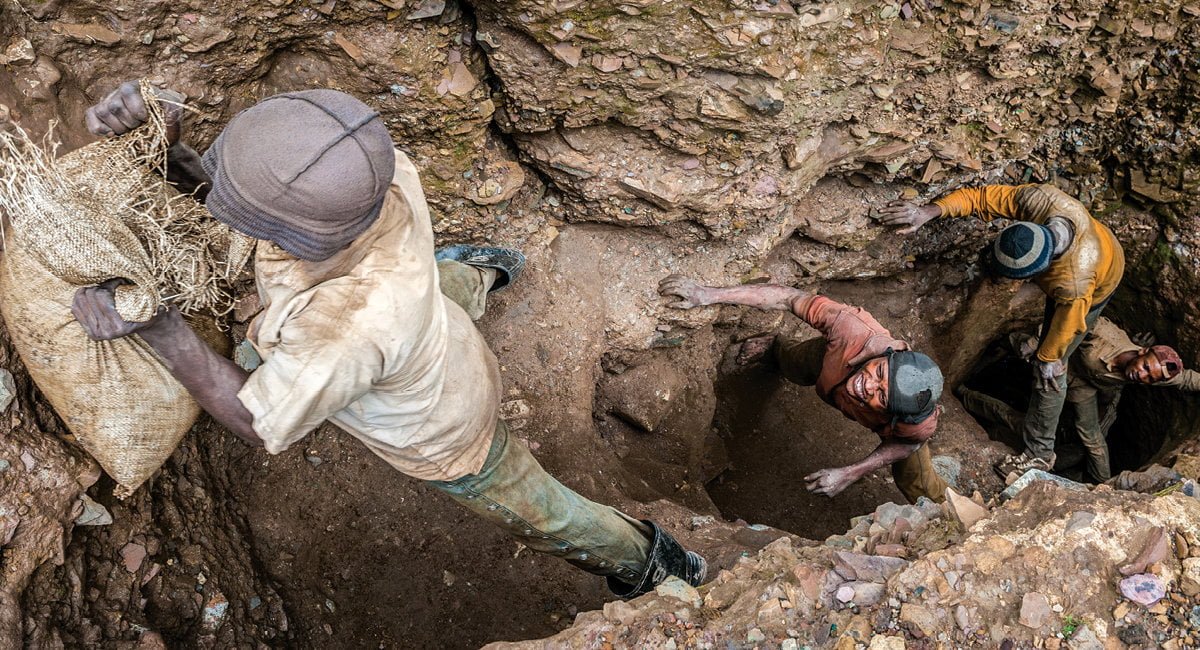

Table of Contents
The DRC's Cobalt Dependence and the Rationale Behind a Potential Ban
The DRC's economy is heavily reliant on cobalt exports, making it vulnerable to price fluctuations and potentially exploitative practices. A ban or quota system could be viewed as a strategic move to gain greater control over its natural resources, stimulate domestic processing, and secure fairer revenue streams for the Congolese people.
-
Current State of Cobalt Mining: Cobalt mining in the DRC encompasses both large-scale industrial operations and extensive artisanal mining, often characterized by unsafe working conditions and environmental damage. Industrial mining is dominated by multinational corporations, while artisanal mining involves thousands of individuals working in precarious circumstances.
-
Environmental and Social Concerns: The environmental impact of cobalt mining in the DRC includes deforestation, water pollution, and soil degradation. Social concerns center around human rights abuses, child labor, and the lack of worker protections in many artisanal mines. These issues have led to international pressure for greater transparency and ethical sourcing.
-
Government Motivations: The DRC government's consideration of a cobalt export ban or quota stems from a desire to add value to its raw materials domestically, attract foreign investment in processing facilities, and increase its share of profits from the global cobalt market. This move also aims to improve the governance of the cobalt sector and address the social and environmental problems associated with its extraction.
-
Existing Regulations and Their Effectiveness: While some regulations exist to govern cobalt mining in the DRC, their enforcement has been inconsistent and insufficient in addressing the pervasive human rights and environmental concerns. The proposed ban or quota system is intended to strengthen regulatory frameworks and ensure more responsible mining practices.
Impact on the Global Cobalt Market and the EV Industry
A ban or significant reduction in cobalt exports from the DRC would severely disrupt the global cobalt market, leading to several potential consequences.
-
Global Cobalt Demand and Growth: The global demand for cobalt is currently high and is projected to grow exponentially with the increasing adoption of EVs and other technologies reliant on lithium-ion batteries. A supply shock from the DRC could cripple this growth.
-
Potential Price Increase: A significant reduction in cobalt supply would inevitably lead to a sharp price increase, impacting the cost of EV batteries and potentially slowing down the global transition to electric vehicles. This could increase the overall price of EVs, making them less competitive compared to internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
-
Implications for the Automotive Industry: Major automakers heavily reliant on cobalt from the DRC would face production delays, increased costs, and potential supply chain disruptions. This could force them to explore alternative battery chemistries or seek cobalt from less reliable sources.
-
Alternative Battery Technologies: The potential cobalt crisis is accelerating research and development into alternative battery technologies, such as lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, which require less or no cobalt. This diversification of battery chemistries is crucial for mitigating the risks associated with cobalt supply chain instability.
-
Impact on Other Industries: Beyond the EV industry, various sectors, including aerospace and electronics, rely on cobalt. A cobalt shortage would have ripple effects across these industries, potentially impacting production and costs.
The Proposed Quota System: A Viable Alternative to a Complete Ban?
Instead of a complete ban, the DRC government may opt for a quota system, limiting the amount of raw cobalt exported while allowing a certain quantity for international markets. This approach aims to balance the need for resource control with the demands of the global market.
-
Details of the Proposed Quota System: The specifics of any quota system are still under discussion, including criteria for allocating quotas to different companies and countries, as well as robust enforcement mechanisms to prevent illegal exports.
-
Impact Compared to a Complete Ban: A quota system would likely cause less disruption than a complete ban, though it would still result in price volatility and supply chain challenges, potentially harming industries that need a stable cobalt supply.
-
Challenges in Implementation and Enforcement: Successfully implementing and enforcing a quota system would necessitate a sophisticated monitoring system to track cobalt exports and prevent illegal activities. This is a significant challenge given the often-unregulated nature of cobalt mining in the DRC.
-
Potential for Corruption: A poorly designed quota system could lead to corruption and favoritism, with certain companies or countries benefiting disproportionately. Transparency and accountability are crucial to mitigate this risk.
Potential Solutions and Mitigation Strategies
Addressing the challenges posed by a potential cobalt export ban or a quota system requires a multifaceted approach involving international cooperation, sustainable mining practices, and investment in responsible sourcing.
-
Role of International Organizations: International organizations like the OECD and the European Union have a crucial role to play in promoting responsible cobalt mining in the DRC, supporting the development of sustainable supply chains, and ensuring ethical sourcing practices. This may include initiatives focusing on due diligence, traceability, and capacity building.
-
Sustainable and Ethical Mining: Investments in sustainable and ethical cobalt mining practices are essential, including measures to improve worker safety, environmental protection, and community development. This requires both governmental and corporate involvement.
-
Diversifying Cobalt Supply: Reducing dependence on the DRC as the sole major cobalt source necessitates exploring and developing alternative sources of cobalt in other countries with better environmental and social standards.
-
Cobalt Recycling and Reuse: Increasing cobalt recycling and reuse from end-of-life batteries and electronic waste is a crucial strategy for reducing reliance on primary cobalt mining. Technological advancements are necessary to make recycling more efficient and cost-effective.
-
Transparency and Traceability: Greater transparency and traceability in the cobalt supply chain are vital to ensure that cobalt is sourced ethically and responsibly. Blockchain technology could play a significant role in enhancing traceability and accountability.
Conclusion
The potential cobalt export ban or quota system from the DRC presents a significant challenge to the global market, especially the EV industry. While a quota system might be a less disruptive alternative to a complete ban, its successful implementation depends on careful planning, robust enforcement, and a commitment to transparency and accountability. Addressing this issue requires concerted international cooperation, a focus on sustainable mining practices, and a shift toward responsible cobalt sourcing. Ignoring the potential ramifications of a DRC cobalt export ban, or failing to invest in responsible sourcing and alternative technologies, carries significant risks to the global supply chain and the transition to a cleaner energy future. Proactive measures and a commitment to ethical sourcing are vital to ensure a stable and responsible future for the cobalt market. Understanding Congo’s cobalt policy is crucial for navigating this critical issue.

Featured Posts
-
 Viet Jets Financial Future Uncertain Following Court Decision
May 16, 2025
Viet Jets Financial Future Uncertain Following Court Decision
May 16, 2025 -
 Barcelona Vs Girona La Liga Match Where To Watch Free Live Stream And Tv Broadcast
May 16, 2025
Barcelona Vs Girona La Liga Match Where To Watch Free Live Stream And Tv Broadcast
May 16, 2025 -
 Examining The Validity Of Trumps Egg Price Prediction
May 16, 2025
Examining The Validity Of Trumps Egg Price Prediction
May 16, 2025 -
 Goldman Sachs Deciphering Trumps Stance On Oil Prices Through Social Media
May 16, 2025
Goldman Sachs Deciphering Trumps Stance On Oil Prices Through Social Media
May 16, 2025 -
 Microsoft Layoffs Impact On Employees And The Tech Industry
May 16, 2025
Microsoft Layoffs Impact On Employees And The Tech Industry
May 16, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Paddy Pimblett Ufc 314 And The Liverpool Fc Connection
May 16, 2025
Paddy Pimblett Ufc 314 And The Liverpool Fc Connection
May 16, 2025 -
 Paddy Pimbletts Road To Ufc 314 Will He Become Champion
May 16, 2025
Paddy Pimbletts Road To Ufc 314 Will He Become Champion
May 16, 2025 -
 Paddy Pimblett Ufc 314 Champion Goat Legends Backing
May 16, 2025
Paddy Pimblett Ufc 314 Champion Goat Legends Backing
May 16, 2025 -
 Paddy Pimbletts Ufc 314 Trip A Liverpool Fc Fans Itinerary
May 16, 2025
Paddy Pimbletts Ufc 314 Trip A Liverpool Fc Fans Itinerary
May 16, 2025 -
 Pimblett Targets Ufc Gold Chandler Fight Prediction And Title Aspirations
May 16, 2025
Pimblett Targets Ufc Gold Chandler Fight Prediction And Title Aspirations
May 16, 2025
