COVID-19: A New Variant May Be Behind The Recent Surge In Cases, WHO Reports
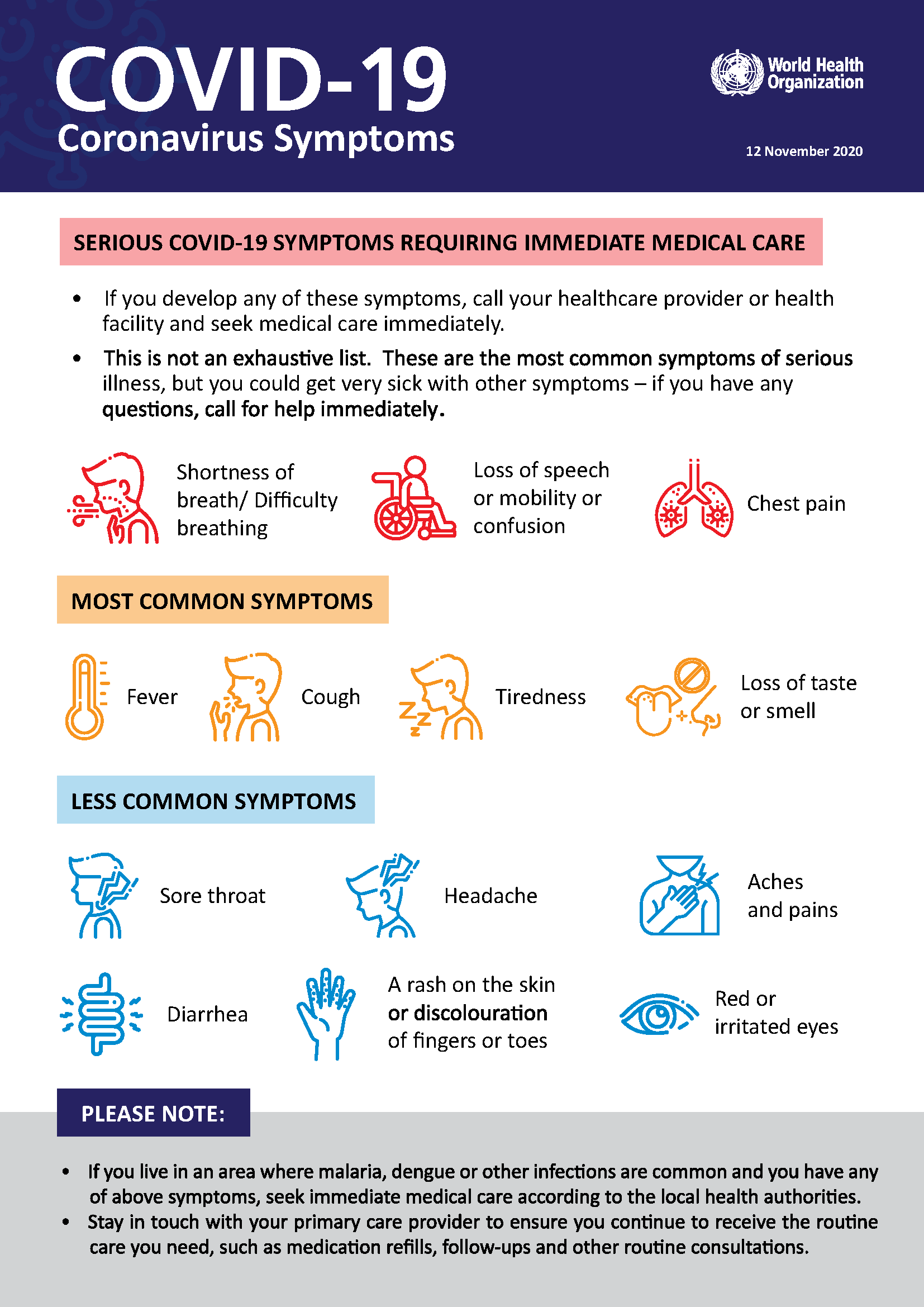
Table of Contents
The Emerging COVID-19 Variant: Characteristics and Concerns
The emergence of a new COVID-19 variant is raising serious concerns worldwide. Understanding its characteristics is vital for implementing effective control measures.
Increased Transmissibility
Early data suggests this new variant exhibits a higher transmissibility rate compared to previous variants like Delta and Omicron.
- Higher R0 value: Preliminary studies indicate a basic reproduction number (R0) significantly higher than previous variants, meaning each infected individual is likely to infect more people.
- Anecdotal evidence of rapid spread: Reports from several regions show a rapid increase in cases, strongly suggesting the variant's enhanced capacity for spread. Clusters in densely populated areas are particularly concerning.
- Mutations affecting viral entry: Specific mutations within the viral genome are suspected to enhance the virus's ability to bind to and enter human cells, contributing to increased infectivity.
This increased transmissibility places a significant strain on healthcare systems, potentially leading to overwhelmed hospitals and a shortage of medical resources. Swift and decisive public health responses are essential to mitigate the impact.
Severity and Symptoms
While initial data suggests the new variant might be more transmissible, its severity remains under investigation.
- Comparison to previous variants: Researchers are currently comparing the symptoms and severity of illness caused by this new variant to those of Delta and Omicron. Initial reports suggest a range of symptoms, similar to previous variants.
- Severity of infection (hospitalizations, deaths): The percentage of infections requiring hospitalization or resulting in death is being closely monitored. This information will be crucial in determining the overall impact on public health.
- Impact on vulnerable populations: Special attention is being paid to the impact of the new variant on vulnerable populations such as the elderly, immunocompromised individuals, and those with pre-existing health conditions. These groups may be at higher risk of severe illness.
Further research is needed to fully understand the severity of illness associated with the new variant and to identify any potential differences in symptom presentation compared to previous strains.
Geographic Spread and Prevalence
The new variant has been detected in several countries, raising concerns about its global spread.
- Countries or regions experiencing significant outbreaks: Reports indicate significant outbreaks linked to the new variant in [insert specific regions/countries as data becomes available].
- Proportion of cases attributed to the new variant: Scientists are actively working to determine the precise proportion of COVID-19 cases attributable to the new variant in affected areas. This data will be crucial for effective response strategies.
- Maps and charts illustrating geographic spread: Real-time tracking of the variant’s spread through maps and charts will help to visualize its global reach and identify potential hotspots.
WHO Response and Global Public Health Efforts
The WHO is actively monitoring the situation and has issued recommendations to address the surge in cases.
WHO Recommendations
The WHO has outlined a series of key recommendations to combat the spread of the new variant.
- Vaccination strategies: The WHO emphasizes the continued importance of vaccination, including booster shots, to maintain high levels of population immunity. Research is ongoing to assess the efficacy of existing vaccines against the new variant.
- Testing and surveillance measures: Increased testing and genomic surveillance are crucial to track the variant's spread and understand its characteristics. Early detection is key to effective response.
- Public health guidelines: The WHO continues to recommend adherence to established public health guidelines, including mask-wearing in indoor settings, social distancing, and good hand hygiene.
- International collaboration: Global collaboration is essential to share data, coordinate responses, and ensure equitable access to vaccines and therapeutics.
Governmental Responses
Governments worldwide are implementing various measures to control the spread of the new variant.
- Travel restrictions: Some countries have imposed travel restrictions from areas with high prevalence of the new variant.
- Lockdown measures or other restrictions: Depending on the severity of the outbreak, governments may implement various restrictions, ranging from mask mandates to localized lockdowns.
- Public health campaigns and information dissemination: Many governments are launching public health campaigns to educate the public about the new variant and promote preventive measures.
The Importance of Vaccination and Prevention Measures
Vaccination and preventive measures remain crucial in mitigating the impact of the new COVID-19 variant.
Vaccine Effectiveness
Current vaccines remain a critical tool in combating the virus, although their effectiveness against the new variant is being evaluated.
- Data on vaccine efficacy: Ongoing studies are assessing the effectiveness of current vaccines in preventing severe illness, hospitalization, and death caused by the new variant.
- Need for booster shots: Booster shots are likely to be crucial in maintaining sufficient levels of protection against severe disease.
- Ongoing research into vaccine adaptations: Researchers are actively working on adapting existing vaccines or developing new ones if necessary to enhance their efficacy against the new variant.
Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions
Non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) continue to play a vital role in reducing transmission.
- Importance of hand hygiene: Frequent and thorough handwashing remains a cornerstone of infection prevention.
- Mask-wearing in crowded indoor spaces: Wearing masks, especially in poorly ventilated indoor settings, significantly reduces transmission risk.
- Social distancing: Maintaining physical distance from others helps to minimize contact and reduce the chance of infection.
- Proper ventilation in indoor settings: Improving ventilation in indoor spaces helps to dilute the concentration of virus particles in the air.
- Testing when symptoms occur: Getting tested promptly when experiencing COVID-19 symptoms allows for early diagnosis and timely isolation to prevent further spread.
Conclusion
The emergence of this new COVID-19 variant underscores the ongoing need for vigilance and proactive public health measures. The WHO's warnings highlight the crucial role of vaccination, booster shots, and the continued practice of preventive measures such as mask-wearing and hand hygiene in mitigating the impact of this new variant and future outbreaks. Stay informed about the latest updates from the WHO and your local health authorities to protect yourself and your community from the COVID-19 virus and its new variants. Learn more about the latest COVID-19 updates and protect yourself by regularly checking the WHO website and following public health guidelines. Don't let your guard down; continue to prioritize COVID-19 prevention and stay informed about the latest developments regarding this new variant and other potential future COVID-19 variants.

Featured Posts
-
 Cape Town Elephant Seal Disrupts Traffic In Suburban Area
May 31, 2025
Cape Town Elephant Seal Disrupts Traffic In Suburban Area
May 31, 2025 -
 Whalebone Lane South Dagenham Details Of Recent Car Crash
May 31, 2025
Whalebone Lane South Dagenham Details Of Recent Car Crash
May 31, 2025 -
 Learn Minimalism A 30 Day Decluttering Program
May 31, 2025
Learn Minimalism A 30 Day Decluttering Program
May 31, 2025 -
 Nfl Draft Mel Kiper Jr S Projection For The Cleveland Browns No 2 Pick
May 31, 2025
Nfl Draft Mel Kiper Jr S Projection For The Cleveland Browns No 2 Pick
May 31, 2025 -
 Watch Canelo Vs Ggg Live Full Fight Replay And Play By Play
May 31, 2025
Watch Canelo Vs Ggg Live Full Fight Replay And Play By Play
May 31, 2025
 Roland Garros 2025 Key Matches To Watch
Roland Garros 2025 Key Matches To Watch
