De Minimis Tariffs On Chinese Imports: Key Considerations For The G-7
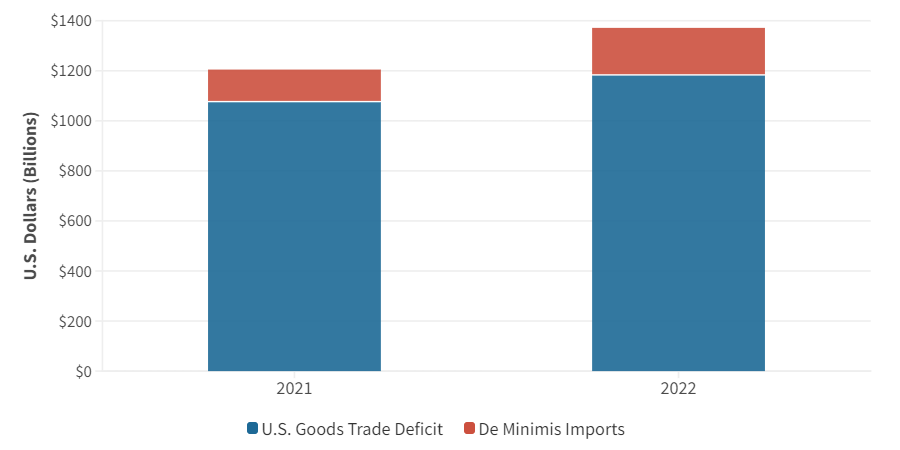
Table of Contents
Defining "De Minimis" in the Context of Chinese Imports
Understanding the term "de minimis" is crucial. It refers to the value threshold below which imported goods are exempt from customs duties or other tariffs. However, the current thresholds for de minimis tariffs vary considerably across G-7 nations, creating an uneven playing field. For instance, some G-7 members may have a significantly lower threshold than others, potentially leading to unfair competition. This variation in de minimis tariff rates on Chinese imports presents significant challenges.
-
Variations across G-7 members: The lack of harmonization in de minimis thresholds across the G-7 creates opportunities for exploitation. A business might strategically ship smaller, lower-value shipments to take advantage of lower tariffs in certain countries, while others face higher import costs on the same goods. This disparity undermines the principle of fair competition and market access for businesses in all G-7 nations.
-
Potential for exploitation: The differing de minimis thresholds create a potential loophole. Businesses could deliberately undervalue goods to fall below the threshold and avoid higher tariffs, ultimately distorting the market. Robust customs enforcement and improved tracking mechanisms are required to mitigate this risk.
-
Comparison with other trading blocs: Analyzing the de minimis thresholds employed by other major trading blocs, such as the EU or ASEAN, is vital. This comparison can help the G-7 assess whether their current approach is competitive and effective in achieving their economic and trade policy goals. This comparative analysis should help inform the setting of future de minimis tariff levels.
Economic Impacts of De Minimis Tariffs on G-7 Economies
The economic impacts of de minimis tariffs are multifaceted and far-reaching. Adjustments to these tariffs, even seemingly minor ones, can ripple through G-7 economies, affecting both consumers and businesses.
-
Consumer prices: Lower de minimis thresholds can lead to lower prices for consumers on certain goods imported from China. However, a sudden increase in thresholds could result in higher consumer prices. The overall impact depends on the specific goods affected and the elasticity of demand.
-
Domestic industry competitiveness: Changes in de minimis tariffs can significantly impact the competitiveness of domestic industries. Lower tariffs might increase competition, potentially putting pressure on domestic producers. Conversely, higher tariffs could offer some protection to local businesses.
-
Job creation/displacement: The impact on employment is directly linked to the competitiveness of domestic industries. If domestic producers struggle due to increased competition from cheaper imports, job losses might occur. Conversely, businesses leveraging cheaper imports to produce goods might see increased job creation.
-
Impact on SMEs: Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are often particularly vulnerable to changes in trade policy. Their limited resources might make them less able to adapt to sudden shifts in tariff levels compared to larger corporations.
-
Trade diversion: De minimis tariff adjustments can lead to trade diversion, where imports shift from one country to another due to changes in relative prices. This can have both positive and negative consequences, depending on the origins of the diverted imports.
Geopolitical Implications of De Minimis Tariff Adjustments
The implications of de minimis tariff adjustments extend beyond purely economic considerations. They have significant geopolitical ramifications, particularly in the context of the G-7's relationship with China.
-
Retaliatory measures: Changes to de minimis tariffs could provoke retaliatory measures from China, escalating trade tensions and potentially leading to broader trade disputes. A coordinated and predictable approach by the G-7 is crucial to mitigate this risk.
-
Impact on broader trade relations: The way the G-7 handles de minimis tariffs will impact the overall trade relationship with China. A transparent and consistent approach could foster trust and cooperation, while inconsistent policies could exacerbate tensions.
-
Influence on global supply chains: Adjusting de minimis tariffs impacts global supply chains. Any disruption caused by tariff changes could have knock-on effects on businesses globally, highlighting the interconnectedness of the global economy.
-
Exacerbation of trade disputes: Poorly managed de minimis tariffs could easily become a flashpoint in already existing trade disputes, leading to further escalation and harm to international cooperation.
-
Implications for international cooperation: The G-7's approach to de minimis tariffs can affect international cooperation and multilateral trade agreements. A collaborative approach that considers global standards is key to fostering a stable and predictable trading environment.
Policy Recommendations for the G-7 on De Minimis Tariffs
The G-7 needs a coordinated and strategic approach to de minimis tariffs to mitigate potential negative consequences.
-
Coordinated approach: G-7 nations should work together to establish more harmonized de minimis thresholds. This would reduce the potential for exploitation and create a fairer trading environment.
-
Mitigation strategies: Strategies to mitigate potential negative economic and geopolitical consequences are essential. This could involve providing support for affected industries, facilitating diversification of supply chains, and investing in domestic capacity building.
-
Enhanced transparency: Measures to enhance transparency and reduce the potential for abuse are needed. This could involve stricter customs enforcement, improved data sharing, and more rigorous monitoring of import values.
-
Regular reviews: Regular reviews and adjustments of de minimis tariffs based on economic data and market conditions are recommended to ensure they remain relevant and effective.
-
International collaboration: Collaboration with international organizations like the WTO is crucial to establishing global standards for de minimis tariffs. This fosters a more level playing field for global trade.
Conclusion
The careful consideration of de minimis tariffs on Chinese imports is crucial for the G-7. A coordinated and transparent approach, focusing on both economic and geopolitical ramifications, is essential to maintaining a stable and fair global trading environment. The G-7 must proactively address these issues to avoid unintended consequences and prevent further escalation of trade tensions. By fostering collaboration and establishing clear, consistent standards for de minimis tariffs, the G-7 can ensure a more balanced and predictable trading relationship with China, promoting growth and stability for all involved. It is vital that the G-7 continues to evaluate and refine its policies on de minimis tariffs on Chinese imports, ensuring they align with economic realities and broader geopolitical goals. A proactive and harmonized approach to de minimis tariffs is essential for the future of G-7-China trade relations.

Featured Posts
-
 Hsv Der Weg Zurueck In Die Bundesliga Ein Erfolgsbericht
May 25, 2025
Hsv Der Weg Zurueck In Die Bundesliga Ein Erfolgsbericht
May 25, 2025 -
 Elever Trois Enfants Avec Un Grand Ecart D Age Le Temoignage De Melanie Thierry Et Raphael
May 25, 2025
Elever Trois Enfants Avec Un Grand Ecart D Age Le Temoignage De Melanie Thierry Et Raphael
May 25, 2025 -
 Three Day Slide Amsterdam Stock Exchange Faces Significant Losses
May 25, 2025
Three Day Slide Amsterdam Stock Exchange Faces Significant Losses
May 25, 2025 -
 Exploring Jensons Fw 22 Extended Line
May 25, 2025
Exploring Jensons Fw 22 Extended Line
May 25, 2025 -
 Dazi Trump Al 20 Conseguenze Per Il Settore Moda Europeo
May 25, 2025
Dazi Trump Al 20 Conseguenze Per Il Settore Moda Europeo
May 25, 2025
