Economic Outlook Uncertain: Inflation And Unemployment Risks Rise
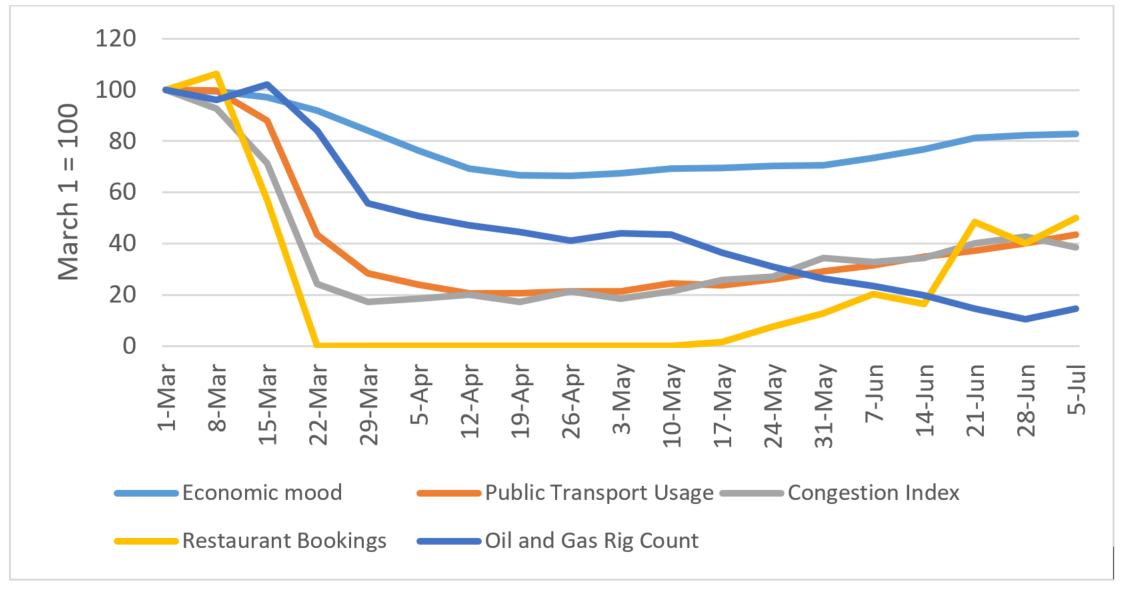
Table of Contents
Inflationary Pressures: A Persistent Threat
Inflation continues to be a major concern, impacting purchasing power and overall economic stability. Several factors contribute to these persistent inflationary pressures.
Supply Chain Disruptions:
Ongoing supply chain bottlenecks significantly impact production costs and consumer prices. These disruptions, exacerbated by geopolitical events and unforeseen circumstances, ripple through the entire economic system.
- Examples of disrupted supply chains: The semiconductor shortage continues to affect the automotive and electronics industries, while energy price volatility impacts transportation and manufacturing across the board. The war in Ukraine has further complicated global supply chains.
- Impact on manufacturing and retail: Increased input costs lead to higher prices for consumers, reducing purchasing power and potentially slowing economic growth. Manufacturers face production delays and increased costs, impacting profitability.
- Geopolitical factors: International conflicts, trade wars, and political instability significantly disrupt global supply chains, creating uncertainty and increasing prices. These supply chain issues are a key driver of cost-push inflation.
Energy Price Volatility:
Fluctuating energy prices, particularly oil and gas, exert a significant influence on inflation and overall economic growth. The energy sector's impact extends far beyond direct energy costs.
- Geopolitical instability: Geopolitical tensions and conflicts often lead to disruptions in energy supplies, resulting in price spikes. The transition to renewable energy sources also presents its own set of challenges.
- Renewable energy transition challenges: The shift towards renewable energy is essential for long-term sustainability, but the transition process itself can be complex and potentially disruptive in the short term.
- Impact on transportation and manufacturing costs: Higher energy prices increase transportation costs for goods, adding to inflation. Manufacturing industries heavily reliant on energy face increased production costs, further fueling inflationary pressures. This impact is felt across various sectors contributing to a broader rise in commodity prices.
Demand-Pull Inflation:
Strong consumer demand, fueled by various factors, also contributes to inflationary pressures. This type of inflation arises when aggregate demand outstrips the economy's capacity to produce goods and services.
- Government stimulus measures: Government stimulus packages designed to boost economic activity can contribute to increased consumer spending and demand-pull inflation.
- Pent-up demand post-pandemic: Following the pandemic lockdowns, pent-up consumer demand further fueled spending and increased pressure on prices.
- Wage increases: Rising wages, while beneficial for workers, can contribute to higher prices if businesses pass on increased labor costs to consumers. This interplay between wages and inflation is crucial to understanding the current economic climate and the resulting inflationary pressures.
Rising Unemployment: A Looming Shadow
While inflation is a pressing concern, the potential for rising unemployment casts a long shadow over the economic outlook. Several factors contribute to this looming risk.
Recessionary Fears:
Concerns about a potential recession are growing, primarily due to aggressive interest rate hikes designed to combat inflation. A recession would lead to job losses and significant economic hardship.
- Interest rate hikes: Central banks worldwide are raising interest rates to curb inflation, but this can also slow economic growth and potentially trigger a recession.
- Decreased consumer spending: Higher interest rates reduce consumer borrowing and spending, potentially leading to a decrease in economic activity and job losses.
- Business investment slowdown: Uncertainty and higher borrowing costs discourage businesses from investing, leading to reduced hiring and potential layoffs. The risk of recession is a major factor driving the current economic uncertainty and negatively impacting the overall economic outlook.
Automation and Technological Displacement:
Automation and technological advancements, while driving productivity, also contribute to job displacement in various sectors. This necessitates workforce adaptation and retraining initiatives.
- Examples of automation in various industries: Automation is transforming various industries, from manufacturing and transportation to customer service and data processing, reducing the need for human labor in certain roles.
- Skills gap: The rapid pace of technological change creates a skills gap, leaving many workers unprepared for the demands of the new economy.
- Need for workforce retraining: Investing in workforce retraining and upskilling programs is crucial to mitigate the negative impacts of automation and equip workers with the skills needed for the jobs of the future. Addressing the issue of technological unemployment is paramount for a smooth economic transition.
Wage Stagnation vs. Wage Growth:
The economic landscape presents a conflict: wage increases contribute to inflation, while stagnant wages contribute to unemployment and income inequality. This delicate balance requires careful consideration.
- Impact of inflation on real wages: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of wages, reducing real wages even if nominal wages increase. This can lead to dissatisfaction and social unrest.
- Labor market dynamics: The labor market is affected by the interplay between wage growth and inflation, impacting job creation and unemployment rates.
- Minimum wage debates: Discussions about raising minimum wages often involve balancing the need for fair compensation with the potential impact on inflation and business costs. Analyzing the impact of real wages is crucial for understanding the effects of current economic policies on overall economic well-being.
Policy Responses and Their Effectiveness
Governments and central banks are employing various policy responses to address the challenges of inflation and unemployment. The effectiveness of these policies remains a subject of ongoing debate.
Monetary Policy:
Central banks play a crucial role in managing inflation through monetary policy tools, primarily interest rate adjustments. However, aggressive action can carry risks.
- Quantitative tightening: Central banks may reduce the money supply through quantitative tightening, aiming to curb inflation.
- Inflation targets: Central banks often set inflation targets and adjust monetary policy to achieve these targets.
- Potential risks of aggressive interest rate hikes: Aggressive interest rate hikes, while effective in combating inflation, can also trigger a recession and increase unemployment. The balance between controlling inflation and avoiding a recession is a delicate one.
Fiscal Policy:
Fiscal policy, involving government spending and taxation, also plays a role in managing the economy. However, government actions can have both positive and negative consequences.
- Government stimulus packages: Government stimulus packages can boost economic activity but can also contribute to inflation if not managed effectively.
- Social safety nets: Robust social safety nets can provide support during economic downturns, mitigating the impact on unemployment and poverty.
- Potential for fiscal deficits: Government spending can lead to fiscal deficits, raising concerns about long-term debt sustainability. The effectiveness of fiscal policy depends largely on its careful and strategic implementation.
Conclusion
The current economic outlook is characterized by a delicate balancing act between controlling inflation and mitigating the risks of rising unemployment. Both inflationary pressures and the potential for a recession pose serious challenges. Policymakers need to carefully navigate these intertwined risks to achieve sustainable economic growth. The interplay between supply chain issues, energy prices, consumer demand, and government policies all contribute to the complex economic landscape we find ourselves in today.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the evolving economic outlook and its implications for your personal finances and business strategies. Continue to monitor news and analysis on the economic outlook to make informed decisions in these uncertain times. Understanding the interplay between inflation and unemployment is crucial for navigating this complex economic landscape and making sound financial and business decisions. Understanding the intricacies of the economic outlook is key to future success.

Featured Posts
-
 Insults Whistles And Gum The French Opens Unfair Treatment Of Opponents
May 30, 2025
Insults Whistles And Gum The French Opens Unfair Treatment Of Opponents
May 30, 2025 -
 Mejora Tu Experiencia Musical Setlist Fm Ahora Con Ticketmaster
May 30, 2025
Mejora Tu Experiencia Musical Setlist Fm Ahora Con Ticketmaster
May 30, 2025 -
 El Legado Del Ex Numero 3 Y Su Mensaje A Marcelo Rios
May 30, 2025
El Legado Del Ex Numero 3 Y Su Mensaje A Marcelo Rios
May 30, 2025 -
 Jon Jones Details His Daily Sparring Sessions With Hasbulla
May 30, 2025
Jon Jones Details His Daily Sparring Sessions With Hasbulla
May 30, 2025 -
 Lowering Water Costs San Diego Water Authoritys Surplus Water Sale Plan
May 30, 2025
Lowering Water Costs San Diego Water Authoritys Surplus Water Sale Plan
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Zverevs Comeback Victory Sends Him To Munich Semifinals
May 31, 2025
Zverevs Comeback Victory Sends Him To Munich Semifinals
May 31, 2025 -
 Munich Open Shelton Beats Darderi To Reach Semifinals
May 31, 2025
Munich Open Shelton Beats Darderi To Reach Semifinals
May 31, 2025 -
 Rome Masters Alcaraz And Passaro Secure Wins At Italian International
May 31, 2025
Rome Masters Alcaraz And Passaro Secure Wins At Italian International
May 31, 2025 -
 Italian International Alcaraz Wins Opener Passaro Upsets Dimitrov In Rome
May 31, 2025
Italian International Alcaraz Wins Opener Passaro Upsets Dimitrov In Rome
May 31, 2025 -
 Bmw Open Zverev Rallies Into Semifinals
May 31, 2025
Bmw Open Zverev Rallies Into Semifinals
May 31, 2025
