Economic Uncertainty: The Threat Of Higher Inflation And Unemployment

Table of Contents
The Rising Threat of Inflation
Understanding Inflation's Impact
Inflation, a general increase in the prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time, significantly erodes purchasing power. When inflation rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. There are various types of inflation, including demand-pull inflation (caused by excessive demand exceeding supply) and cost-push inflation (driven by rising production costs). High inflation impacts consumer spending, as individuals find their disposable income shrinking. Businesses, too, are affected, facing increased costs and potentially reduced investment.
- Examples of inflationary pressures:
- Rising energy costs (oil, gas)
- Supply chain disruptions leading to shortages
- Increased wages and labor costs
- Government spending and expansionary monetary policies
Keywords: inflation rate, consumer price index (CPI), purchasing power, stagflation, hyperinflation.
Causes of Current Inflationary Pressures
The current inflationary environment is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors. Government spending, particularly during periods of economic crisis, can fuel demand-pull inflation. Monetary policy, such as low interest rates, can also contribute to inflationary pressures by making borrowing cheaper and increasing spending. Global supply chain bottlenecks, exacerbated by geopolitical events and pandemics, have constrained supply, driving up prices.
- Specific examples of current events contributing to inflation:
- The war in Ukraine impacting energy and food prices.
- Global supply chain disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Increased demand for goods and services following the pandemic lockdowns.
Keywords: monetary policy, fiscal policy, supply chain bottlenecks, commodity prices.
The Shadow of Unemployment
Understanding Unemployment's Ripple Effects
Unemployment, the state of being without a job while actively seeking employment, has profound social and economic consequences. Different types of unemployment exist, including frictional (temporary unemployment between jobs), structural (mismatch between worker skills and job availability), and cyclical (job losses due to economic downturns). High unemployment leads to reduced consumer spending, decreased tax revenue for governments, and increased strain on social safety nets.
- Statistics on unemployment rates and their impact on various demographics: (Note: Insert relevant statistics and data here, citing sources) Unemployment disproportionately affects low-income households and specific demographics, leading to increased poverty and social inequality.
Keywords: unemployment rate, job losses, recession, economic hardship, social security.
Factors Contributing to Unemployment Risk
Several factors contribute to the risk of unemployment. Automation and technological advancements displace workers in certain sectors. Globalization, while offering benefits, can lead to job losses in countries with lower labor costs. Economic downturns, such as recessions, inevitably result in widespread job losses across various industries.
- Examples of industries vulnerable to job losses:
- Manufacturing (automation)
- Retail (e-commerce)
- Customer service (AI)
Keywords: job market, automation, globalization, economic slowdown, workforce participation rate.
The Interplay Between Inflation and Unemployment
The Phillips Curve and its Limitations
The Phillips Curve traditionally suggests an inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment: low unemployment is associated with higher inflation, and vice versa. However, this model has limitations. The relationship isn't always stable, and factors like stagflation (simultaneous high inflation and high unemployment) demonstrate exceptions to the rule.
- Historical examples where the Phillips Curve failed to accurately predict economic trends: (Note: Include examples such as the stagflation of the 1970s)
Keywords: Phillips Curve, stagflation, economic models, inflation-unemployment trade-off.
Strategies for Mitigating Risks
Governments and central banks employ various strategies to address inflation and unemployment. Monetary policy tools, such as interest rate hikes, aim to curb inflation by reducing borrowing and spending. Fiscal policy tools, such as tax cuts or government spending, can stimulate economic activity and reduce unemployment. The effectiveness of these interventions depends on various factors and timing.
- Examples of successful and unsuccessful policy interventions in the past: (Note: Include specific examples and analysis of their effectiveness.)
Keywords: monetary policy tools, fiscal policy tools, economic stimulus, government intervention.
Conclusion: Preparing for Economic Uncertainty: The Threat of Higher Inflation and Unemployment
In conclusion, the intertwined threats of higher inflation and unemployment present significant challenges to the global economy. Understanding the causes, consequences, and interplay of these factors is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers. The traditional economic models, like the Phillips Curve, offer insights but also have limitations. Effective mitigation strategies require careful consideration of both monetary and fiscal policies, tailored to the specific economic context.
Individuals and businesses can prepare for economic uncertainty by diversifying investments, building emergency funds, and focusing on upskilling to adapt to changing job markets. Understanding economic uncertainty is crucial for navigating these challenging times. Stay informed and prepare for the threats of higher inflation and unemployment. Learn more about managing economic uncertainty today!

Featured Posts
-
 Problemas Ticketmaster 8 De Abril Informacion Y Actualizaciones De Grupo Milenio
May 30, 2025
Problemas Ticketmaster 8 De Abril Informacion Y Actualizaciones De Grupo Milenio
May 30, 2025 -
 Securing Gorillaz Concert Tickets In London A Step By Step Guide
May 30, 2025
Securing Gorillaz Concert Tickets In London A Step By Step Guide
May 30, 2025 -
 Le Vietnam Et La France Investir Dans La Mobilite Durable
May 30, 2025
Le Vietnam Et La France Investir Dans La Mobilite Durable
May 30, 2025 -
 Europe 1 Soir Du 19 03 2025 L Integrale De L Emission
May 30, 2025
Europe 1 Soir Du 19 03 2025 L Integrale De L Emission
May 30, 2025 -
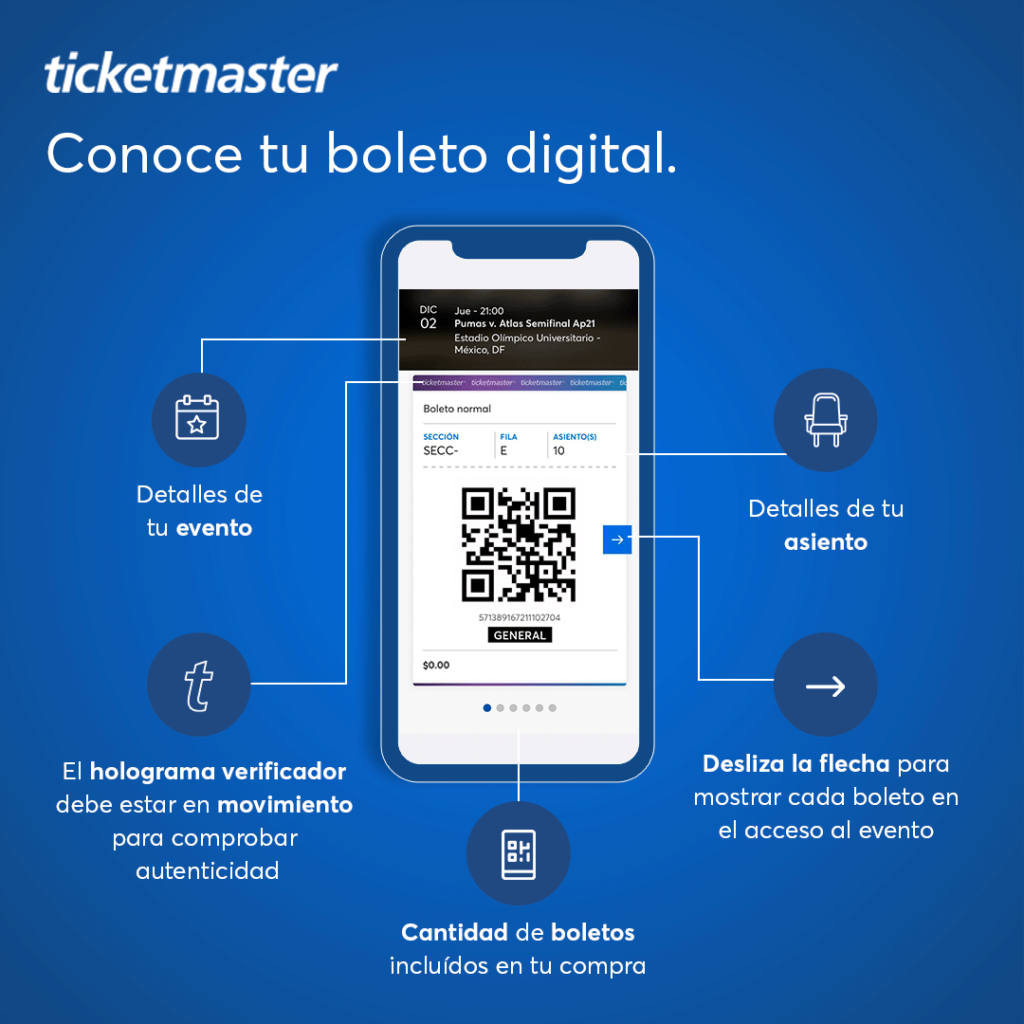 Ticketmaster Revoluciona La Compra De Boletos Descubre Virtual Venue
May 30, 2025
Ticketmaster Revoluciona La Compra De Boletos Descubre Virtual Venue
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Rome Masters Alcaraz And Passaro Secure Wins At Italian International
May 31, 2025
Rome Masters Alcaraz And Passaro Secure Wins At Italian International
May 31, 2025 -
 Italian International Alcaraz Wins Opener Passaro Upsets Dimitrov In Rome
May 31, 2025
Italian International Alcaraz Wins Opener Passaro Upsets Dimitrov In Rome
May 31, 2025 -
 Bmw Open Zverev Rallies Into Semifinals
May 31, 2025
Bmw Open Zverev Rallies Into Semifinals
May 31, 2025 -
 Covid 19 Case Rise Attributed To New Variant According To Who
May 31, 2025
Covid 19 Case Rise Attributed To New Variant According To Who
May 31, 2025 -
 Zverev Fights Back To Reach Bmw Open Semifinals
May 31, 2025
Zverev Fights Back To Reach Bmw Open Semifinals
May 31, 2025
