Gas Prices Surge: Nearly 20-Cent Increase Per Gallon
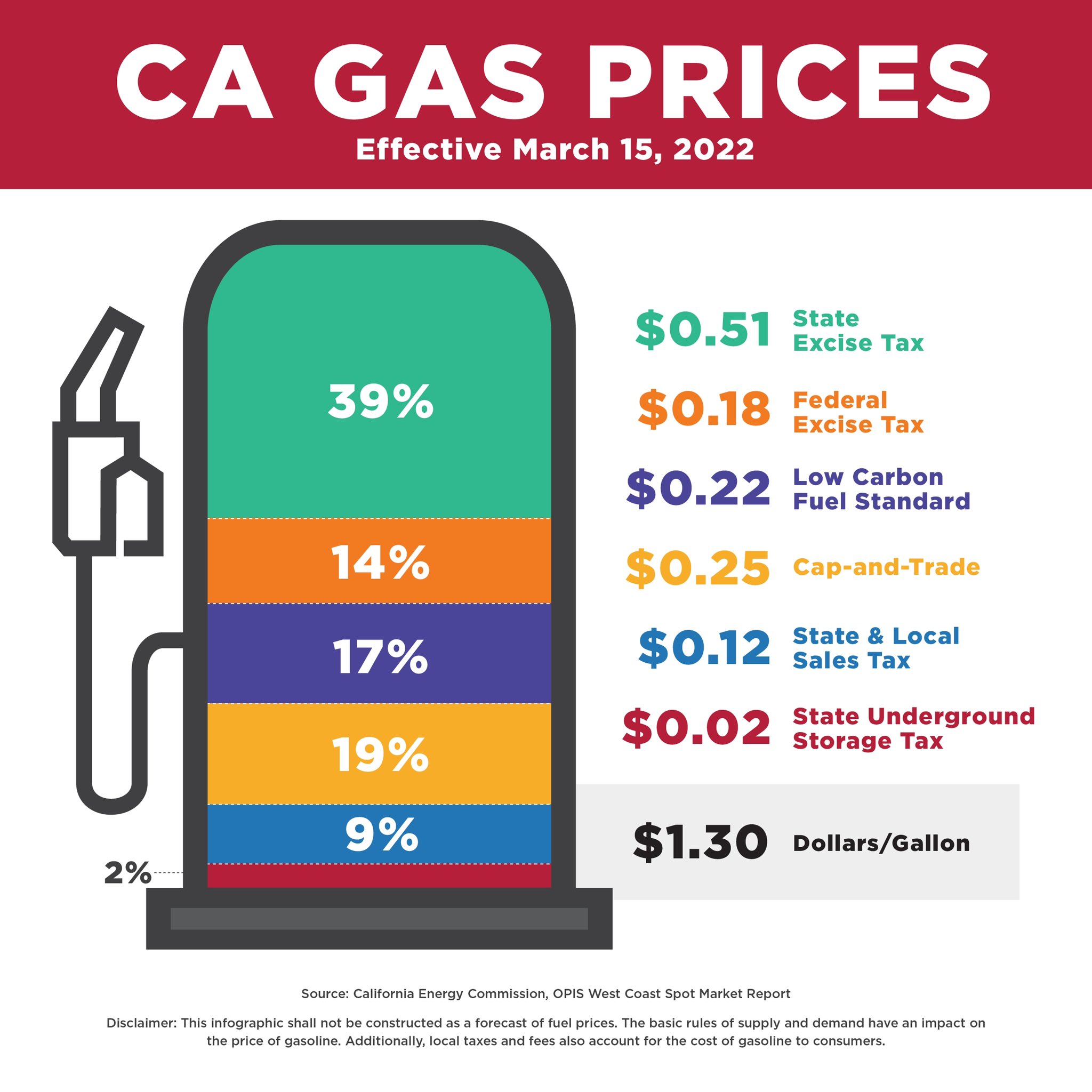
Table of Contents
Reasons Behind the Nearly 20-Cent Gas Price Increase
Several interconnected factors contribute to this alarming increase in gas prices. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial to anticipating future price fluctuations.
Crude Oil Price Volatility
Global crude oil prices are the primary driver of gasoline costs. Recent fluctuations have sent shockwaves through the energy market.
- Geopolitical Instability: The ongoing conflict in Ukraine continues to disrupt global oil supplies, pushing prices higher. Sanctions imposed on Russia, a major oil producer, have further constrained the market.
- OPEC+ Decisions: The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC+) has influenced supply by adjusting production quotas, impacting global oil availability and consequently, gas prices.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Ongoing supply chain challenges, including logistical bottlenecks and transportation issues, contribute to increased costs throughout the oil and gas production and distribution chain.
Data shows a direct correlation between crude oil price increases and the rise in gasoline prices. For example, a 5% increase in crude oil prices often translates to a 2-3% increase in gas prices at the pump. This recent surge reflects a significant jump in crude oil prices.
Refinery Capacity and Maintenance
Reduced refinery capacity plays a crucial role in gas price spikes. Planned and unplanned maintenance at refineries can temporarily decrease gasoline production, leading to tighter supplies and higher prices.
- Unexpected Shutdowns: Unforeseen operational issues or equipment failures at refineries can drastically reduce output, impacting the supply chain immediately.
- Seasonal Maintenance: Refineries often undergo scheduled maintenance during certain periods of the year, potentially leading to temporary production cuts.
- Bottlenecks in Refining: Inefficiencies or capacity constraints at individual refineries can create bottlenecks, resulting in reduced overall gasoline production.
The impact of even a small decrease in refinery output can be substantial, leading to a noticeable increase in gas prices at the pump.
Seasonal Demand and Increased Travel
Summer travel season significantly increases the demand for gasoline. This surge in consumption directly impacts prices, pushing them upward.
- Peak Travel Periods: Holidays, long weekends, and summer vacations all contribute to a peak in gasoline consumption.
- Increased Road Trips: More people hit the road during summer, driving up overall fuel demand.
- Tourism and Recreation: Increased tourism and recreational activities translate to more vehicles on the road, intensifying fuel demand.
Historical data clearly shows a seasonal pattern in gas prices, with prices consistently higher during peak travel months.
Geopolitical Factors and Sanctions
Geopolitical events and international sanctions continue to exert significant pressure on global energy markets.
- International Conflicts: Conflicts and political instability in oil-producing regions disrupt supply chains and create uncertainty, influencing prices.
- Sanctions and Embargoes: Sanctions and embargoes targeting specific oil-producing nations create supply shortages and can drastically impact global prices.
- Energy Security Concerns: Growing concerns about energy security among nations lead to increased demand and potential price spikes.
The current geopolitical climate plays a considerable role in driving up gas prices, as seen in the recent dramatic increases.
Impact of the Gas Price Surge on Consumers and the Economy
The nearly 20-cent gas price increase has widespread ramifications for consumers and the broader economy.
Increased Transportation Costs
Higher gas prices directly translate to increased costs for businesses and individuals relying on transportation.
- Commuting Costs: Daily commutes become more expensive, impacting household budgets.
- Delivery Services: Increased fuel costs are passed onto consumers through higher prices for goods and services.
- Transportation of Goods: The cost of transporting goods increases, impacting the price of various products on store shelves.
Data indicates that a significant portion of household budgets are allocated to transportation costs, making gas price increases particularly impactful.
Inflationary Pressure
Rising gas prices contribute to overall inflation, impacting the purchasing power of consumers.
- Ripple Effect: Increased transportation costs ripple through the economy, impacting prices of various goods and services.
- Food Prices: Higher transportation costs for food products lead to increased grocery bills.
- General Inflation: Energy prices, including gasoline, are a major component of overall inflation rates.
The impact of higher gas prices on inflation is considerable, affecting households across different income levels.
Impact on Consumer Spending
Increased gas prices reduce consumer spending and disposable income.
- Reduced Discretionary Income: Higher fuel costs leave less money for other expenses, impacting consumer purchasing power.
- Shift in Spending Habits: Consumers may reduce spending on non-essential goods and services to offset higher fuel costs.
- Economic Slowdown: Reduced consumer spending can contribute to an economic slowdown.
Data shows a clear correlation between gas price increases and a decline in consumer confidence and spending.
Potential Future Trends and Mitigation Strategies
Predicting future gas prices is complex, but several factors warrant consideration.
Predictions for Gas Prices
Experts predict continued volatility in gas prices, influenced by several factors.
- Geopolitical Uncertainty: Continued geopolitical instability will likely maintain upward pressure on prices.
- OPEC+ Policies: OPEC+ decisions regarding production quotas will significantly impact global oil supply and prices.
- Economic Growth: Global economic growth can increase demand for energy, driving up prices.
Forecasts vary, but many experts predict continued price fluctuations in the coming months and years.
Government Policies and Regulations
Governments can implement various policies to mitigate gas price volatility.
- Strategic Petroleum Reserves: Releasing oil from strategic reserves can temporarily alleviate supply constraints and lower prices.
- Investment in Renewable Energy: Investing in renewable energy sources reduces reliance on fossil fuels and increases energy security.
- Fuel Efficiency Standards: Implementing stricter fuel efficiency standards for vehicles reduces overall gasoline consumption.
Government intervention plays a critical role in managing energy prices and ensuring energy security.
Consumer Strategies for Managing Rising Gas Costs
Consumers can take proactive steps to reduce their fuel consumption and manage rising gas costs.
- Fuel-Efficient Driving: Driving at steady speeds, avoiding aggressive acceleration and braking, and properly maintaining your vehicle can improve fuel efficiency.
- Car Maintenance: Regular car maintenance, including tire inflation checks and tune-ups, can significantly improve fuel economy.
- Alternative Transportation: Exploring alternatives like public transportation, cycling, or carpooling can reduce reliance on personal vehicles.
By adopting these strategies, consumers can reduce their overall fuel expenses.
Conclusion
The nearly 20-cent gas price surge is a result of a complex interplay of factors, including crude oil price volatility, refinery capacity issues, seasonal demand, and geopolitical events. This increase has significant implications for consumers, impacting transportation costs, inflation, and overall consumer spending. Looking ahead, predicting future gas prices remains challenging, but government policies and individual strategies can help mitigate the impact of these fluctuations. Stay informed about the latest developments in gas prices and take steps to mitigate their impact on your budget. Understanding the factors driving these gas price changes empowers you to make informed decisions and manage your expenses effectively.

Featured Posts
-
 Pinata Smashling And Jellystone Key Additions To Teletoon S Spring Streaming Slate
May 22, 2025
Pinata Smashling And Jellystone Key Additions To Teletoon S Spring Streaming Slate
May 22, 2025 -
 Rodgers Steelers Visit Fuels Nfl Trade Speculation
May 22, 2025
Rodgers Steelers Visit Fuels Nfl Trade Speculation
May 22, 2025 -
 Israeli Embassy Victims Identified Young Couple Days From Engagement
May 22, 2025
Israeli Embassy Victims Identified Young Couple Days From Engagement
May 22, 2025 -
 Rio Tintos Response To Claims Of Pilbara Environmental Degradation
May 22, 2025
Rio Tintos Response To Claims Of Pilbara Environmental Degradation
May 22, 2025 -
 Tuerkiye Ve Italya Nin Ortak Nato Goerevi Planin Ayrintilari
May 22, 2025
Tuerkiye Ve Italya Nin Ortak Nato Goerevi Planin Ayrintilari
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 How To Write A Compelling Brief A Step By Step Guide
May 23, 2025
How To Write A Compelling Brief A Step By Step Guide
May 23, 2025 -
 Navigating Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 Key Concepts In Rock 101
May 23, 2025
Navigating Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 Key Concepts In Rock 101
May 23, 2025 -
 Understanding The Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 From X101 5
May 23, 2025
Understanding The Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 From X101 5
May 23, 2025 -
 Decoding The Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 97 1 Double Q
May 23, 2025
Decoding The Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 97 1 Double Q
May 23, 2025 -
 The Karate Kid A Comprehensive Guide To The Film Series
May 23, 2025
The Karate Kid A Comprehensive Guide To The Film Series
May 23, 2025
