Global Deforestation Surges: Wildfires Exacerbate Environmental Disaster
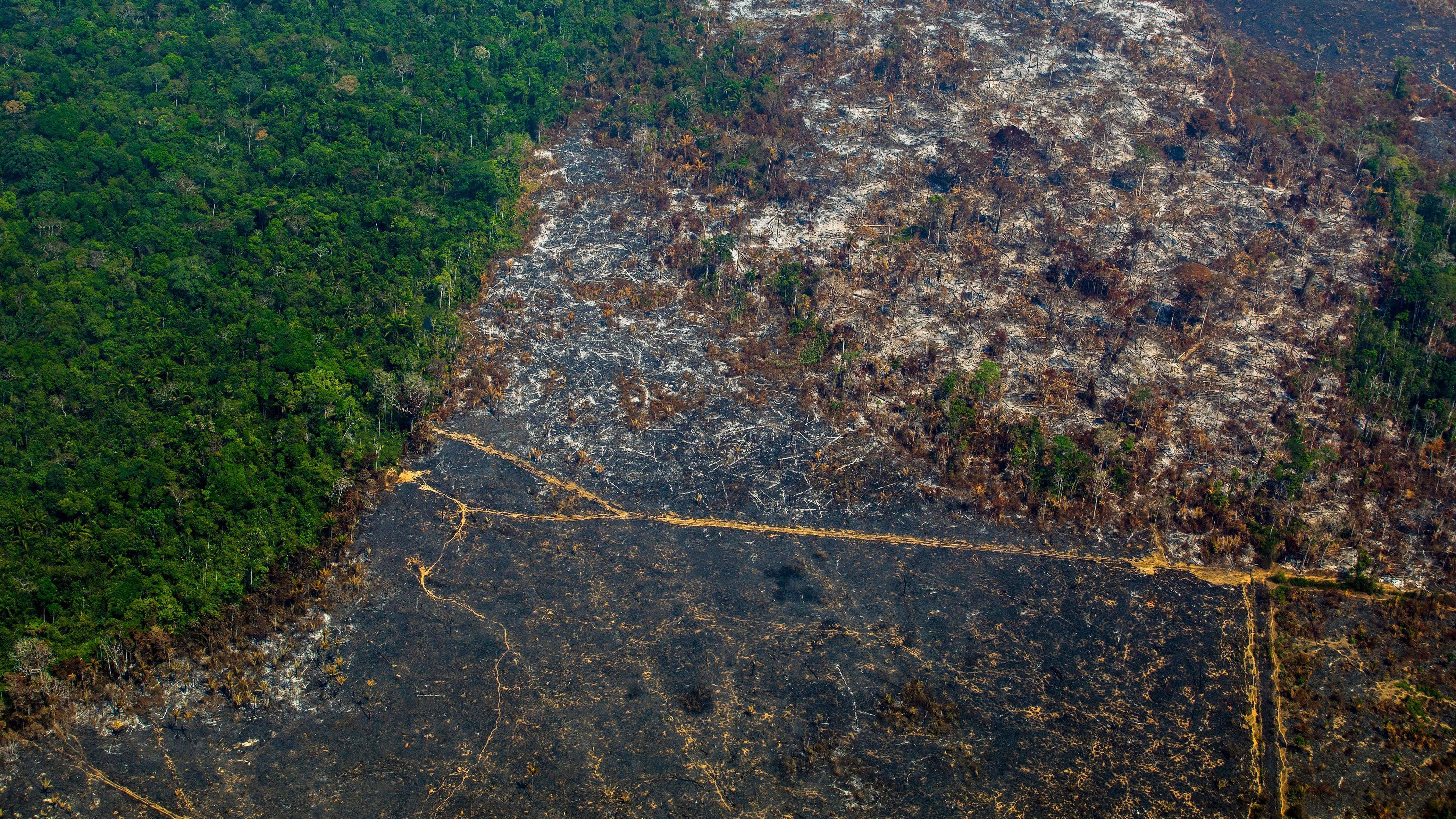

Table of Contents
The Alarming Rate of Global Deforestation
Deforestation, the clearing of forests for other land uses, is a complex problem with devastating consequences. Its primary drivers include logging for timber, agricultural expansion (particularly for cattle ranching and palm oil plantations), mining operations, and urbanization. The scale of deforestation is staggering. The Amazon rainforest, often called the "lungs of the planet," is experiencing record levels of deforestation, with millions of hectares lost annually. Similar alarming trends are observed in the Congo Basin and Borneo, regions crucial for global biodiversity.
- Biodiversity Loss: Deforestation leads to habitat destruction, pushing countless plant and animal species towards extinction. The loss of these species disrupts entire ecosystems and weakens their resilience.
- Climate Change: Forests act as crucial carbon sinks, absorbing atmospheric carbon dioxide. Deforestation releases this stored carbon, contributing significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and accelerating climate change. The resulting increased temperatures exacerbate the frequency and intensity of wildfires, creating a vicious cycle.
- Threats to Indigenous Communities: Many indigenous communities rely on forests for their livelihoods and cultural survival. Deforestation displaces these communities, destroying their traditional ways of life and access to vital resources.
- Economic Consequences: While short-term economic gains may be achieved through deforestation, the long-term economic costs are substantial. Loss of ecosystem services, reduced agricultural productivity, and decreased tourism revenue represent significant financial burdens.
Wildfires: A Major Driver of Deforestation
Wildfires are inextricably linked to deforestation. Not only do they directly destroy vast swathes of forest, but they also leave behind landscapes vulnerable to further deforestation. Burned areas are often more susceptible to erosion, making them less suitable for forest regeneration and more prone to future fires. Climate change, characterized by prolonged droughts and higher temperatures, is significantly increasing the frequency and intensity of wildfires globally. Human activities, such as accidental and intentional forest fires, also play a major role.
- Examples of Devastating Wildfires: The 2019-2020 Australian bushfires, the 2021 Northwest Pacific wildfires, and the recurring Amazonian wildfires are stark examples of the devastating impact of wildfires on forest ecosystems. These fires not only destroyed unique and irreplaceable habitats but also released massive amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
- Role of Drought and Human Ignition: Prolonged droughts create tinder-dry conditions, making forests highly susceptible to ignition. Human activities, such as carelessly discarded cigarettes or intentional setting of fires for land clearing, are often the primary causes of wildfires.
- Difficulty of Control: Controlling large-scale wildfires, particularly in remote and inaccessible areas, is incredibly challenging, requiring significant resources and coordinated efforts.
The Environmental Consequences of Global Deforestation and Wildfires
The environmental consequences of global deforestation and wildfires are far-reaching and interconnected. The impacts extend beyond the immediate destruction of forests, affecting global climate patterns and the delicate balance of ecosystems worldwide.
- Biodiversity Loss and Extinction Risks: The loss of habitat due to deforestation and wildfires drives species extinction and severely reduces biodiversity, impacting the stability and resilience of ecosystems.
- Increased Greenhouse Gas Emissions: The release of stored carbon from deforestation and the combustion of biomass during wildfires contributes significantly to global warming, exacerbating climate change.
- Disruption of Water Cycles: Deforestation disrupts water cycles, leading to altered rainfall patterns, increased risk of flooding in some areas, and more severe droughts in others.
- Soil Erosion and Land Degradation: The removal of forest cover leaves the soil exposed to erosion, leading to land degradation and reduced agricultural productivity.
- Impact on Air Quality: Wildfires release massive amounts of pollutants into the atmosphere, significantly degrading air quality and posing serious health risks to humans and wildlife.
Combating Global Deforestation and Wildfire Threats: Solutions and Strategies
Combating global deforestation and wildfire threats requires a multi-pronged approach involving sustainable forestry practices, responsible land management, technological advancements, and international cooperation.
- Sustainable Forestry Practices: Implementing sustainable logging techniques, promoting responsible forest management, and encouraging reforestation efforts are crucial for mitigating deforestation.
- Responsible Land Management and Conservation Initiatives: Protecting existing forests through the establishment of protected areas, promoting sustainable agriculture, and reducing pressure on forest resources are essential.
- Technological Solutions: Utilizing satellite imagery for monitoring deforestation and wildfire detection, employing advanced fire suppression techniques, and developing early warning systems can improve our ability to respond to these threats.
- International Cooperation and Policy Changes: International agreements and strong environmental policies are vital for promoting responsible land use and combating illegal logging and deforestation.
Specific Actions:
- Support sustainable businesses and products certified by organizations like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC).
- Advocate for stronger environmental policies at local and national levels.
- Reduce your carbon footprint through sustainable consumption and lifestyle choices.
- Donate to reputable conservation organizations working to protect forests and combat deforestation.
- Support reforestation projects by planting trees and participating in community initiatives.
Conclusion: Taking Action Against the Global Deforestation Crisis
Global deforestation and the escalating frequency of wildfires present a grave threat to our planet's future. The interconnected nature of these issues, their impact on climate change, and the devastating consequences for biodiversity and human communities demand urgent and decisive action. We must transition towards sustainable practices, strengthen conservation efforts, and support policies that prioritize the protection of our forests. To prevent deforestation, combat deforestation, and ultimately stop deforestation, we need collective action. Learn more about global deforestation, support environmental organizations working to protect our forests, and advocate for policy changes that prioritize sustainable land management and climate action. The future of our planet depends on it.

Featured Posts
-
 Blue Origin Rocket Launch Abruptly Halted Subsystem Malfunction
May 22, 2025
Blue Origin Rocket Launch Abruptly Halted Subsystem Malfunction
May 22, 2025 -
 Mission Patrimoine 2025 Plouzane Et Clisson Deux Sites Bretons Restaures
May 22, 2025
Mission Patrimoine 2025 Plouzane Et Clisson Deux Sites Bretons Restaures
May 22, 2025 -
 Bank Of Canadas Inflation Dilemma Core Inflation Heats Up
May 22, 2025
Bank Of Canadas Inflation Dilemma Core Inflation Heats Up
May 22, 2025 -
 Ftcs Appeal Against Court Approval Of Microsoft Activision Merger
May 22, 2025
Ftcs Appeal Against Court Approval Of Microsoft Activision Merger
May 22, 2025 -
 William Goodge Conquering Australia On Foot A New Record
May 22, 2025
William Goodge Conquering Australia On Foot A New Record
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Ukrayina Poza Nato Politichni Ta Bezpekovi Naslidki
May 22, 2025
Ukrayina Poza Nato Politichni Ta Bezpekovi Naslidki
May 22, 2025 -
 Nato Nun Tuerkiye Ve Italya Icin Hazirladigi Yeni Plan
May 22, 2025
Nato Nun Tuerkiye Ve Italya Icin Hazirladigi Yeni Plan
May 22, 2025 -
 Unian Patrushev Preduprezhdaet O Planakh Nato Po Zakhvatu Kaliningrada
May 22, 2025
Unian Patrushev Preduprezhdaet O Planakh Nato Po Zakhvatu Kaliningrada
May 22, 2025 -
 Nato Ta Ukrayina Riziki Vidmovi Vid Chlenstva Za Otsinkoyu Yevrokomisiyi
May 22, 2025
Nato Ta Ukrayina Riziki Vidmovi Vid Chlenstva Za Otsinkoyu Yevrokomisiyi
May 22, 2025 -
 Tuerkiye Ve Italya Nin Ortak Nato Goerevi Planin Ayrintilari
May 22, 2025
Tuerkiye Ve Italya Nin Ortak Nato Goerevi Planin Ayrintilari
May 22, 2025
