Impact Of Weakening Ocean Currents On US Sea Level Rise
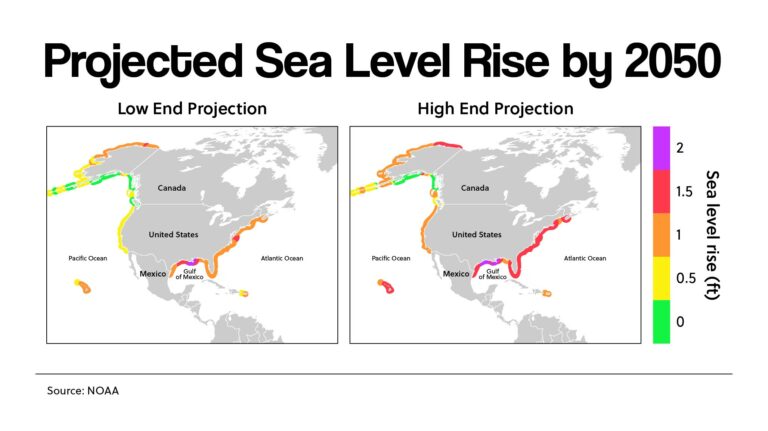
Table of Contents
The Role of Ocean Currents in Regulating Sea Level
Ocean currents play a vital role in regulating global climate and sea levels. These massive, continuous flows of water distribute heat around the planet, influencing weather patterns and coastal dynamics. A key system is the thermohaline circulation (THC), often called the "global ocean conveyor belt," driven by differences in water temperature and salinity.
Thermohaline Circulation and its Impact
The THC is a complex system of interconnected currents that transports warm, salty water from the tropics towards the poles, and cold, denser water back towards the equator. This system is crucial for regulating global heat distribution. Changes in salinity and temperature, however, can significantly disrupt the THC.
- The Gulf Stream: This powerful warm current flows along the US East Coast, moderating the climate and influencing sea levels. A slowdown in the Gulf Stream could lead to a significant rise in sea levels along the eastern seaboard.
- Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC): The AMOC is a crucial part of the THC, and its weakening is a major concern. Studies suggest a potential slowdown, with significant implications for the distribution of heat and the rate of sea level rise along the US coastline. Research indicates a correlation between AMOC weakening and accelerated sea level rise in certain regions.
- Other Major Currents: Disruptions to other major ocean currents, even regionally, can have significant impacts on coastal sea levels and weather patterns across various parts of the US. For example, changes in Pacific currents influence the West Coast's climate and sea levels.
Scientific data and research, including satellite altimetry and oceanographic modeling, show observable changes in ocean currents and a strong correlation with the acceleration of sea level rise in several areas. Terms like "Gulf Stream slowdown," "AMOC weakening," and "ocean circulation changes" are increasingly prevalent in scientific literature addressing this issue.
The Impact of Weakening Ocean Currents on US Coastal Regions
The consequences of weakening ocean currents and the resulting sea level rise on US coastal regions are far-reaching and devastating.
Increased Flooding and Erosion
Altered ocean currents directly contribute to increased coastal flooding and erosion. As sea levels rise, even minor storm surges can cause significant inundation, damaging infrastructure and displacing populations.
- Vulnerable Regions: Coastal areas like Florida, Louisiana, and parts of the East Coast are particularly vulnerable to increased flooding and erosion due to their low-lying geography and exposure to powerful storms.
- Economic Consequences: The economic impacts are immense, including damage to coastal properties, disruption of tourism and fishing industries, and increased costs associated with flood mitigation and infrastructure repair.
- Social and Environmental Impacts: Coastal communities face displacement, loss of livelihoods, and damage to crucial ecosystems like wetlands and estuaries. This can lead to climate migration and exacerbate existing social inequalities.
Maps and charts illustrating coastal vulnerability clearly show the areas at highest risk. Case studies detailing the damage from recent storms and the escalating costs associated with sea level rise highlight the urgency of addressing this issue. Keywords like "coastal erosion," "flood risk," "infrastructure damage," and "climate migration" capture the scope of this problem.
Climate Change as the Primary Driver of Weakening Ocean Currents
The primary driver behind the weakening of ocean currents is climate change. The melting of glaciers and ice sheets, accelerated by global warming, introduces vast amounts of freshwater into the ocean.
Melting Ice and Freshwater Influx
This influx of freshwater disrupts the delicate balance of salinity gradients that drive the THC. Less salty water is less dense, reducing the sinking process that fuels the deep ocean currents.
- Global Warming's Role: Global warming is the primary culprit, causing increased temperatures that accelerate ice melt in Greenland, Antarctica, and glaciers worldwide.
- Increased Precipitation: Changes in precipitation patterns also contribute, increasing freshwater runoff into the oceans and further diluting the salinity of surface waters.
- Feedback Loops: The weakening of currents can further exacerbate global warming, creating a dangerous feedback loop. A slower THC might lead to less efficient heat distribution, resulting in further warming in some areas and potentially amplifying ice melt.
Scientific data and graphs showing the relationship between rising global temperatures, ice melt, freshwater input, and the weakening of ocean currents provide compelling evidence for this connection. Keywords like "global warming," "ice melt," "freshwater influx," "salinity changes," and "climate feedback loops" are crucial for understanding the complexity of this issue.
Predicting Future Impacts and Mitigation Strategies
Predicting the future impacts of weakening ocean currents requires sophisticated climate models.
Climate Models and Projections
While climate models provide valuable projections, there remains significant uncertainty regarding the precise extent and timing of future changes.
- Uncertainty in Predictions: The complexity of the ocean-climate system makes precise predictions challenging. However, the overall trend of weakening currents and rising sea levels is clear.
- Mitigation Strategies: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is paramount to slowing down the rate of climate change and mitigating the effects on ocean currents. This requires global cooperation and a transition to cleaner energy sources.
- Coastal Adaptation Measures: Coastal communities must adapt to the inevitable impacts of sea level rise, investing in infrastructure improvements, developing early warning systems, and implementing strategies for managed retreat in particularly vulnerable areas.
The latest climate model projections, alongside discussions of strategies for adapting to sea level rise and the impacts of weakening ocean currents, highlight the necessity for urgent action. Keywords such as "climate model projections," "sea level rise predictions," "climate mitigation," "coastal adaptation," and "sustainability" are critical in this context.
Conclusion
Weakening ocean currents are significantly contributing to rising sea levels along the US coastline, posing a major threat to coastal communities and infrastructure. The primary driver is climate change, accelerating ice melt and disrupting the delicate balance of ocean salinity. Predicting the precise future impacts remains challenging, but the overall trend is alarming. We must urgently reduce greenhouse gas emissions and implement effective coastal adaptation strategies to mitigate the devastating consequences of this growing crisis. Learn more about weakening ocean currents and take action to combat sea level rise. Protecting our coasts from the impact of weakening ocean currents requires immediate and sustained global efforts.

Featured Posts
-
 Indias Trade Relations A Look At The Distance From Pakistan Turkey And Azerbaijan
May 18, 2025
Indias Trade Relations A Look At The Distance From Pakistan Turkey And Azerbaijan
May 18, 2025 -
 Reviewing The Brooklyn Bridges Infrastructure Stability And Sustainability
May 18, 2025
Reviewing The Brooklyn Bridges Infrastructure Stability And Sustainability
May 18, 2025 -
 Best Bitcoin And Crypto Casinos In 2025 The Ultimate Guide
May 18, 2025
Best Bitcoin And Crypto Casinos In 2025 The Ultimate Guide
May 18, 2025 -
 Analyse Steun Voor Uitbreiding Nederlandse Defensie Neemt Toe
May 18, 2025
Analyse Steun Voor Uitbreiding Nederlandse Defensie Neemt Toe
May 18, 2025 -
 Bmw Porsche And The Complexities Of The Chinese Auto Market
May 18, 2025
Bmw Porsche And The Complexities Of The Chinese Auto Market
May 18, 2025
