Increased Retail Sales: Will The Bank Of Canada Cut Rates?
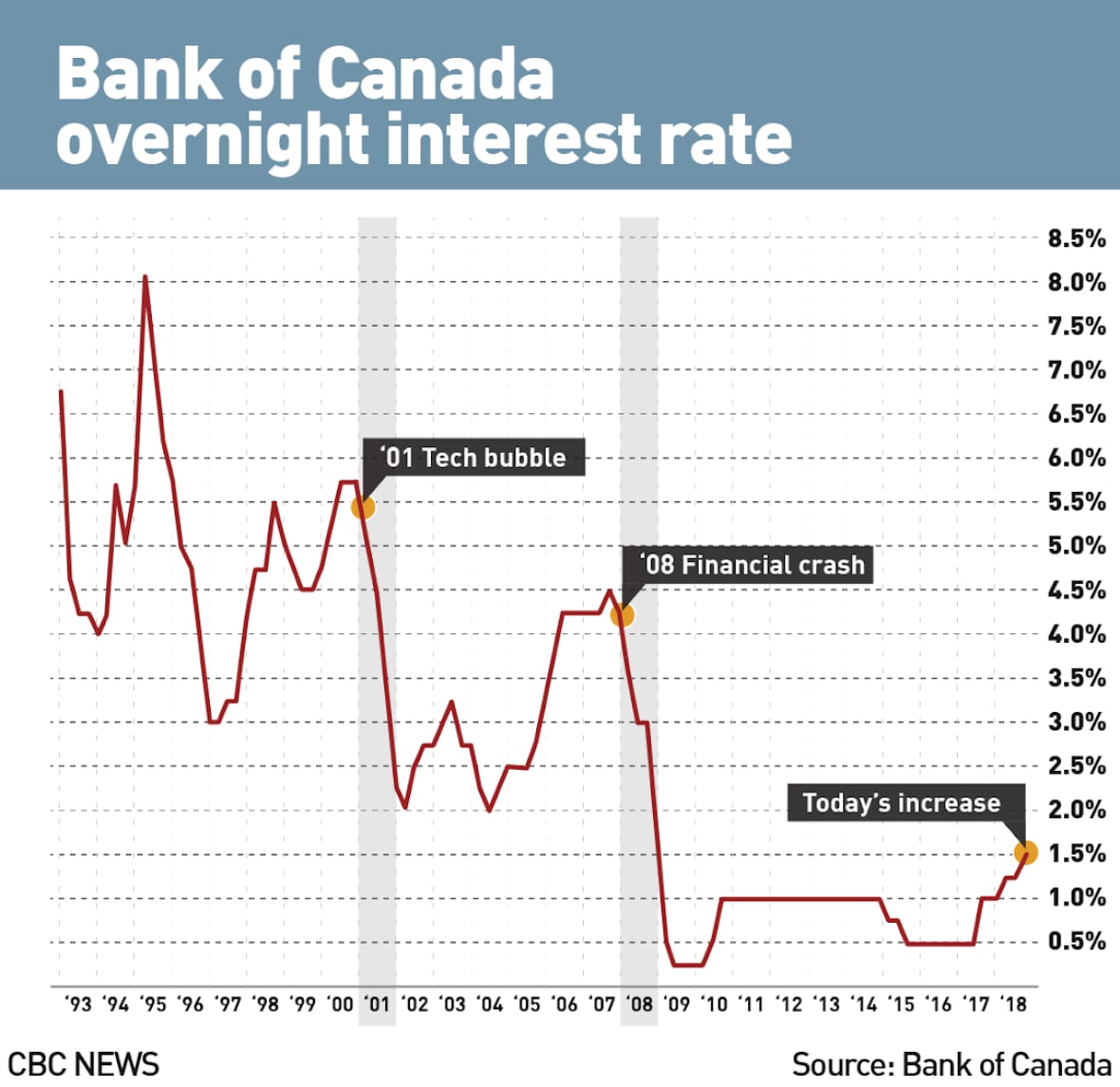
Table of Contents
Recent data reveals a significant increase in Canadian retail sales, sparking considerable debate about the Bank of Canada's next move. This surge in consumer spending presents a complex economic picture, raising questions about inflation, economic growth, and the likelihood of a future interest rate cut. This article will explore the intricate relationship between increased retail sales and the Bank of Canada's monetary policy decisions, examining the potential scenarios that may unfold.
The Impact of Increased Retail Sales on Inflation
Higher retail sales figures often translate to increased inflationary pressures within an economy. This connection stems from several key factors:
- Increased demand leading to higher prices: When consumers spend more, demand for goods and services rises. If supply struggles to keep pace, businesses may respond by increasing prices to maximize profits, leading to inflation. This is particularly true in the current environment where supply chains are still recovering from various disruptions.
- Potential for wage increases due to strong employment: Robust retail sales often indicate a strong economy and high employment rates. This can lead to increased competition for workers, driving up wages. Businesses might then pass these increased labor costs onto consumers in the form of higher prices, further fueling inflation.
- Supply chain constraints exacerbating inflationary effects: Even with strong demand, ongoing global supply chain issues can restrict the availability of goods. This scarcity further contributes to price increases, intensifying inflationary pressures.
- Examination of the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and its recent trends: The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a key metric used to measure inflation. Closely monitoring the CPI, and comparing it to the Bank of Canada’s inflation target, is crucial to understanding the impact of increased retail sales on price stability.
The Bank of Canada has a specific inflation target, typically around 2%. Any significant deviation from this target, whether upward or downward, influences their monetary policy decisions. Understanding the Bank's tolerance for inflation fluctuations is key to anticipating their response to surging retail sales.
Economic Growth and its Influence on Interest Rates
A positive correlation exists between robust retail sales and overall economic growth. Strong retail sales figures often act as a leading indicator of consumer confidence and spending habits:
- Strong retail sales as an indicator of consumer confidence: Healthy retail sales suggest that consumers feel confident about the economy and their personal financial situations, encouraging them to spend more.
- Impact of economic growth on employment rates: Increased consumer spending typically translates into higher demand for goods and services, creating more jobs and boosting employment rates.
- Potential for overheating if growth is unsustainable: While robust growth is generally positive, excessively rapid growth can lead to an overheated economy, characterized by excessive inflation and potential instability.
- GDP growth figures and their implications for monetary policy: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth provides a broader picture of economic expansion. High GDP growth coupled with high retail sales might prompt the Bank of Canada to consider raising interest rates to cool down the economy and prevent inflation from spiralling.
The Bank of Canada's mandate includes maintaining economic stability. This means balancing economic growth with price stability – a delicate act requiring careful consideration of all economic indicators.
The Bank of Canada's Current Monetary Policy Stance
Understanding the Bank of Canada's current monetary policy stance is essential to predicting their next move:
- Review of past interest rate decisions: Examining the Bank's recent history of interest rate adjustments provides context for their current thinking.
- Analysis of the Bank of Canada's recent statements and communication: Official statements, press releases, and Governor's speeches offer valuable insights into the Bank's assessment of the economic landscape.
- Discussion of potential factors influencing future rate decisions beyond retail sales (e.g., global economic conditions, exchange rates): The Bank considers a wide range of factors, including global economic conditions, exchange rates, and geopolitical events, when making interest rate decisions. Retail sales are just one piece of a much larger puzzle.
Given the current economic indicators, the likelihood of a rate cut remains uncertain. The Bank will likely prioritize controlling inflation while trying to avoid stifling economic growth. A pause in rate increases, rather than a cut, might be a more likely scenario in the near term.
Alternative Economic Scenarios
Several economic scenarios could influence the Bank of Canada's decision regarding interest rates:
- Scenario 1: Sustained retail growth leading to further rate hikes: If retail sales continue to rise strongly and inflation remains elevated, the Bank might choose to further increase interest rates to curb inflationary pressures.
- Scenario 2: Retail sales growth slowing down, leading to a pause or rate cut: If retail sales growth slows or consumer spending weakens, indicating a cooling economy, the Bank might pause rate hikes or even consider a rate cut to stimulate economic activity.
- Scenario 3: Global economic downturn influencing Canadian monetary policy: A global recession could significantly impact the Canadian economy, potentially leading the Bank of Canada to cut interest rates to mitigate the negative effects.
Conclusion
Increased retail sales present a complex challenge for the Bank of Canada. While strong consumer spending signals economic health, it also raises concerns about inflation. The Bank will need to carefully balance these competing factors when making future interest rate decisions. The likelihood of a rate cut remains uncertain, dependent on various economic indicators beyond just retail sales.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the latest developments in Canadian monetary policy and the impact of increased retail sales on interest rates. Follow our blog for regular updates on the Bank of Canada and its potential future rate cuts related to increased retail sales. Subscribe to receive timely economic analysis and insights.

Featured Posts
-
 Ai Driven Podcast Production Processing Repetitive Scatological Documents
May 26, 2025
Ai Driven Podcast Production Processing Repetitive Scatological Documents
May 26, 2025 -
 Holocaust Remembrance Meta Israel And Israeli Celebrities Launch Fifth Annual Instagram Project
May 26, 2025
Holocaust Remembrance Meta Israel And Israeli Celebrities Launch Fifth Annual Instagram Project
May 26, 2025 -
 Trump Vs Europe A Deep Dive Into The Trade Conflicts
May 26, 2025
Trump Vs Europe A Deep Dive Into The Trade Conflicts
May 26, 2025 -
 Jenson And The Fw 22 Extended A Deep Dive
May 26, 2025
Jenson And The Fw 22 Extended A Deep Dive
May 26, 2025 -
 Saksikan Aksi Sengit Moto Gp Inggris Jadwal Lengkap Semua Sesi
May 26, 2025
Saksikan Aksi Sengit Moto Gp Inggris Jadwal Lengkap Semua Sesi
May 26, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Offre Limitee Samsung Galaxy S25 128 Go A 814 22 E
May 28, 2025
Offre Limitee Samsung Galaxy S25 128 Go A 814 22 E
May 28, 2025 -
 Promo Samsung Galaxy S25 128 Go 5 Etoiles 814 22 E
May 28, 2025
Promo Samsung Galaxy S25 128 Go 5 Etoiles 814 22 E
May 28, 2025 -
 Meilleur Prix Galaxy S25 128 Go Seulement 814 22 E
May 28, 2025
Meilleur Prix Galaxy S25 128 Go Seulement 814 22 E
May 28, 2025 -
 Bon Plan Samsung Galaxy S25 128 Go 5 Etoiles A 814 22 E
May 28, 2025
Bon Plan Samsung Galaxy S25 128 Go 5 Etoiles A 814 22 E
May 28, 2025 -
 Meilleur Prix Samsung Galaxy S25 512 Go 985 56 E
May 28, 2025
Meilleur Prix Samsung Galaxy S25 512 Go 985 56 E
May 28, 2025
