India's INSACOG Detects New COVID-19 Variants BA.1 And LF.7: Risk Evaluation

Table of Contents
Understanding INSACOG's Role in Variant Surveillance
INSACOG plays a vital role in India's fight against COVID-19. This consortium, a network of leading genomic laboratories across the country, is responsible for the genomic surveillance of SARS-CoV-2. Its primary function is the rapid detection and characterization of new COVID-19 variants circulating within India. Early detection is crucial for informing public health responses and mitigating the potential impact of emerging variants.
- INSACOG's Network: The consortium's strength lies in its extensive network of labs, enabling widespread genomic sequencing and analysis. This nationwide reach ensures comprehensive surveillance across diverse populations and geographic regions.
- Genomic Sequencing: INSACOG employs advanced genomic sequencing techniques to identify mutations and track the evolution of the virus. This detailed analysis allows researchers to understand the characteristics of new variants and predict their potential behavior.
- Global Collaboration: INSACOG actively participates in global variant tracking initiatives, sharing data with international organizations like the WHO. This collaboration fosters a better understanding of global pandemic trends and facilitates coordinated responses.
Characteristics and Potential Risks of BA.1 and LF.7 Variants
BA.1 and LF.7 are Omicron subvariants, and while initial data is still being analyzed, understanding their potential risks is paramount. These variants may exhibit characteristics that differentiate them from earlier strains, such as increased transmissibility, altered severity of illness, or the ability to evade existing immunity.
- Transmission Rate: While definitive conclusions require further research, preliminary data suggests that BA.1 and LF.7 might possess higher transmission rates compared to earlier Omicron subvariants. This increased transmissibility could lead to faster spread within the population.
- Severity of Illness: The severity of illness caused by these variants is currently under investigation. Further studies are needed to determine if BA.1 and LF.7 cause more severe disease or different clinical outcomes than previous variants.
- Immune Evasion: The potential for immune evasion is a significant concern. These variants may possess mutations that allow them to escape the protective effects of both prior infection and vaccination, leading to reinfections.
- Vaccine Effectiveness: Current vaccines likely offer some degree of protection against severe illness caused by these variants, but their overall effectiveness might be reduced compared to earlier strains. Booster doses might enhance protection against these emerging variants.
Public Health Implications and Response Strategies in India
The detection of BA.1 and LF.7 highlights the continued need for robust public health strategies in India. These strategies must adapt to the evolving nature of the virus.
- Vaccination Coverage: High vaccination coverage remains crucial. Boosters enhance protection, particularly against severe illness and hospitalization, from emerging variants.
- Testing and Surveillance: Continued genomic surveillance through INSACOG, coupled with increased testing, allows for the early identification of new variants and the monitoring of their spread.
- Preventive Measures: Basic preventive measures, including masking in crowded areas, maintaining social distancing, and practicing good hygiene, continue to be effective in reducing transmission.
- Public Health Communication: Clear and consistent communication from public health authorities is vital in informing the public about the risks, encouraging vaccination, and promoting preventive measures.
The Importance of Continued Vigilance and Global Collaboration
The emergence of BA.1 and LF.7 underscores the importance of continued global collaboration in pandemic preparedness and response. Rapid information sharing and coordinated international efforts are essential for effectively tracking and responding to emerging COVID-19 variants. International health security depends on effective collaboration and transparent data sharing.
Conclusion
INSACOG's detection of BA.1 and LF.7 highlights the dynamic nature of COVID-19 and the ongoing need for robust surveillance. While the precise risks associated with these variants are still under investigation, the potential for increased transmissibility and immune evasion necessitates continued vigilance. Maintaining high vaccination coverage, implementing effective testing and surveillance protocols, and adhering to preventive measures remain crucial. Stay informed about the latest updates on COVID-19 variants from reliable sources like INSACOG and the WHO. Remaining informed about INSACOG’s monitoring of COVID-19 variants is essential for personal and public health. Your continued vigilance and adherence to public health guidelines are critical in mitigating the risk of new COVID-19 variants.

Featured Posts
-
 10 Must Have Android Apps For Every Traveler
May 31, 2025
10 Must Have Android Apps For Every Traveler
May 31, 2025 -
 How To Lose Your Mother By Molly Jong A Concise Overview
May 31, 2025
How To Lose Your Mother By Molly Jong A Concise Overview
May 31, 2025 -
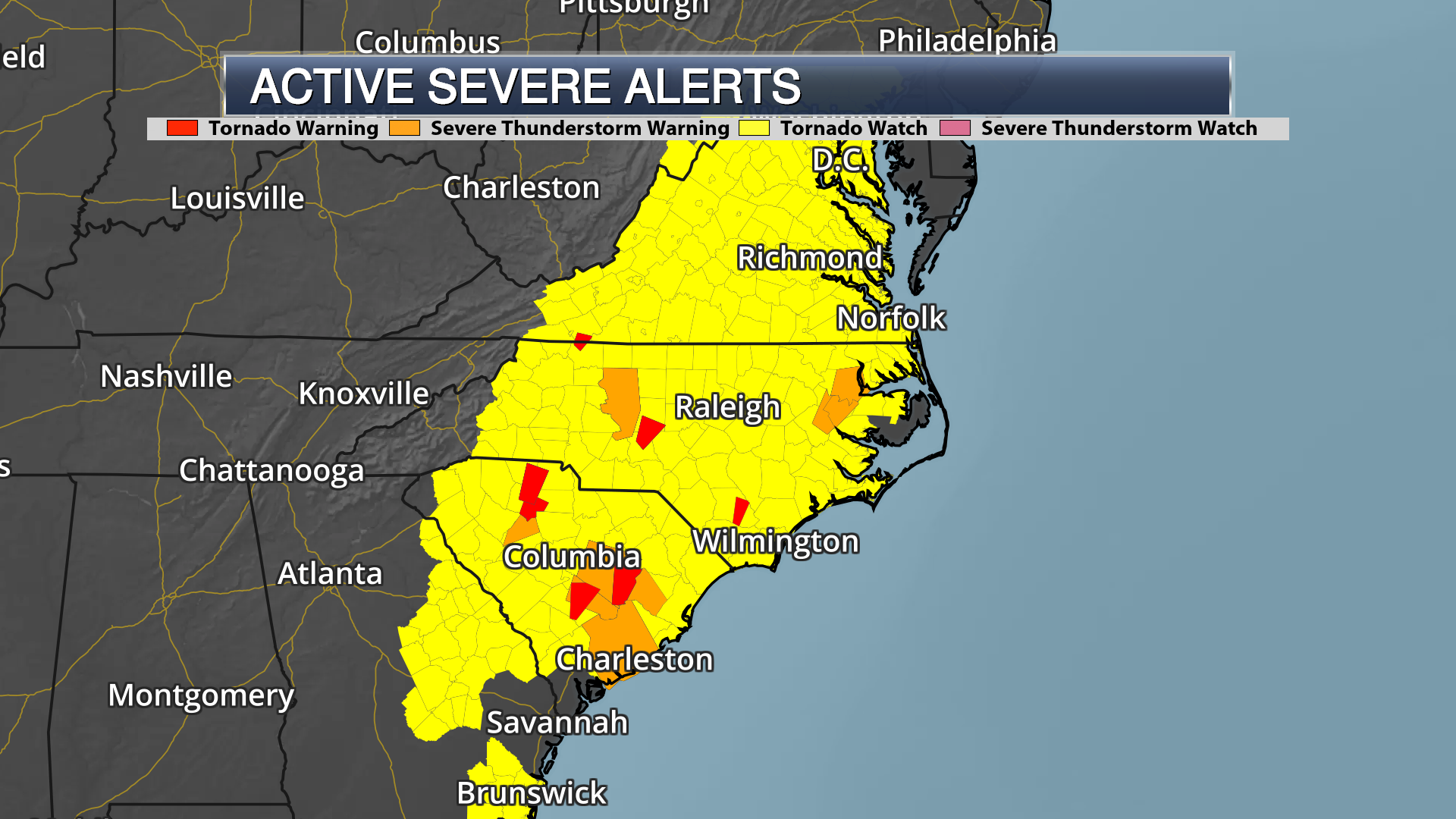 Severe Weather In The Carolinas How To Differentiate Active And Expired Storm Alerts
May 31, 2025
Severe Weather In The Carolinas How To Differentiate Active And Expired Storm Alerts
May 31, 2025 -
 Memorial Day Weekend Detroit Braces For 150 000 Visitors
May 31, 2025
Memorial Day Weekend Detroit Braces For 150 000 Visitors
May 31, 2025 -
 Bernard Kerik Ex Nypd Commissioner Receives Medical Care Full Recovery Anticipated
May 31, 2025
Bernard Kerik Ex Nypd Commissioner Receives Medical Care Full Recovery Anticipated
May 31, 2025
