INSACOG Reports BA.1 And LF.7 COVID-19 Variants In India: Public Health Implications
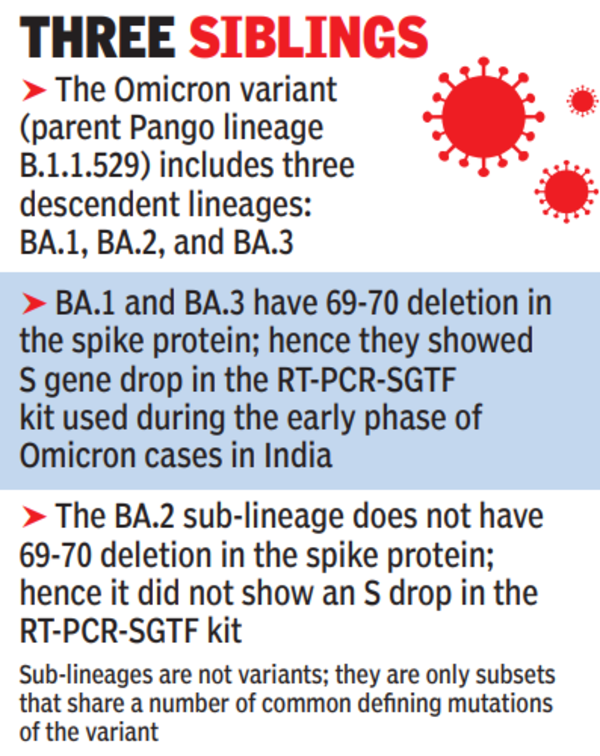
Table of Contents
Understanding the BA.1 and LF.7 COVID-19 Variants
The BA.1 and LF.7 variants represent specific lineages within the larger Omicron variant family of SARS-CoV-2. While both are Omicron subvariants, their specific characteristics and potential impacts may differ.
-
BA.1: This variant, a relatively early Omicron sublineage, was known for its high transmissibility. While generally associated with less severe illness than previous variants like Delta, its ability to evade some immune responses posed a challenge.
-
LF.7: This subvariant, while less prevalent than BA.1 historically, warrants monitoring due to its potential for immune escape and altered transmissibility compared to earlier Omicron strains. More research is needed to fully understand its characteristics.
Key Characteristics & Comparison:
-
Transmissibility: Both BA.1 and LF.7 demonstrated high transmissibility, exceeding earlier variants. Further research is needed to directly compare the relative transmissibility of LF.7 to BA.1.
-
Severity: While generally associated with milder symptoms than previous variants, severe illness and hospitalization are still possible, particularly in vulnerable populations.
-
Immune Evasion: Both variants showed some capacity to evade immune responses conferred by prior infection or vaccination, highlighting the need for updated vaccination strategies and booster shots. The degree of immune evasion differs between the two and requires further analysis.
Understanding the evolutionary pathways of these Omicron subvariants (including BA.1 and LF.7) and their relationship to the original SARS-CoV-2 virus is critical for predicting future viral evolution and developing effective countermeasures. Keywords: Omicron subvariants, SARS-CoV-2, viral evolution, variant characteristics, transmissibility, severity, immune evasion.
INSACOG's Surveillance and Detection Methodology
INSACOG plays a pivotal role in India's COVID-19 response through its robust genomic surveillance network. This network comprises numerous laboratories across the country, enabling real-time monitoring of circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants.
-
Genomic Surveillance Network: The network collects samples from various regions, representing a diverse range of the Indian population.
-
Whole-Genome Sequencing: Sophisticated whole-genome sequencing techniques are employed to identify and characterize the genetic makeup of the virus, allowing for precise variant identification.
-
Early Detection: The rapid detection of new variants, like BA.1 and LF.7, is crucial for informing public health strategies, allowing for timely interventions to mitigate potential outbreaks. This early warning system is paramount to pandemic preparedness. Keywords: genomic surveillance, whole-genome sequencing, variant detection, real-time surveillance, outbreak management.
Public Health Implications of BA.1 and LF.7 Variants in India
The emergence of BA.1 and LF.7 in India necessitates a careful evaluation of their public health implications.
-
Impact on Immunity: The potential for these variants to partially evade vaccine-induced and naturally acquired immunity raises concerns about the effectiveness of current protection strategies. Booster shots targeting newer variants may be necessary.
-
Healthcare Burden: While generally less severe, a surge in infections caused by these highly transmissible variants could still place a strain on India's healthcare system, leading to increased hospitalizations.
-
Infection Resurgence: The potential for resurgence or the emergence of new waves of infections is a significant concern, particularly if these variants gain dominance.
-
Public Health Interventions: Continued vigilance and implementation of effective public health interventions, including vaccination campaigns, targeted testing, and adherence to basic preventative measures (like hand hygiene and mask-wearing in high-risk situations), are crucial to minimize the impact of these variants. Keywords: vaccine effectiveness, natural immunity, hospitalization rates, healthcare burden, public health interventions, vaccination strategies, infection resurgence, social distancing.
Government Response and Preparedness
The Indian government's response to the detection of BA.1 and LF.7 involved strengthening existing surveillance measures and reinforcing public health guidelines. This included:
-
Enhanced Surveillance: INSACOG's activities were intensified to monitor the spread and evolution of these variants.
-
Public Health Messaging: Public awareness campaigns were conducted to educate the public about the risks and importance of preventative measures.
-
Healthcare Preparedness: Hospitals and healthcare facilities were encouraged to maintain preparedness for potential surges in cases, ensuring sufficient capacity and resources. Keywords: government response, public health guidelines, healthcare preparedness, pandemic preparedness, policy changes.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Importance of INSACOG Surveillance for COVID-19 Variants in India
The detection of BA.1 and LF.7 variants highlights the ongoing need for robust genomic surveillance in India. INSACOG's crucial role in early variant detection is undeniable. The potential for immune evasion and increased transmissibility underscores the importance of continued vigilance and proactive measures to prevent future outbreaks. Staying informed about INSACOG updates, following public health guidelines, and actively participating in vaccination programs are essential steps to protect against COVID-19 variants like BA.1 and LF.7. Let's continue to prioritize public health awareness and work collectively to safeguard our communities from emerging threats. Keywords: INSACOG updates, COVID-19 prevention, variant tracking, public health awareness, protect against COVID-19 variants.

Featured Posts
-
 Griekspoor Stuns Zverev In Indian Wells Second Round
May 31, 2025
Griekspoor Stuns Zverev In Indian Wells Second Round
May 31, 2025 -
 From Surprise To Fortune How A Banksy Changed Two Lives
May 31, 2025
From Surprise To Fortune How A Banksy Changed Two Lives
May 31, 2025 -
 Climate Whiplash A Growing Threat To Cities Worldwide
May 31, 2025
Climate Whiplash A Growing Threat To Cities Worldwide
May 31, 2025 -
 Yesilcam In Unutulmaz Guezeli Guelsen Bubikoglu Nun Son Durumu Mine Tugay In Reaksiyonu
May 31, 2025
Yesilcam In Unutulmaz Guezeli Guelsen Bubikoglu Nun Son Durumu Mine Tugay In Reaksiyonu
May 31, 2025 -
 Cape Town Elephant Seal Disrupts Traffic In Suburban Area
May 31, 2025
Cape Town Elephant Seal Disrupts Traffic In Suburban Area
May 31, 2025
