Interest Rate Outlook: The Federal Reserve's Balancing Act
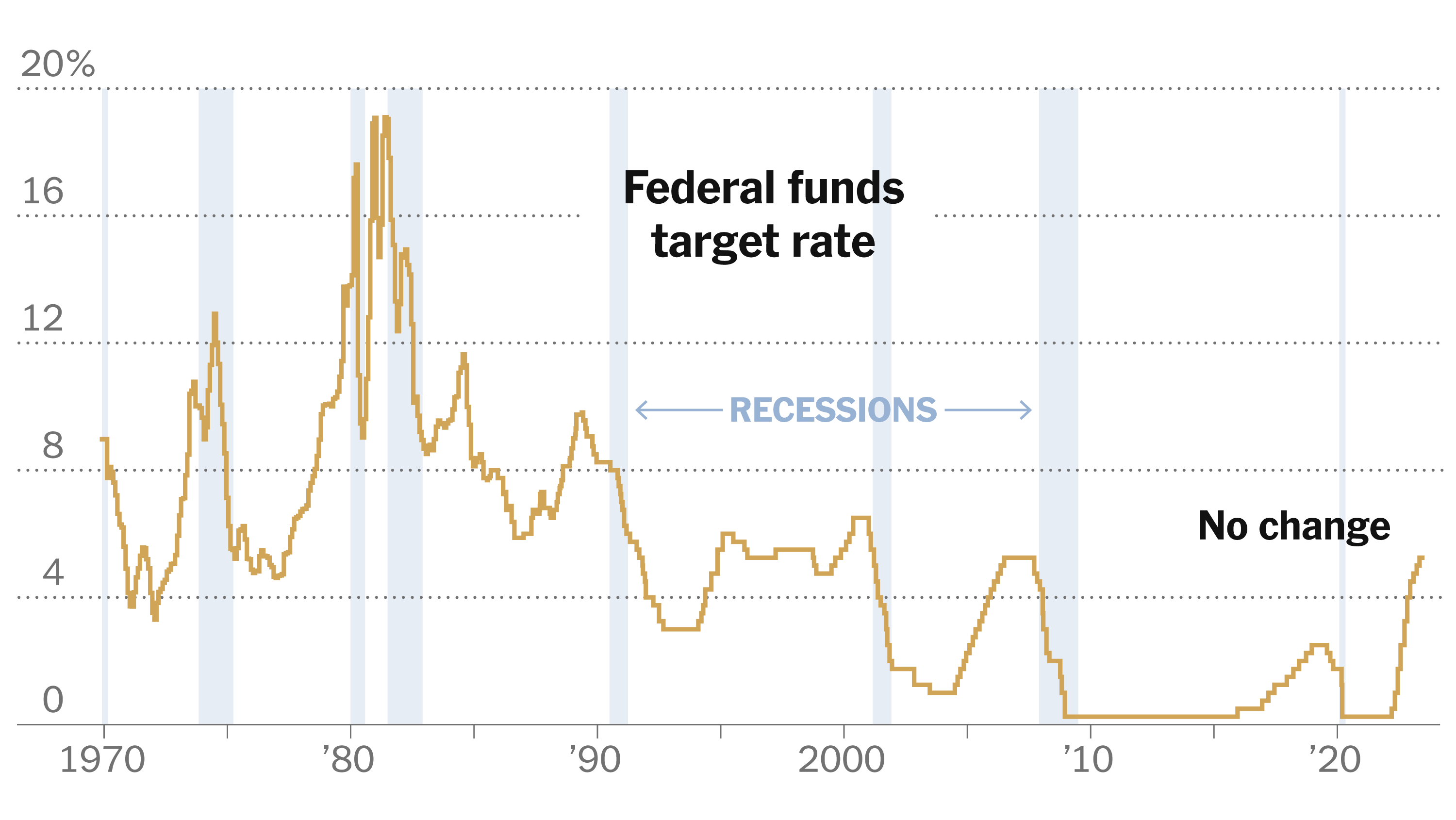
Table of Contents
Inflationary Pressures and the Fed's Response
Persistent Inflation
Stubbornly high inflation rates continue to pose a significant challenge to the US economy. Inflation's impact is far-reaching, affecting consumer spending, business investment, and overall economic growth. The persistence of high inflation necessitates a robust response from the Federal Reserve.
- CPI data: The Consumer Price Index (CPI) remains above the Fed's target rate of 2%, indicating ongoing inflationary pressures. Analyzing monthly CPI reports is crucial for understanding the trajectory of inflation.
- Core inflation: Excluding volatile food and energy prices, core inflation remains elevated, suggesting underlying inflationary pressures within the economy. Monitoring core inflation provides a clearer picture of persistent price increases.
- Supply chain disruptions: Global supply chain bottlenecks continue to contribute to higher prices for goods and services. Easing these disruptions is vital for bringing down inflation.
- Energy prices: Fluctuations in energy prices, particularly oil and gas, significantly impact overall inflation. Geopolitical events and supply constraints influence energy costs.
- Wage growth: Strong wage growth, while positive for workers, can contribute to inflationary pressures if it outpaces productivity gains. The relationship between wage growth and inflation requires careful monitoring.
The relationship between inflation and interest rates is inverse. Higher interest rates aim to curb inflation by reducing borrowing and spending, thus cooling demand.
The Fed's Monetary Policy Tools
The Federal Reserve utilizes various tools to manage interest rates and influence the economy. These tools aim to control inflation while maintaining economic stability.
- Federal Funds Rate targets: The Fed sets a target range for the federal funds rate, the rate banks charge each other for overnight loans. Changes to this rate influence other interest rates throughout the economy.
- Impact on borrowing costs: Higher interest rates increase borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, reducing investment and spending. Lower interest rates have the opposite effect.
- Quantitative easing (QE) vs. quantitative tightening (QT): QE involves the Fed purchasing government bonds to increase the money supply and lower interest rates. QT is the opposite, reducing the money supply and potentially increasing rates. The Fed's current focus is on QT to combat inflation.
It's important to understand that monetary policy operates with a lag. The full effects of interest rate changes are not immediately felt, often taking several months or even longer to manifest.
Economic Growth and Recession Risks
Slowing Economic Growth
The US economy is experiencing a slowdown in growth, raising concerns about a potential recession. Several key economic indicators reflect this trend.
- GDP growth rate: The rate of GDP growth is slowing, signaling a weakening economy. Negative GDP growth for two consecutive quarters is often considered a recession.
- Unemployment rate: While the unemployment rate remains relatively low, it's a lagging indicator, and its direction might not fully reflect the current economic reality.
- Consumer sentiment index: Consumer confidence is declining, reflecting growing uncertainty and pessimism about the economy.
- Business investment: Businesses are becoming more cautious about investment due to higher interest rates and economic uncertainty.
Interest rate hikes directly correlate with an economic slowdown. Higher borrowing costs make investments more expensive, reducing business activity and potentially leading to job losses.
Recessionary Scenarios
The probability of a recession is a key concern among economists and investors. Several models and indicators are used to assess this risk.
- Yield curve inversion: A yield curve inversion, where short-term interest rates exceed long-term rates, is often seen as a leading indicator of a recession. This suggests investors expect future economic weakness.
- Leading economic indicators: Various leading economic indicators, such as manufacturing activity and consumer confidence, provide insights into future economic trends.
- Recessionary models: Economists use various econometric models to predict the probability and severity of a recession, taking into account various factors.
Interest rate policy significantly impacts recession probabilities. While intended to curb inflation, aggressive interest rate hikes increase the risk of triggering a recession by sharply slowing economic activity.
Global Economic Factors and Their Influence
Geopolitical Uncertainty
Global events significantly impact the US economy and the Fed's interest rate decisions. These events can exacerbate inflation and slow economic growth.
- Energy prices: The war in Ukraine has created significant energy price volatility, fueling inflation worldwide.
- Supply chain disruptions: Geopolitical instability and other events often disrupt global supply chains, leading to shortages and higher prices.
- Global inflation rates: High inflation in other countries can affect US inflation through imported goods and global supply chains.
- International trade: Trade disruptions due to geopolitical events or other factors impact the US economy.
The Fed must consider these global factors when making interest rate decisions, as they influence domestic inflation and economic growth.
International Interest Rate Policies
Interest rate policies in other major economies directly influence the US economy and the Fed's actions.
- European Central Bank policies: The ECB's monetary policy decisions impact the euro-dollar exchange rate and global financial markets.
- Bank of Japan policies: The BOJ's policies also affect global financial markets and currency exchange rates.
- Currency exchange rates: Fluctuations in exchange rates affect the prices of imported goods and the competitiveness of US exports.
The interconnectedness of global financial markets requires the Fed to carefully consider international interest rate policies when setting its own monetary policy.
Conclusion
The interest rate outlook remains uncertain, with the Federal Reserve facing a complex balancing act between controlling inflation and fostering sustainable economic growth. While persistent inflation necessitates continued vigilance, the risk of triggering a recession remains a significant concern. The Fed's future decisions will hinge on carefully monitoring economic data, navigating global uncertainties, and assessing the lagged effects of its policies. To stay informed on the evolving interest rate outlook and its impact on your investments and business decisions, regularly consult reputable financial news sources and economic analysis. Understanding the intricacies of the interest rate outlook is crucial for making informed financial decisions in today's dynamic economic environment. Stay updated on the latest developments in the interest rate outlook.

Featured Posts
-
 Colapinto Rumors Intensify What Williams Said About Doohan
May 09, 2025
Colapinto Rumors Intensify What Williams Said About Doohan
May 09, 2025 -
 Opasnye Snegopady V Yaroslavskoy Oblasti Aktualnaya Informatsiya
May 09, 2025
Opasnye Snegopady V Yaroslavskoy Oblasti Aktualnaya Informatsiya
May 09, 2025 -
 Dakota Johnson With Family At Materialist L A Screening
May 09, 2025
Dakota Johnson With Family At Materialist L A Screening
May 09, 2025 -
 Draisaitl Hellebuyck And Kucherov Vie For The Hart Trophy
May 09, 2025
Draisaitl Hellebuyck And Kucherov Vie For The Hart Trophy
May 09, 2025 -
 Woman Claiming Madeleine Mc Cann Identity Arrested On Stalking Charges
May 09, 2025
Woman Claiming Madeleine Mc Cann Identity Arrested On Stalking Charges
May 09, 2025
