Managing The Increasing Wolf Population In The North State
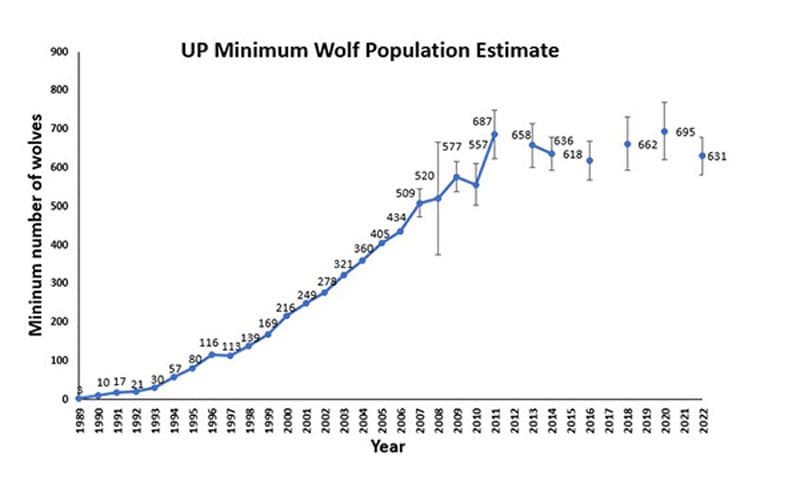
Table of Contents
H2: Understanding the Current North State Wolf Population Dynamics
The North State wolf population is experiencing a period of robust growth, driven by several interconnected factors. Accurate estimates remain challenging due to the elusive nature of wolves, but recent studies suggest a substantial increase in pack numbers and overall population size. This expansion is fueled by several key elements:
- Habitat Expansion: Increased forest protection and restoration efforts have expanded suitable wolf habitat, providing more space for packs to establish territories and thrive.
- Prey Availability: Abundant populations of deer and elk within the North State provide a stable food source, supporting increased wolf reproduction and survival rates.
- Successful Breeding: Higher survival rates among pups and successful breeding within established packs have contributed significantly to population growth.
Specific regions within the North State, including [mention specific counties or areas experiencing significant increases], are seeing the most dramatic population increases.
- Current wolf population size estimates: [Insert current population estimates with source citation].
- Geographic distribution within the North State: [Describe the geographic distribution with map links if possible].
- Recent studies and data on population growth: [Cite relevant scientific studies and data sources].
- Analysis of prey base and its impact on wolf numbers: [Discuss the relationship between prey abundance and wolf population growth].
H2: Challenges Posed by the Expanding Wolf Population
The increasing wolf population presents several significant challenges, requiring careful consideration and strategic management:
-
Conflicts with Livestock Ranchers: The primary concern revolves around livestock depredation, resulting in economic losses for ranchers. This necessitates finding effective and humane ways to mitigate these conflicts.
-
Threats to Endangered or Threatened Species: While wolves are a keystone species, their growing numbers could potentially impact populations of other vulnerable animals within the ecosystem. Careful monitoring is crucial to prevent unintended negative consequences.
-
Human Safety Concerns: While attacks on humans are extremely rare, raising public awareness about wolf behavior and promoting responsible practices in wolf habitats is vital for ensuring public safety.
-
Economic impacts on ranchers due to livestock depredation: [Quantify the economic impact and cite relevant sources].
-
Methods for mitigating livestock losses (e.g., non-lethal deterrents, compensation programs): [Discuss effective methods, including range riders, guard animals, and financial compensation].
-
Conservation implications for other vulnerable species: [Analyze potential impacts on other species and propose mitigation strategies].
-
Public safety concerns and strategies for conflict avoidance: [Highlight safety precautions and public education initiatives].
H2: Strategies for Effective Wolf Population Management in the North State
Effective wolf population management requires a multifaceted, collaborative approach that prioritizes non-lethal strategies:
-
Non-Lethal Management Strategies: Focusing on non-lethal methods, such as improved livestock protection techniques, habitat management to reduce human-wildlife conflicts, and extensive public education campaigns, is paramount.
-
Government Agencies and Regulatory Frameworks: State and federal agencies play a crucial role in developing and enforcing regulations that balance wolf conservation with the needs of other stakeholders.
-
Stakeholder Collaboration: Successful wolf management hinges on collaboration between ranchers, conservation organizations, government agencies, and local communities. Open dialogue and the development of shared management plans are vital.
-
Examples of successful non-lethal wolf deterrents: [Provide specific examples and case studies].
-
Details of current state and federal regulations: [Summarize relevant regulations and legal frameworks].
-
Evaluation of the effectiveness of current management plans: [Analyze existing plans and suggest improvements].
-
Opportunities for community-based conservation initiatives: [Highlight the role of citizen science and community involvement].
H2: The Role of Public Education and Community Engagement
Public education and community engagement are critical components of successful wolf management:
-
Public Awareness: Increasing public understanding of wolf behavior, ecology, and the importance of coexistence is crucial in fostering tolerance and reducing human-wildlife conflict.
-
Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in the management process through participatory initiatives and collaborative decision-making fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility.
-
Positive Perception of Wolves: Promoting a positive perception of wolves through education and responsible storytelling can help mitigate negative attitudes and foster a culture of respect.
-
Educational resources for the public about wolves: [List websites, educational materials, and outreach programs].
-
Community outreach programs and initiatives: [Highlight examples of successful community engagement strategies].
-
Methods to foster a positive perception of wolves: [Suggest strategies for promoting understanding and appreciation of wolves].
-
Promoting responsible recreation in wolf habitats: [Discuss guidelines for safe and respectful recreation in wolf habitats].
Conclusion: A Path Forward for Managing the Increasing Wolf Population in the North State
Managing the increasing wolf population in the North State demands a proactive, comprehensive, and collaborative approach. Addressing the challenges associated with livestock depredation, ensuring the conservation of other vulnerable species, and maintaining public safety requires a nuanced strategy combining non-lethal conflict mitigation, robust regulatory frameworks, and a commitment to ongoing public education and community engagement. By working together, we can pave the way for a future where wolves and humans coexist successfully within the rich ecosystems of the North State. Learn how you can contribute to responsible wolf management by visiting [link to relevant government website or conservation organization]. Get involved in shaping the future of wolf conservation in the North State! Discover more about managing the increasing wolf population in your region by exploring the resources available at [link to additional resources].

Featured Posts
-
 Kosova Dhe Uefa Perfitimet Nga Ngritja Ne Ligen B Te Liges Se Kombeve
May 23, 2025
Kosova Dhe Uefa Perfitimet Nga Ngritja Ne Ligen B Te Liges Se Kombeve
May 23, 2025 -
 Why Eric Andre Didnt Cast Kieran Culkin Behind The Scenes Of A Real Pain
May 23, 2025
Why Eric Andre Didnt Cast Kieran Culkin Behind The Scenes Of A Real Pain
May 23, 2025 -
 Ispovest Vanje Mijatovic Razvod Tezina I Borba Za Svoju Pricu
May 23, 2025
Ispovest Vanje Mijatovic Razvod Tezina I Borba Za Svoju Pricu
May 23, 2025 -
 Promena Imena Vanje Mijatovic Detalji I Razlozi
May 23, 2025
Promena Imena Vanje Mijatovic Detalji I Razlozi
May 23, 2025 -
 Kristi Ano Ronaldo A Pozdravi Proslavata Na Kho Lund Kopiranje Na Legendarniot Stil
May 23, 2025
Kristi Ano Ronaldo A Pozdravi Proslavata Na Kho Lund Kopiranje Na Legendarniot Stil
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Kieran Culkin To Play Caesar Flickerman In Sunrise On The Reaping
May 23, 2025
Kieran Culkin To Play Caesar Flickerman In Sunrise On The Reaping
May 23, 2025 -
 Macaulay And Kieran Culkins Mother Allegations Of Financial Hardship Despite Sons Wealth
May 23, 2025
Macaulay And Kieran Culkins Mother Allegations Of Financial Hardship Despite Sons Wealth
May 23, 2025 -
 Sunrise On The Reaping Kieran Culkin Cast As Caesar Flickerman
May 23, 2025
Sunrise On The Reaping Kieran Culkin Cast As Caesar Flickerman
May 23, 2025 -
 Macaulay Culkin And Kieran Culkins Mothers Financial Struggle A Report
May 23, 2025
Macaulay Culkin And Kieran Culkins Mothers Financial Struggle A Report
May 23, 2025 -
 Succession Sky Atlantic Hd Exploring The Themes And Symbolism
May 23, 2025
Succession Sky Atlantic Hd Exploring The Themes And Symbolism
May 23, 2025
