National Average Gas Price Jumps Almost 20 Cents
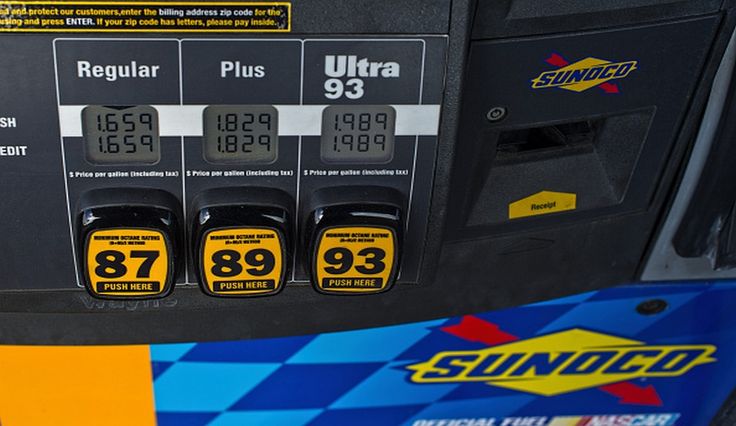

Table of Contents
Reasons Behind the National Average Gas Price Surge
Several intertwined factors contribute to the recent dramatic increase in the national average gas price. Understanding these elements is crucial to predicting future gas prices and preparing for potential fluctuations.
Increased Global Demand
Global demand for oil is significantly impacting crude oil prices, and consequently, gasoline prices.
- Increased travel post-pandemic: With travel restrictions easing worldwide, there's a surge in air and road travel, boosting the demand for fuel.
- Economic growth in certain regions: Strong economic growth in several countries translates into increased industrial activity and energy consumption, further driving up oil demand.
- Geopolitical instability: Geopolitical tensions and conflicts in oil-producing regions create uncertainty in the market, often leading to price increases due to supply disruptions and speculation. These geopolitical factors significantly influence oil prices.
These factors combine to increase the pressure on global oil prices, directly influencing the national average gas price.
Refinery Capacity Constraints
Limited refining capacity plays a crucial role in determining the gasoline supply and consequently, prices.
- Refinery maintenance: Scheduled and unscheduled maintenance at refineries temporarily reduces refinery output, leading to tighter supplies.
- Unexpected shutdowns: Unexpected refinery shutdowns due to accidents or other unforeseen circumstances can severely restrict gasoline supply, causing immediate price spikes.
- Limited investment in new refining capacity: A lack of investment in building new refineries or upgrading existing ones limits the potential to increase gasoline supply to meet rising demand.
These constraints on refinery output directly contribute to the increase in fuel prices.
Speculation and Market Volatility
The energy market is susceptible to speculation and market volatility, influencing commodity prices, including oil.
- Geopolitical events: Uncertainties arising from geopolitical events can trigger investor anxieties, leading to price increases as investors seek safe havens.
- Economic forecasts: Negative economic forecasts can also impact investor sentiment, resulting in increased volatility and potentially higher oil market volatility.
- Investor sentiment: Overall investor confidence in the oil market significantly affects pricing, with pessimistic views often leading to price hikes.
These elements of speculation amplify the impact of other factors driving up the national average gas price.
Impact of the National Average Gas Price Increase on Consumers and the Economy
The increase in fuel prices has significant consequences for both consumers and the overall economy.
Increased Transportation Costs
Higher gas prices directly translate into increased transportation costs for individuals and businesses.
- Higher commuting costs: Consumers face higher expenses for daily commutes, reducing their disposable income.
- Increased shipping costs for goods: Businesses experience increased costs for transporting goods, potentially leading to higher prices for consumers.
- Impact on discretionary spending: Higher fuel costs can limit consumers' discretionary spending, affecting various sectors of the economy.
This increased burden on consumer spending has significant macroeconomic implications.
Potential Economic Ripple Effects
The rising national average gas price has broader macroeconomic impact, potentially affecting economic growth and inflation.
- Impact on inflation: Higher fuel prices contribute to overall inflation rate, eroding purchasing power and potentially impacting interest rates.
- Potential slowdown in economic growth: Increased fuel costs can dampen economic activity as businesses and consumers adjust their spending patterns.
- Effects on different sectors: Certain sectors, such as transportation and logistics, are disproportionately affected by increased fuel costs.
The sustained increase in the national average gas price poses a significant challenge to economic stability.
What Can Consumers Do to Mitigate the Impact of Higher Gas Prices?
While we can't control gas prices, consumers can take steps to minimize the impact on their budgets.
Fuel Efficiency Strategies
Improving fuel efficiency can significantly reduce fuel consumption and save money.
- Maintain vehicle properly: Regular maintenance, such as tire inflation checks and tune-ups, improves gas mileage.
- Drive efficiently: Avoid aggressive acceleration and braking, and maintain a consistent speed to optimize fuel efficiency.
- Carpool: Sharing rides can significantly reduce individual fuel costs.
- Consider public transportation: Utilizing public transport when feasible reduces reliance on personal vehicles.
These driving habits can greatly impact your fuel savings.
Comparing Gas Prices and Finding the Best Deals
Finding the best gas price comparison can save money on fuel.
- Use gas price comparison apps: Several apps provide real-time gas prices in your area, helping you locate the cheapest options.
- Look for discounts and loyalty programs: Many gas stations offer discounts through loyalty programs or partnerships with credit cards.
- Time your fill-ups strategically: Gas prices can fluctuate throughout the week; strategically timing your fill-ups can result in fuel savings.
These strategies can help you find cheaper gas and manage your fuel costs effectively.
Conclusion: Navigating the Rising National Average Gas Price
The recent surge in the national average gas price, driven by increased global demand, refinery capacity constraints, and market speculation, has significant implications for consumers and the economy. Understanding the factors contributing to these price increases allows for better preparation and mitigation. By employing fuel-efficient driving habits and utilizing resources to find the best gas prices, consumers can manage their fuel costs effectively. Stay informed about national average gas price trends and utilize available resources to navigate these fluctuations. Continuously monitor gas price forecasts and adjust your strategies accordingly to effectively manage fuel costs.

Featured Posts
-
 Irate Pub Landladys Tirade Employees Resignation Sparks Explosive Reaction
May 22, 2025
Irate Pub Landladys Tirade Employees Resignation Sparks Explosive Reaction
May 22, 2025 -
 Ai Mode The Future Of Google Search
May 22, 2025
Ai Mode The Future Of Google Search
May 22, 2025 -
 Ftcs Appeal Against Court Approval Of Microsoft Activision Merger
May 22, 2025
Ftcs Appeal Against Court Approval Of Microsoft Activision Merger
May 22, 2025 -
 G 7 And Us Finance Ministers Work Towards Economic Stability Despite Trade Turmoil
May 22, 2025
G 7 And Us Finance Ministers Work Towards Economic Stability Despite Trade Turmoil
May 22, 2025 -
 Los 5 Mejores Podcasts De Misterio Suspenso Y Terror En Ano
May 22, 2025
Los 5 Mejores Podcasts De Misterio Suspenso Y Terror En Ano
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Final Concacaf Todo Sobre El Partido Mexico Vs Panama
May 23, 2025
Final Concacaf Todo Sobre El Partido Mexico Vs Panama
May 23, 2025 -
 Liga Natsiy Onovlennya Rezultativ Ta Rozkladu Na 20 03 2025
May 23, 2025
Liga Natsiy Onovlennya Rezultativ Ta Rozkladu Na 20 03 2025
May 23, 2025 -
 Mexico Vs Panama Guia Completa Para Ver La Final De La Liga De Naciones Concacaf
May 23, 2025
Mexico Vs Panama Guia Completa Para Ver La Final De La Liga De Naciones Concacaf
May 23, 2025 -
 Dublins Metallica Weekend Two Nights At Aviva Stadium In June 2026
May 23, 2025
Dublins Metallica Weekend Two Nights At Aviva Stadium In June 2026
May 23, 2025 -
 Rezultati Ta Rozklad Matchiv Ligi Natsiy 20 03 2025
May 23, 2025
Rezultati Ta Rozklad Matchiv Ligi Natsiy 20 03 2025
May 23, 2025
