Navigating The Risks: Japan's Steep Bond Yield Curve And Investment Strategies
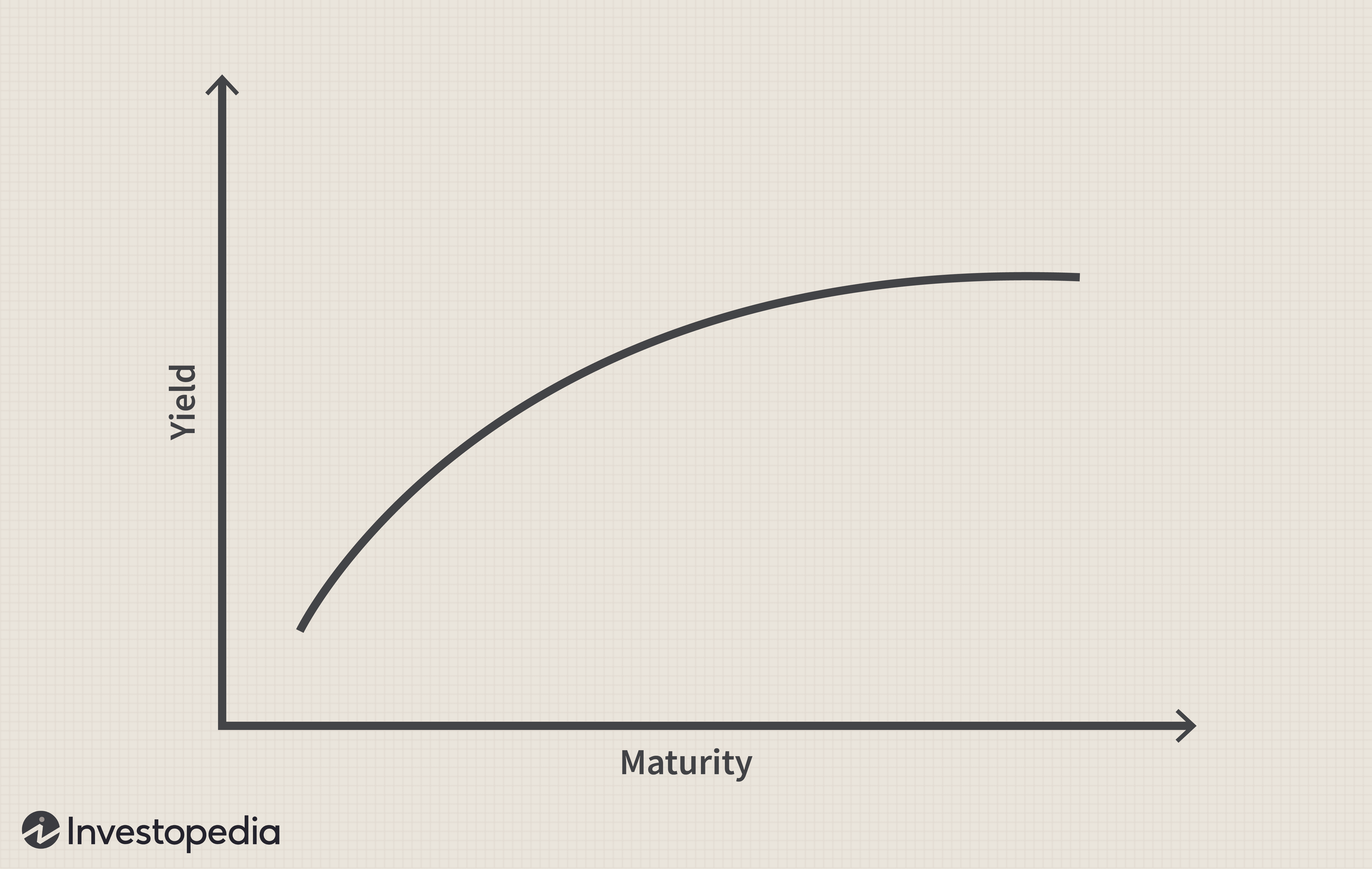
Table of Contents
Understanding Japan's Steepening Bond Yield Curve
A yield curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the yields (interest rates) of bonds with different maturities. A typical yield curve is upward-sloping (normal), meaning longer-term bonds offer higher yields than shorter-term bonds, reflecting investors' demand for higher returns to compensate for longer-term risks. A "steep" yield curve signifies a significant difference between short-term and long-term yields. This steepening in Japan's bond market indicates a growing expectation of future interest rate hikes.
Several factors contribute to this steepening:
-
Bank of Japan (BOJ) policy shifts and potential future changes: The BOJ's recent adjustments to its yield curve control (YCC) policy, including allowing longer-term yields to rise, have significantly impacted the shape of the curve. Further adjustments or a complete abandonment of YCC are anticipated by many market analysts, further influencing the yield curve. This creates uncertainty and volatility in the Japanese bond market.
-
Inflationary pressures and their impact on interest rates: Rising inflation in Japan, though still relatively moderate compared to other developed nations, is pushing the BOJ to reconsider its ultra-loose monetary policy. This inflationary pressure is a key driver behind the expectation of higher future interest rates and contributes directly to the steepening yield curve. The Japanese government's response to inflation, including fiscal policy decisions, further impacts the market.
-
Global economic conditions and their influence on Japanese bonds: Global economic factors, such as rising interest rates in the US and Europe, influence investor sentiment towards Japanese bonds. Capital flows shift as investors seek higher returns elsewhere, putting upward pressure on Japanese bond yields. Geopolitical events also play a role in influencing global capital flows and investor confidence in the Japanese market.
-
Increased government borrowing: Japan's high level of government debt necessitates substantial borrowing, increasing the supply of Japanese government bonds (JGBs) in the market. This increased supply can put downward pressure on bond prices and upward pressure on yields, particularly if demand does not keep pace.
The relationship between the yield curve and economic forecasts is significant. A steepening yield curve often signals expectations of economic growth and higher inflation, while a flattening or inverting curve can indicate an impending economic slowdown or recession. The current steepening in Japan suggests a shift away from the prolonged period of deflation and ultra-low interest rates.
Investment Risks Associated with Japan's Bond Market
The steepening yield curve in Japan introduces several investment risks:
-
Increased risk of capital losses due to rising interest rates: As interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds with lower coupon rates falls. This poses a significant risk of capital losses for investors holding longer-term Japanese government bonds (JGBs). This risk is amplified for investors who are not hedging against rising interest rates.
-
Potential for interest rate volatility and its effect on bond prices: The uncertainty surrounding future BOJ policy and global economic conditions creates interest rate volatility, leading to unpredictable fluctuations in bond prices. This volatility increases the risk of capital losses for bond investors. The longer the maturity of the bond, the greater the sensitivity to interest rate changes.
-
Impact of currency fluctuations (JPY) on returns for international investors: Fluctuations in the Japanese Yen (JPY) exchange rate significantly affect the returns of international investors in Japanese bonds. A weakening JPY will reduce returns when converted back to the investor's home currency. Hedging currency risk is crucial for international investors.
-
Potential for credit risk within the Japanese bond market: While JGBs are generally considered low-risk, credit risk exists within the broader Japanese bond market, especially in corporate bonds. Investors must conduct thorough due diligence to assess the creditworthiness of individual issuers. Specific sectors facing economic headwinds may carry higher credit risk.
-
Duration risk: Longer-term bonds have higher duration, making them more sensitive to interest rate changes. Holding long-duration bonds in a rising rate environment significantly increases the risk of capital losses.
-
Reinvestment risk: In a rising interest rate environment, the coupons received from existing bonds will need to be reinvested at higher rates. Failure to reinvest at favorable rates reduces overall returns.
Investment Strategies for Navigating the Risks
Despite the risks, opportunities exist for savvy investors. Effective strategies include:
-
Mitigating interest rate risk:
- Shortening portfolio duration: Reducing exposure to longer-term bonds lowers sensitivity to interest rate changes.
- Diversification across different bond maturities: Spreading investments across various maturities reduces the impact of interest rate changes on the overall portfolio.
- Using interest rate derivatives (e.g., futures, swaps): These financial instruments can be used to hedge against interest rate risk.
-
Exploring opportunities presented by the steep yield curve:
- Potential for higher yields on longer-term bonds (with increased risk): Longer-term JGBs currently offer higher yields, but this comes with increased interest rate risk.
- Active bond management strategies: Actively managing a bond portfolio allows for adjustments based on changing market conditions. This requires expertise and ongoing monitoring of the market.
-
Thorough due diligence and understanding individual bond issuer creditworthiness: Investors should carefully assess the credit risk of each bond before investing. This includes analyzing financial statements and macroeconomic factors affecting the issuer.
-
Consider alternative investment strategies within the Japanese market: Diversification into Japanese equities or real estate can reduce overall portfolio risk and provide alternative sources of returns. Japanese real estate investment trusts (J-REITs) are another option to consider.
The Role of the Bank of Japan (BOJ) in Shaping the Yield Curve
The BOJ's monetary policies are the primary driver of Japan's bond yield curve. The BOJ's past policy of yield curve control (YCC), aimed at keeping long-term interest rates low, artificially suppressed yields. Recent adjustments to this policy have allowed longer-term yields to rise, leading to the steepening curve.
Future BOJ actions remain uncertain, but several scenarios are possible: a complete abandonment of YCC, further gradual adjustments to YCC, or maintaining the current policy. Each scenario will significantly impact the yield curve's shape and investors' returns. Market reaction to BOJ announcements is usually swift and substantial, highlighting the central bank's significant role in shaping investor expectations. The effectiveness of BOJ interventions is a subject of ongoing debate among economists and market analysts. The effectiveness of past interventions will heavily influence future policy decisions.
Conclusion
Japan's steepening bond yield curve presents a complex investment landscape, requiring careful consideration of both risks and opportunities. Understanding the contributing factors, such as BOJ policy shifts and global economic trends, is paramount. By employing diversified strategies, mitigating interest rate risk, and conducting thorough due diligence, investors can navigate the challenges and potentially capitalize on the opportunities presented by Japan's evolving bond market. To make informed investment decisions regarding Japan's bond yield curve, consult with a financial professional. Don't hesitate to reach out for expert advice on navigating the complexities of Japan's bond yield curve and developing a robust investment strategy.

Featured Posts
-
 Controversy Wnba Star Criticizes Angel Reese For Tampering
May 17, 2025
Controversy Wnba Star Criticizes Angel Reese For Tampering
May 17, 2025 -
 Pandemic Fraud Lab Owner Convicted For Fake Covid Tests
May 17, 2025
Pandemic Fraud Lab Owner Convicted For Fake Covid Tests
May 17, 2025 -
 Ftcs Appeal Against Microsoft Activision Merger Approval
May 17, 2025
Ftcs Appeal Against Microsoft Activision Merger Approval
May 17, 2025 -
 Yankees Vs Mariners Mlb Game Prediction Picks And Betting Odds
May 17, 2025
Yankees Vs Mariners Mlb Game Prediction Picks And Betting Odds
May 17, 2025 -
 How Josh Cavallo Is Changing Football With His Story
May 17, 2025
How Josh Cavallo Is Changing Football With His Story
May 17, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Get The Scoop Moto News On Gncc Mx Sx Flat Track And Enduro
May 17, 2025
Get The Scoop Moto News On Gncc Mx Sx Flat Track And Enduro
May 17, 2025 -
 Moto News Gncc Mx Sx Flat Track Enduro Race Reports And More
May 17, 2025
Moto News Gncc Mx Sx Flat Track Enduro Race Reports And More
May 17, 2025 -
 Comprehensive Moto News Gncc Mx Sx Flat Track And Enduro Racing
May 17, 2025
Comprehensive Moto News Gncc Mx Sx Flat Track And Enduro Racing
May 17, 2025 -
 Your Guide To Moto News Gncc Mx Sx Flat Track And Enduro
May 17, 2025
Your Guide To Moto News Gncc Mx Sx Flat Track And Enduro
May 17, 2025 -
 Moto Racing News Gncc Mx Sx Flat Track And Enduro Coverage
May 17, 2025
Moto Racing News Gncc Mx Sx Flat Track And Enduro Coverage
May 17, 2025
