Negative European Electricity Prices: A Solar Energy Success Story?
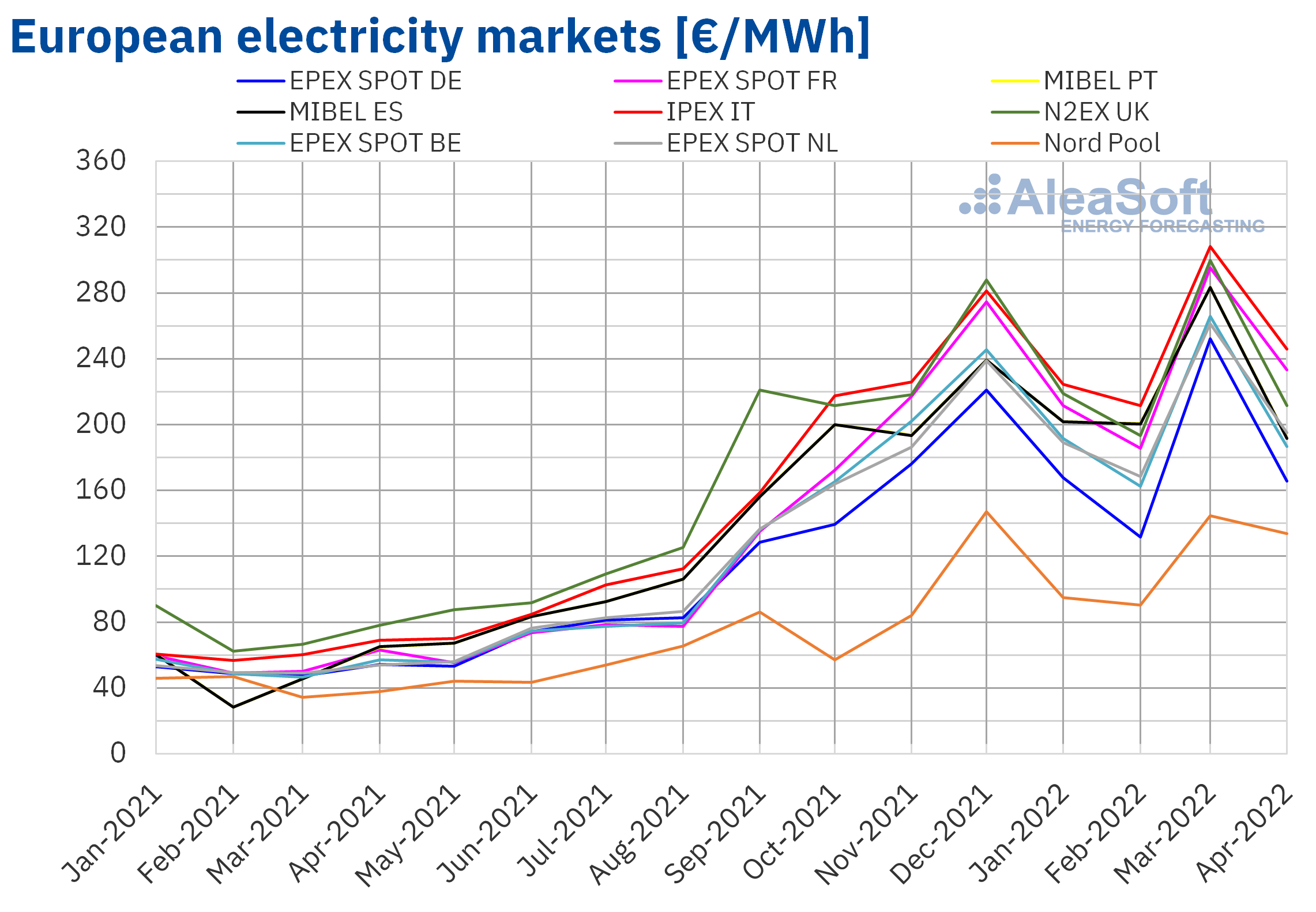
Table of Contents
Imagine a scenario where electricity becomes so abundant that it's actually worth less than nothing. This isn't science fiction; negative electricity prices in Europe have become an increasingly frequent reality, prompting both excitement and concern. This phenomenon of "Negative European Electricity Prices" is raising crucial questions about the energy transition and the expanding role of solar power. This article explores whether the surge in negative pricing events is a testament to the success of solar energy or a symptom of broader challenges facing the European electricity grid.
H2: The Phenomenon of Negative Electricity Prices:
Negative electricity prices mean that producers are paying consumers to take electricity off their hands. This seemingly paradoxical situation arises when the supply of electricity significantly exceeds demand. Several factors contribute to this:
- Overproduction of Renewable Energy: The intermittent nature of solar and wind power leads to periods of massive overproduction, especially during sunny midday hours or strong winds. This surplus pushes prices down, sometimes even into negative territory.
- Low Electricity Demand: During off-peak hours (nights, weekends), demand for electricity drops significantly. Combined with high renewable energy output, this creates a supply-demand imbalance.
- Grid Management Challenges: Europe's electricity grid infrastructure isn't always equipped to handle the rapid fluctuations in renewable energy generation. Efficient energy storage solutions are still under development, making it difficult to balance supply and demand effectively.
- Limited Energy Storage: The lack of widespread and affordable large-scale energy storage solutions exacerbates the problem. Excess renewable energy cannot be easily stored for later use, leading to a surplus during peak production times.
- Examples: Countries like Germany and Denmark have experienced numerous instances of negative electricity prices, particularly during periods of high solar irradiance and low energy demand.
H2: The Role of Solar Energy in Negative Pricing:
The exponential growth of solar energy capacity across Europe is undeniable. Millions of solar panels are now generating vast quantities of electricity, contributing significantly to the overall energy mix. However, solar power's intermittent nature—dependent on sunshine—directly impacts price volatility.
- Intermittency and Volatility: Solar energy production peaks during the day, often coinciding with lower overall electricity demand. This mismatch creates periods of surplus electricity, pushing prices down.
- Correlation with Negative Prices: Statistical analysis clearly shows a strong correlation between high solar energy generation and the occurrence of negative electricity prices. Charts depicting solar output alongside electricity prices illustrate this relationship vividly. (Insert chart or graph here).
H2: Economic Implications of Negative Prices:
Negative electricity prices have profound economic consequences:
- Impact on Conventional Power Plants: Fossil fuel and nuclear power plants, which often operate at a relatively constant output, face significant challenges. They may be forced to curtail generation, incurring losses, or even shut down entirely during periods of negative prices.
- Benefits for Consumers and Businesses: Consumers and businesses can benefit from free or even subsidized electricity during periods of negative pricing, potentially leading to lower energy bills.
- Challenges for Grid Operators: Grid operators face the complex task of managing supply and demand imbalances. Maintaining grid stability during periods of extreme price volatility requires sophisticated control systems and potentially costly investments.
- New Business Models: Negative prices could stimulate the development of innovative business models, such as demand-side management programs that incentivize consumers to shift their energy consumption to periods of higher prices.
H2: Challenges and Future Outlook:
While negative electricity prices highlight the potential of renewable energy, significant challenges remain:
- Limitations of Energy Storage: Current energy storage technologies, such as batteries and pumped hydro, are still expensive and often lack the capacity to store large amounts of energy.
- Smarter Grid Infrastructure: Modernizing the electricity grid with smart grids and advanced control systems is crucial to better manage the fluctuating supply from renewable sources.
- Government Policies and Regulations: Supportive government policies and regulations are essential to encourage further investment in renewable energy, energy storage, and smart grid technologies.
- Future Prospects: The frequency and magnitude of negative electricity prices are likely to increase in the coming years as renewable energy penetration grows. This necessitates a strategic approach to managing this phenomenon.
H2: Is it a Success Story? A Balanced Perspective:
Negative European electricity prices are a complex issue. While they signal the growing success of renewable energy in terms of sheer generation capacity, they also highlight the need for better grid management and energy storage solutions. It's not a simple "success story" but rather a complex situation with both positive and negative aspects that requires a nuanced approach. The transition to a renewable energy system requires careful planning, investment, and technological innovation.
Conclusion:
The increasing frequency of negative European electricity prices is inextricably linked to the expansion of solar energy and other renewable sources. While this phenomenon presents challenges for grid operators and conventional power plants, it also offers opportunities for consumers and the development of new business models. The overall picture is complex, with both benefits and drawbacks. It is not solely a "success story," but a reflection of the ongoing energy transition. To truly harness the potential of solar power and manage the complexities of negative European electricity pricing, further research and investment in smart grid technologies and large-scale energy storage are crucial. Understanding negative European electricity pricing and developing effective strategies for managing negative electricity price events are essential steps in securing a sustainable energy future. The future of negative European electricity prices will depend on our ability to address these challenges effectively.

Featured Posts
-
 Fhi Rapport Begrenset Effekt Av Adhd Medisin Pa Skole
Apr 29, 2025
Fhi Rapport Begrenset Effekt Av Adhd Medisin Pa Skole
Apr 29, 2025 -
 V Mware Costs To Skyrocket At And T Details A 1050 Price Hike From Broadcom
Apr 29, 2025
V Mware Costs To Skyrocket At And T Details A 1050 Price Hike From Broadcom
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Significant Nuclear Power Expansion In China 10 Reactors Added
Apr 29, 2025
Significant Nuclear Power Expansion In China 10 Reactors Added
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Austin City Limits Celebrating Willie Nelson And Familys Legacy
Apr 29, 2025
Austin City Limits Celebrating Willie Nelson And Familys Legacy
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Chargers To Kick Off 2025 Season In Brazil Justin Herbert Leads The Charge
Apr 29, 2025
Chargers To Kick Off 2025 Season In Brazil Justin Herbert Leads The Charge
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Preparing For Summer Hail Protecting Pools And Gardens
May 12, 2025
Preparing For Summer Hail Protecting Pools And Gardens
May 12, 2025 -
 Early Summer Hailstorms Cause Significant Landscape Damage
May 12, 2025
Early Summer Hailstorms Cause Significant Landscape Damage
May 12, 2025 -
 Severe Hailstorms Assessing Damage To Pools And Lawns
May 12, 2025
Severe Hailstorms Assessing Damage To Pools And Lawns
May 12, 2025 -
 Summer Storms Hail Pummels Pools And Green Spaces
May 12, 2025
Summer Storms Hail Pummels Pools And Green Spaces
May 12, 2025 -
 Hailstorms Damage Summer Landscapes Pools And Gardens Impacted
May 12, 2025
Hailstorms Damage Summer Landscapes Pools And Gardens Impacted
May 12, 2025
