New COVID-19 Variant: WHO Reports Surge In Cases
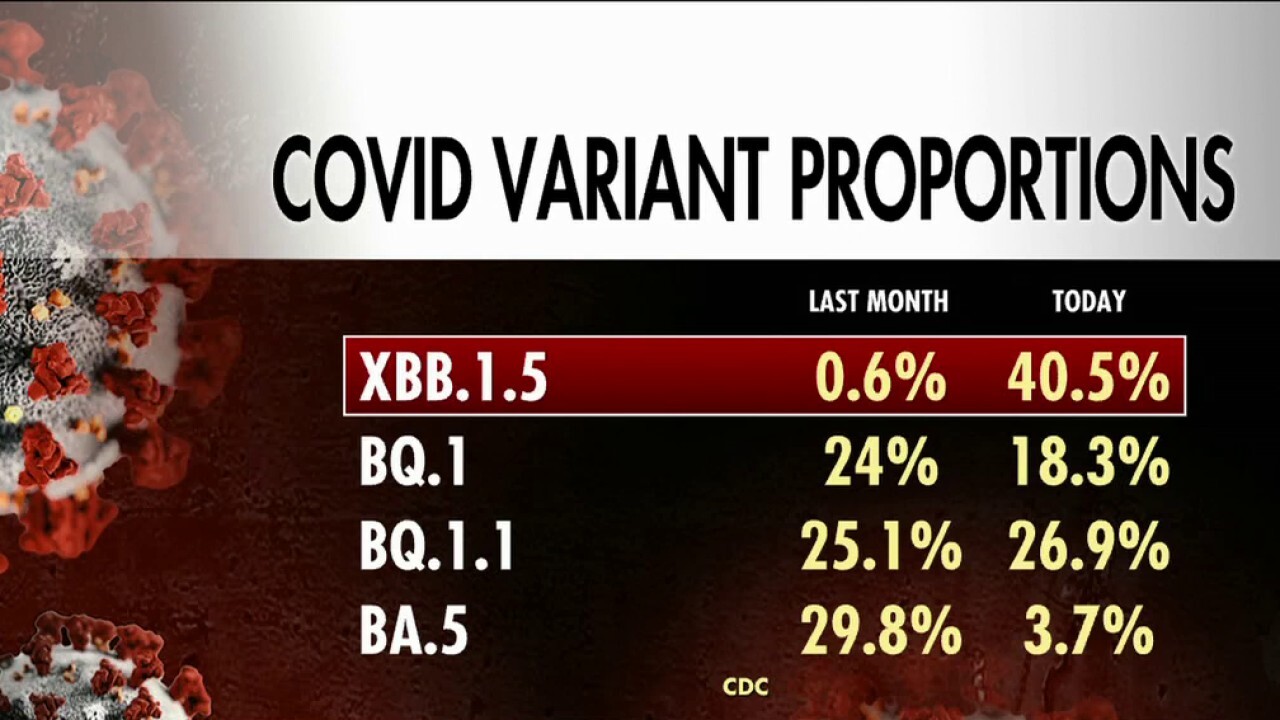
Table of Contents
Identification and Characteristics of the New COVID-19 Variant
Identifying and characterizing new COVID-19 variants is crucial for effective pandemic management. This process relies heavily on genomic surveillance and genetic sequencing to pinpoint mutations and understand their impact on viral behavior. Let's examine the key characteristics:
-
Variant Designation: While official naming conventions may vary (e.g., Greek letters or numerical designations), let's assume for this example the variant is designated as "Variant X." (Note: Replace "Variant X" with the actual official designation when available).
-
Genetic Mutations: Variant X exhibits several key genetic mutations compared to previous variants, including (example mutations - replace with actual mutations): a spike protein mutation affecting receptor binding, and mutations impacting viral replication efficiency. These mutations are crucial in determining the variant's transmissibility, severity, and potential resistance to existing vaccines.
-
Genomic Surveillance: The identification of Variant X is a testament to the ongoing global genomic surveillance efforts. Through continuous monitoring and sequencing of viral samples, scientists can quickly detect the emergence of new variants and track their spread.
-
Contagiousness and Transmission Rate: Early data suggests Variant X may be more contagious than previous variants, with a higher transmission rate. This increased contagiousness poses a significant challenge to public health efforts. Further research is needed to fully understand its transmission dynamics.
Global Spread and Impact of the New COVID-19 Variant
The rapid spread of Variant X is a cause for significant concern. The WHO is closely monitoring its global distribution and impact on healthcare systems.
-
Case Numbers and Geographic Distribution: As of [Date], confirmed cases of Variant X have been reported in [Number] countries across [Regions]. [Specific countries] are experiencing particularly high infection rates. (Replace bracketed information with actual data).
-
Impact on Healthcare Systems: The surge in cases is placing a strain on healthcare systems in many regions. Hospitals are facing increased admissions, potentially leading to delays in treatment for other conditions.
-
Economic Consequences: The spread of Variant X and the necessary public health measures to control it can have significant economic consequences, impacting businesses, trade, and overall economic growth.
Symptoms and Severity of the New COVID-19 Variant
Understanding the symptoms and severity of Variant X is vital for effective clinical management and public health messaging.
-
Common Symptoms: Symptoms associated with Variant X appear to be similar to previous variants, including fever, cough, fatigue, loss of taste or smell, and shortness of breath. However, further research is needed to fully characterize the clinical presentation.
-
Severity Compared to Previous Variants: While early data suggests Variant X may not be inherently more severe than previous variants, its increased transmissibility could lead to a greater overall number of severe cases.
-
At-Risk Populations: Unvaccinated individuals, the elderly, and those with underlying health conditions remain at higher risk of severe illness from Variant X.
-
Long COVID Potential: The potential for long-term health consequences (Long COVID) associated with Variant X remains under investigation.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies for the New COVID-19 Variant
Combating the spread of Variant X requires a multi-pronged approach that combines effective public health measures with individual responsibility.
-
Vaccination and Booster Shots: Vaccination remains the most effective tool in preventing severe illness and reducing the spread of COVID-19, including Variant X. Booster shots are crucial for maintaining high levels of immunity.
-
Preventative Measures: Practicing preventative measures such as mask-wearing in public indoor settings, maintaining social distancing, and practicing good hand hygiene are still vital in slowing transmission.
-
Testing and Surveillance: Increased testing and genomic surveillance are essential for detecting and tracking the spread of Variant X and informing public health response.
-
Public Health Guidelines: Adherence to public health guidelines issued by local and national authorities is crucial for effective pandemic management.
Conclusion
The emergence of this new COVID-19 variant underscores the ongoing need for vigilance and proactive measures to control the pandemic. The WHO's report highlights the critical importance of global collaboration and rapid response to effectively manage this surge in cases. The increased contagiousness of Variant X necessitates a renewed commitment to prevention strategies. Stay informed about the latest updates on the new COVID-19 variant from reliable sources like the WHO and your local health authorities. Practice COVID-19 prevention measures diligently to protect yourself and your community from this new COVID-19 variant and its potential impact. Get vaccinated and boosted if eligible. Don't let your guard down; continue to prioritize your health and the health of others. Stay informed about this new COVID-19 variant and protect yourself and your community.

Featured Posts
-
 Are Veterinary Watchdog Complaints As Bad As They Seem
May 31, 2025
Are Veterinary Watchdog Complaints As Bad As They Seem
May 31, 2025 -
 Sophia Huynh Tran Tu Gia The Den Thanh Cong Trong The Gioi Pickleball
May 31, 2025
Sophia Huynh Tran Tu Gia The Den Thanh Cong Trong The Gioi Pickleball
May 31, 2025 -
 Scoreless Inning For Chase Lee In Mlb Return May 12 2025
May 31, 2025
Scoreless Inning For Chase Lee In Mlb Return May 12 2025
May 31, 2025 -
 Emergency Relocation Rogart Vets In Tain Following Fire
May 31, 2025
Emergency Relocation Rogart Vets In Tain Following Fire
May 31, 2025 -
 Cheaper Than An I Pad Samsungs 101 Tablet Deal
May 31, 2025
Cheaper Than An I Pad Samsungs 101 Tablet Deal
May 31, 2025
