Prostate Cancer Screening: President Biden's 2014 Checkup

Table of Contents
President Biden's 2014 Prostate Cancer Screening Experience
In 2014, then-Vice President Joe Biden underwent a routine physical examination which included prostate cancer screening. Specific details regarding his PSA (prostate-specific antigen) test results were not publicly released in full detail, respecting his medical privacy. However, the event itself served as a significant public reminder about the importance of regular checkups and prostate cancer screening for men.
The PSA test is a blood test commonly used in prostate cancer screening. It measures the level of PSA in the blood, a protein produced by the prostate gland. Elevated PSA levels can indicate prostate cancer, but they can also be caused by other factors like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), an enlarged prostate. This is a crucial point to understand: the PSA test has limitations. It's not a definitive diagnostic tool and can lead to both false positives (elevated PSA without cancer) and false negatives (normal PSA despite the presence of cancer).
- Date of screening: 2014
- Type of test(s) performed: PSA test and likely a digital rectal exam (DRE), a physical examination of the prostate gland.
- Reported outcome: No specific details were publicly released beyond the confirmation of the screening.
- Subsequent follow-up procedures: No publicly available information exists about specific follow-up procedures resulting from the 2014 screening.
Understanding Prostate Cancer Risk Factors
Several factors increase a man's risk of developing prostate cancer. Understanding these risks is crucial for making informed decisions about prostate cancer screening.
- Age: Risk significantly increases with age, particularly after age 50.
- Ethnicity: African American men have a higher incidence rate of prostate cancer and often experience more aggressive forms of the disease.
- Family History: A family history of prostate cancer, especially in first-degree relatives (father, brother), increases the likelihood of developing the disease.
- Genetics: Specific genetic mutations can elevate the risk of prostate cancer.
These risk factors influence when and how frequently a man should discuss prostate cancer screening with his doctor. Higher-risk individuals may benefit from earlier and more frequent screening.
The Debate Surrounding Prostate Cancer Screening
The optimal approach to prostate cancer screening remains a subject of ongoing debate.
-
Arguments for routine screening: Early detection through regular PSA tests and DREs can lead to earlier treatment, potentially improving outcomes and survival rates.
-
Arguments against routine screening: The PSA test's limitations can lead to overdiagnosis (detecting cancers that would never cause symptoms or harm) and overtreatment (undergoing unnecessary and potentially harmful treatments for slow-growing cancers that might not require intervention). These treatments can have significant side effects, including impotence and incontinence.
-
Importance of individual risk assessment: The decision to undergo prostate cancer screening should be personalized, considering individual risk factors, age, life expectancy, and preferences.
-
The role of patient preferences and values: Shared decision-making between the patient and physician is paramount. The doctor should present the risks and benefits of screening, allowing the patient to make an informed choice aligned with their values and priorities.
PSA Test Accuracy and Limitations
The PSA test is not a perfect diagnostic tool. False positives, where an elevated PSA doesn't indicate cancer, are common, leading to unnecessary anxiety and further investigations like biopsies. False negatives, where a normal PSA masks the presence of cancer, are also a concern. Therefore, relying solely on PSA levels for diagnosis is insufficient. Doctors consider various factors, including age, family history, and digital rectal exam findings, to make a comprehensive assessment.
Post-2014 Updates and Biden's Health
No publicly verified information regarding President Biden's health status related to prostate cancer since 2014 is available. Maintaining patient privacy is crucial.
Making Informed Decisions About Prostate Cancer Screening
President Biden's 2014 experience underscores the importance of regular health checkups and open communication with your healthcare provider about prostate cancer screening. The decision about screening should be a shared one, balancing the potential benefits of early detection against the risks of overdiagnosis and overtreatment. Remember to discuss your individual risk factors, family history, and preferences with your doctor to determine the best approach for you. Don't hesitate to schedule a consultation with your healthcare provider today to discuss your prostate cancer screening options and create a personalized healthcare plan. For more information, consult resources like the American Cancer Society and the National Institutes of Health.

Featured Posts
-
 The David Walliams Britains Got Talent Controversy Explained
May 22, 2025
The David Walliams Britains Got Talent Controversy Explained
May 22, 2025 -
 Massive Zebra Mussel Infestation Discovered In Casper
May 22, 2025
Massive Zebra Mussel Infestation Discovered In Casper
May 22, 2025 -
 Understanding The Value Of Middle Management In Todays Business Environment
May 22, 2025
Understanding The Value Of Middle Management In Todays Business Environment
May 22, 2025 -
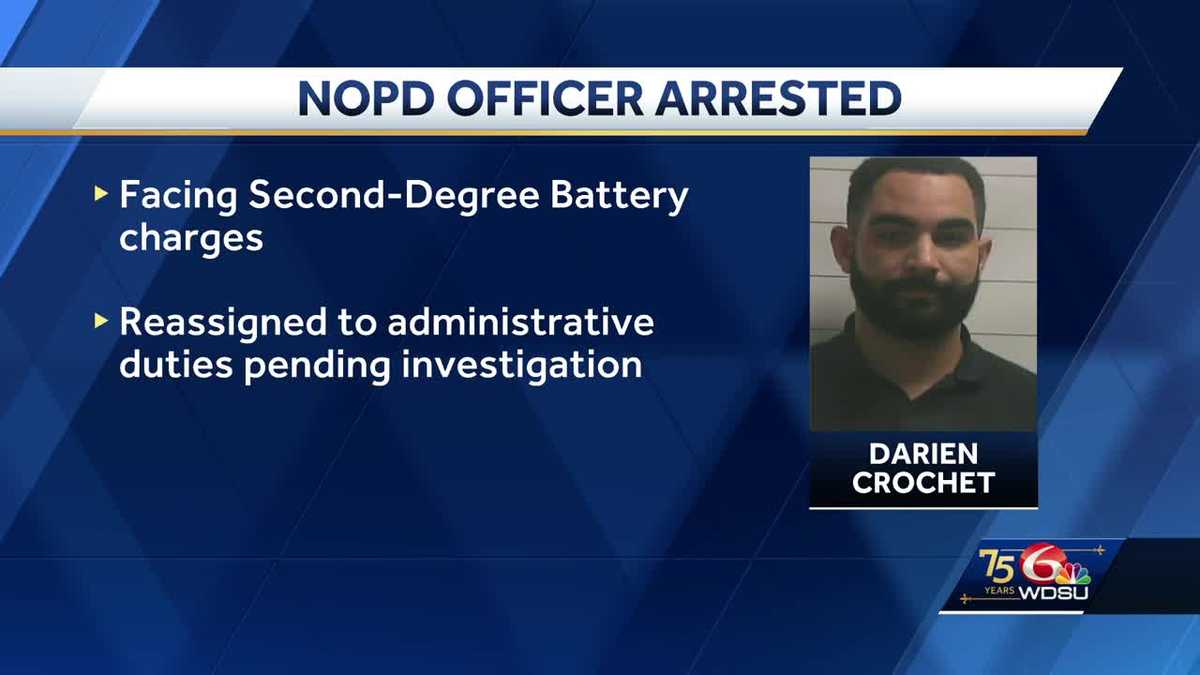 New Orleans Sheriffs Reelection Campaign Suspended Following Jail Escape
May 22, 2025
New Orleans Sheriffs Reelection Campaign Suspended Following Jail Escape
May 22, 2025 -
 Directeur Hypotheken Abn Amro Florius And Moneyou Welkom Karin Polman
May 22, 2025
Directeur Hypotheken Abn Amro Florius And Moneyou Welkom Karin Polman
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Nyt Wordle Help Hints And Solution For April 8 Puzzle 1389
May 22, 2025
Nyt Wordle Help Hints And Solution For April 8 Puzzle 1389
May 22, 2025 -
 20 Cent Gas Price Hike Impact On Drivers Nationwide
May 22, 2025
20 Cent Gas Price Hike Impact On Drivers Nationwide
May 22, 2025 -
 Wordle Answer Today March 2nd 1352 Hints And Help
May 22, 2025
Wordle Answer Today March 2nd 1352 Hints And Help
May 22, 2025 -
 Wordle 1393 Hints And Solution April 12th
May 22, 2025
Wordle 1393 Hints And Solution April 12th
May 22, 2025 -
 Wordle 1389 Hints And Answer April 8 Nyt
May 22, 2025
Wordle 1389 Hints And Answer April 8 Nyt
May 22, 2025
