Stock Market Valuation Concerns: BofA's Perspective And Rebuttal

Table of Contents
BofA's Concerns Regarding Stock Market Valuation
BofA's concerns stem from a confluence of factors, primarily centering around high valuations, interest rate sensitivity, and inflationary pressures. Let's delve into each of these concerns.
High Price-to-Earnings Ratios (P/E)
BofA points to elevated Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratios across various sectors as a primary indicator of overvaluation. The P/E ratio is a valuation metric that compares a company's stock price to its earnings per share. A high P/E ratio suggests investors are willing to pay a premium for each dollar of earnings, potentially signaling overvaluation.
- Examples of sectors with high P/E ratios: Technology, consumer discretionary, and some areas of healthcare have historically shown higher P/E ratios. These sectors often command premium valuations due to perceived high-growth potential.
- Historical comparisons of current P/E ratios: Comparing current P/E ratios to historical averages can provide context. However, it's crucial to remember that past performance isn't indicative of future results, and economic conditions vary significantly over time.
- Limitations of using P/E ratios alone: P/E ratios should not be considered in isolation. Other valuation metrics, such as Price-to-Sales (P/S) and Price-to-Book (P/B) ratios, should be considered alongside P/E to gain a comprehensive understanding of a company's valuation.
Interest Rate Sensitivity
BofA rightly highlights the impact of rising interest rates on stock valuations. Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing for companies, potentially impacting earnings and reducing investor appetite for riskier assets.
- Explanation of the inverse relationship between interest rates and stock prices: Generally, higher interest rates lead to lower stock prices, as investors shift their investments towards higher-yielding bonds. This is because bonds become more attractive alternatives to stocks when interest rates rise.
- Potential for future rate hikes and their impact: The Federal Reserve's monetary policy decisions significantly influence interest rates. Anticipation of future rate hikes can cause stock market volatility and put downward pressure on valuations.
- Effect on discounted cash flow valuations: Higher discount rates, often linked to rising interest rates, reduce the present value of future cash flows, thereby lowering the intrinsic value of stocks. This is a crucial consideration in discounted cash flow (DCF) valuation models.
Inflationary Pressures
Persistent inflation erodes purchasing power and impacts both corporate profitability and investor expectations, contributing to BofA's valuation concerns.
- Impact of inflation on consumer spending: High inflation can reduce consumer spending as purchasing power diminishes, impacting revenue growth for many companies.
- Impact on input costs for businesses: Inflation increases input costs for businesses, squeezing profit margins and potentially impacting earnings growth.
- Effect on corporate earnings growth: The combination of reduced consumer spending and increased input costs can significantly affect corporate earnings growth, making higher valuations less sustainable.
Rebuttal to BofA's Stock Market Valuation Concerns
While BofA's concerns are valid, a counterargument can be made based on several factors:
Long-Term Growth Potential
The argument for current valuations can rest on the significant long-term growth potential within certain sectors.
- Examples of high-growth sectors: Technology, renewable energy, and biotechnology are often cited as sectors with substantial long-term growth potential, potentially justifying higher valuations.
- Potential for technological advancements: Technological advancements consistently drive economic growth and create new opportunities, fueling expansion in specific sectors.
- Long-term economic projections: Positive long-term economic projections can support the argument that current valuations aren't necessarily unjustified, considering future earnings potential.
Low Interest Rates (Historically)
Context is key when discussing interest rates. While rates are rising, they remain historically low compared to previous decades.
- Comparison to historical interest rate levels: Interest rates are significantly lower than they were during previous periods of economic expansion.
- The impact of low rates on borrowing costs for companies: Low interest rates reduce borrowing costs for companies, enabling them to invest more and potentially boost earnings.
- Potential for sustained low rates in certain scenarios: Depending on economic conditions, interest rates may remain relatively low for a prolonged period.
Strong Corporate Earnings (in specific sectors)
Many companies and sectors continue to report strong earnings, countering the narrative of widespread overvaluation.
- Specific examples of companies exceeding expectations: Numerous companies have reported earnings above analyst expectations, demonstrating financial strength in certain sectors.
- Analysis of industry-specific drivers of earnings growth: Industry-specific factors, such as technological disruption or increased demand, can contribute to strong earnings growth, supporting premium valuations.
Conclusion
This analysis of BofA's perspective on stock market valuation concerns and the presented counterarguments emphasizes the complexity of assessing market valuations. While BofA's concerns regarding high P/E ratios, interest rate sensitivity, and inflationary pressures are valid, a balanced view considers long-term growth potential, historically low interest rates in context, and strong corporate earnings in specific sectors. Ultimately, understanding stock market valuation concerns requires a thorough and nuanced approach, considering multiple factors and individual investment strategies. Conduct your own thorough research before making investment decisions, and remember that expert opinions can provide valuable insight but should be viewed within a broader context. Continue to monitor stock market valuations and stay informed.

Featured Posts
-
 Zheng Qinwens Unexpected Defeat At The Madrid Open
May 30, 2025
Zheng Qinwens Unexpected Defeat At The Madrid Open
May 30, 2025 -
 Subventions Regionales Pour Le Concert De Medine En Grand Est Le Rassemblement National Proteste
May 30, 2025
Subventions Regionales Pour Le Concert De Medine En Grand Est Le Rassemblement National Proteste
May 30, 2025 -
 Sparks Mad Album Review Strengths Weaknesses And Overall Impression
May 30, 2025
Sparks Mad Album Review Strengths Weaknesses And Overall Impression
May 30, 2025 -
 Odigos Tiletheasis Gia Tin Kyriaki 4 And 5 Maioy
May 30, 2025
Odigos Tiletheasis Gia Tin Kyriaki 4 And 5 Maioy
May 30, 2025 -
 Review 2025 Kawasaki Ninja 650 Krt Edition
May 30, 2025
Review 2025 Kawasaki Ninja 650 Krt Edition
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
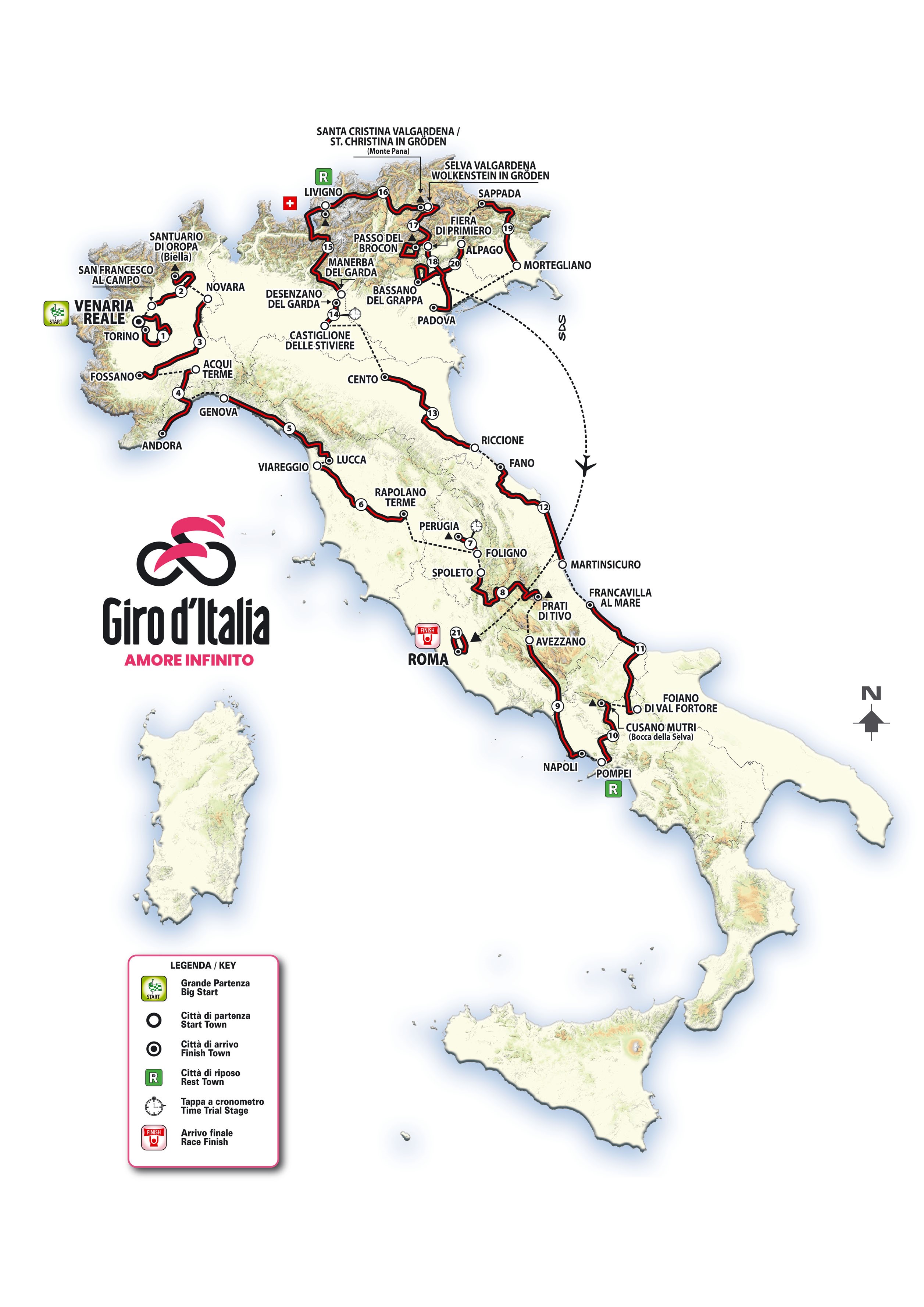 Vatican City To Host Grand Finale Of Giro D Italia 2025
May 31, 2025
Vatican City To Host Grand Finale Of Giro D Italia 2025
May 31, 2025 -
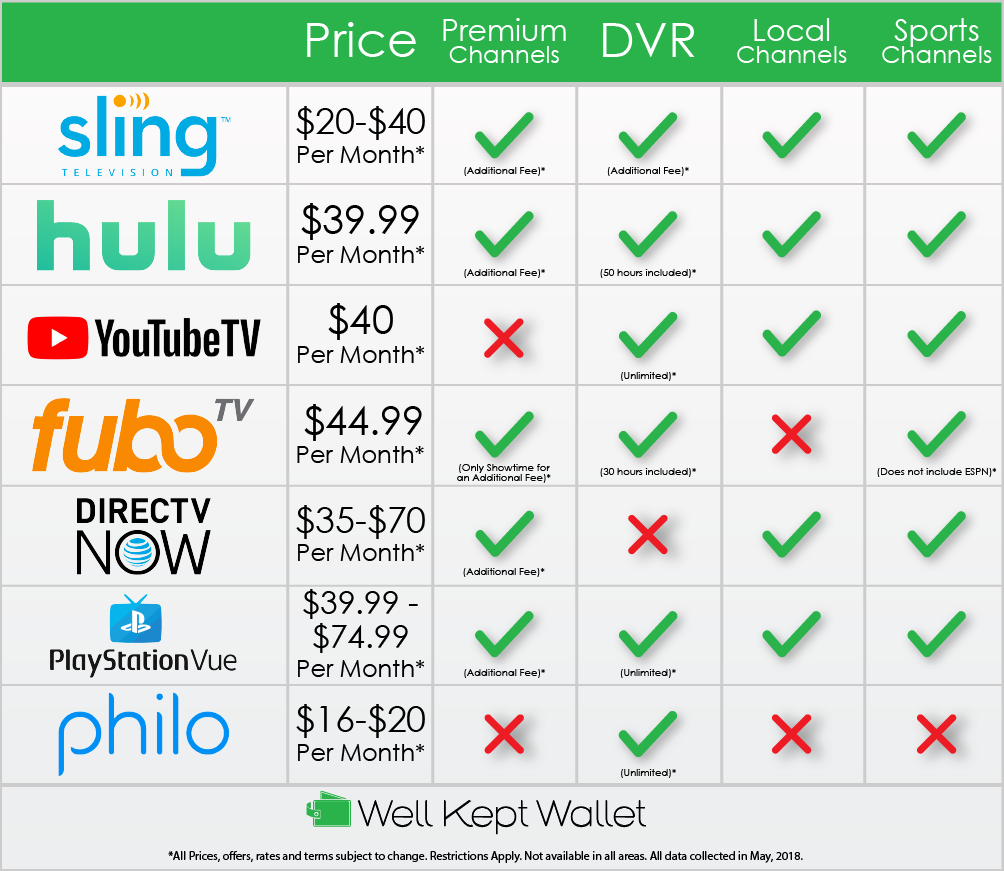 Giro D Italia 2025 Live Free Online Streaming Options
May 31, 2025
Giro D Italia 2025 Live Free Online Streaming Options
May 31, 2025 -
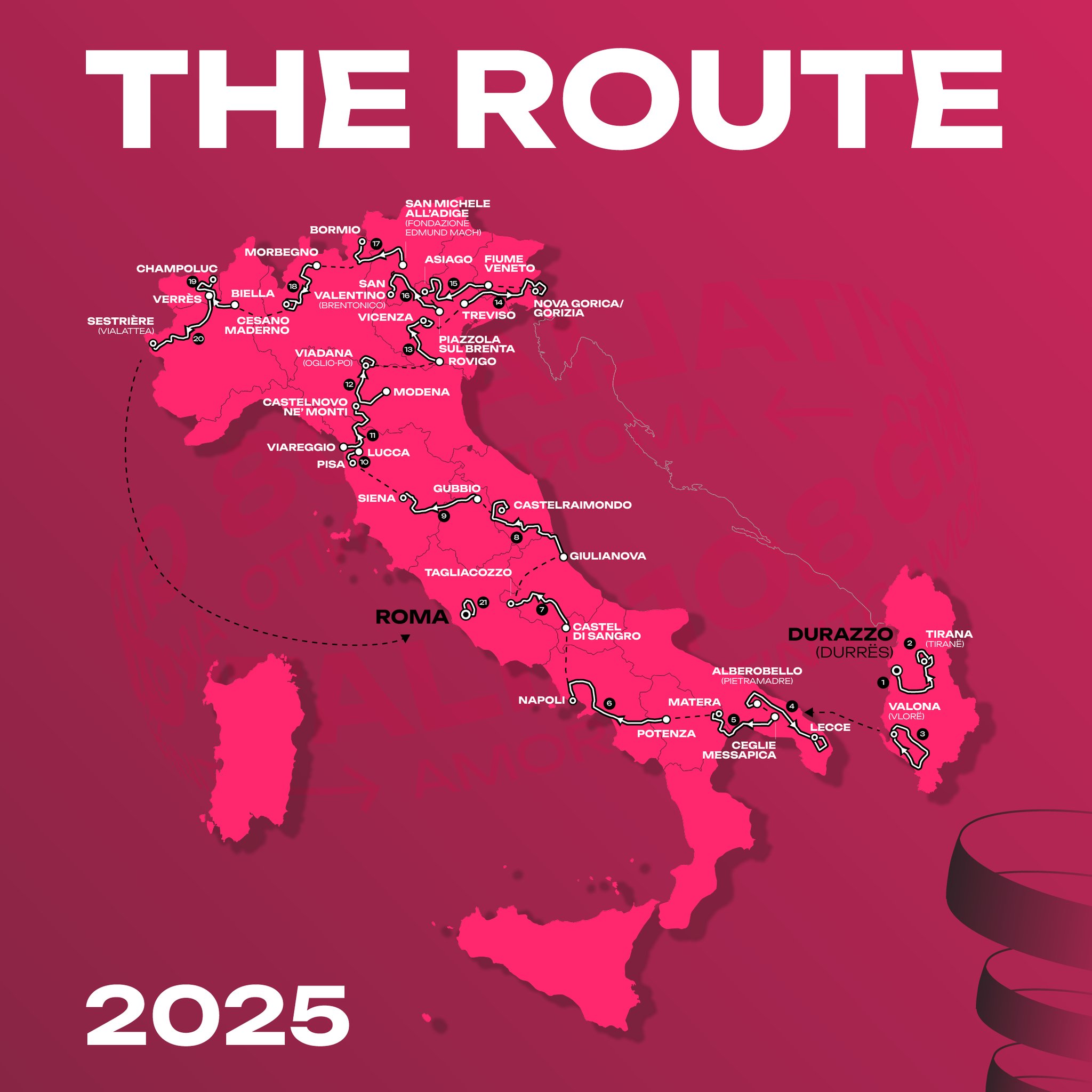 Giro D Italia 2025 Route Final Leg Through Vatican City
May 31, 2025
Giro D Italia 2025 Route Final Leg Through Vatican City
May 31, 2025 -
 Tudor Pelagos Fxd Chrono Pink Release Specs Price And Availability
May 31, 2025
Tudor Pelagos Fxd Chrono Pink Release Specs Price And Availability
May 31, 2025 -
 Pope Leo Xiv To Greet Giro D Italia Cyclists At The Vatican
May 31, 2025
Pope Leo Xiv To Greet Giro D Italia Cyclists At The Vatican
May 31, 2025
