Tariff Shock: Bond Market Repercussions
Table of Contents
Impact on Inflation and Interest Rates
Tariffs, designed to protect domestic industries, often increase the cost of imported goods, directly contributing to inflationary pressure. This inflationary pressure is a key element of a tariff shock's impact on the bond market. This increase in prices forces central banks to consider countermeasures, typically in the form of interest rate hikes. These hikes are intended to cool down the economy and curb inflation. However, higher interest rates have a direct and often inverse impact on bond yields and prices.
- Increased import costs fuel inflation: When tariffs are implemented, consumers face higher prices for imported goods, leading to a general increase in the price level.
- Central banks respond by raising interest rates: To combat this inflation, central banks typically raise interest rates, making borrowing more expensive and reducing demand.
- Rising interest rates lead to decreased bond prices: This is because bond prices and interest rates have an inverse relationship. When interest rates rise, newly issued bonds offer higher yields, making existing bonds with lower yields less attractive, thus lowering their prices.
- Higher yields on new bonds make existing bonds less attractive: This leads to a sell-off of existing bonds, further driving down their prices.
Further complicating the picture is the potential for stagflation – a situation characterized by slow economic growth coupled with high inflation. Stagflation presents a particularly challenging environment for bond investors, as the usual strategies for mitigating inflation (raising interest rates) can exacerbate slow economic growth. Different types of bonds, such as Treasury bonds and corporate bonds, exhibit varying sensitivities to these interest rate changes, further emphasizing the need for a nuanced understanding of the market.
Investor Behavior and Flight to Safety
Economic uncertainty caused by tariff shocks often triggers a significant shift in investor behavior known as a "flight to safety." During periods of heightened uncertainty, investors often become more risk-averse, moving their capital from riskier assets into perceived safe havens. Government bonds, particularly those issued by countries with stable economies, are often seen as such safe havens. This increased demand for government bonds can temporarily lower their yields. However, it's crucial to remember that this "flight to safety" may not fully offset the losses experienced in other, more volatile, sectors of the market.
- Investors seek safer investments during times of uncertainty: A tariff shock often increases market volatility and uncertainty, prompting investors to seek lower-risk alternatives.
- Government bonds are viewed as relatively safe haven assets: Government bonds are generally considered less risky than corporate bonds or equities, making them a preferred investment during uncertain times.
- Increased demand for government bonds can temporarily lower yields: The increased demand pushes bond prices up, resulting in lower yields.
- Diversification strategies become crucial to mitigate risk: A diversified portfolio across different asset classes can help to mitigate the impact of a tariff shock on overall investment returns.
The reaction to tariff shocks varies across different investor segments. Institutional investors, with their larger portfolios and sophisticated risk management strategies, might react differently compared to retail investors. Understanding these nuanced responses is crucial for comprehending the overall impact on bond market liquidity and stability.
Long-Term Economic Consequences and Bond Market Outlook
Prolonged tariff disputes can significantly hamper global economic growth, potentially pushing the economy into a recession. This has far-reaching consequences for the bond market. Reduced global trade flows, a common outcome of escalating tariffs, can lead to decreased investment, reduced consumer spending, and ultimately, lower economic growth. This impacts long-term bond yields, which reflect long-term economic expectations. Increased uncertainty also increases credit risk and default risk, particularly for corporate bonds issued by companies heavily reliant on international trade.
- Reduced global trade can hamper economic growth: Tariffs create barriers to trade, reducing the overall volume of goods and services exchanged globally.
- Recessionary risks increase with prolonged tariff disputes: Prolonged trade wars can negatively impact business confidence and investment, increasing the likelihood of a recession.
- Long-term bond yields reflect long-term economic expectations: Lower expected future growth tends to result in lower long-term bond yields.
- Credit risk and default risk increase during economic downturns: Companies struggling with reduced sales and profits are more likely to default on their debt obligations.
- Careful evaluation of specific bond issuers is critical: Investors need to assess the creditworthiness of individual bond issuers, considering their vulnerability to tariff-related disruptions.
Different economic models predict varying impacts of tariffs on long-term growth. These predictions, in turn, influence how bond market valuations are adjusted to reflect these uncertain long-term economic outlooks.
Conclusion
Tariff shocks create significant uncertainty in the bond market, influencing inflation, interest rates, investor behavior, and long-term economic prospects. Understanding these complex dynamics is vital for formulating effective investment strategies in the face of such challenges. The interplay between inflation, interest rates, investor sentiment, and the broader economic climate significantly impacts bond yields and market stability.
Navigating the complexities of a tariff shock requires a well-informed approach. Learn more about mitigating risk and developing a robust bond investment strategy tailored to your specific risk tolerance and investment goals. Stay informed about the latest developments in the bond market and the potential impact of future tariff shocks to make informed decisions and protect your portfolio. Understanding the potential impact of a tariff shock is crucial for any investor navigating the complexities of the fixed income market.

Featured Posts
-
 Yankees Vs Brewers Injured Players For The Series March 27 30
May 12, 2025
Yankees Vs Brewers Injured Players For The Series March 27 30
May 12, 2025 -
 L Histoire D Amour D Eric Antoine Revelations Sur Sa Vie Sentimentale
May 12, 2025
L Histoire D Amour D Eric Antoine Revelations Sur Sa Vie Sentimentale
May 12, 2025 -
 Asylum Minister Faber Survives No Confidence Vote
May 12, 2025
Asylum Minister Faber Survives No Confidence Vote
May 12, 2025 -
 Martinelli Obtiene Asilo En Colombia Analisis De La Decision
May 12, 2025
Martinelli Obtiene Asilo En Colombia Analisis De La Decision
May 12, 2025 -
 Five Drivers On The Bubble Who Might Miss The 2025 Indy 500
May 12, 2025
Five Drivers On The Bubble Who Might Miss The 2025 Indy 500
May 12, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Paso Robles Heat Advisory Temperature Predictions And Safety Tips
May 13, 2025
Paso Robles Heat Advisory Temperature Predictions And Safety Tips
May 13, 2025 -
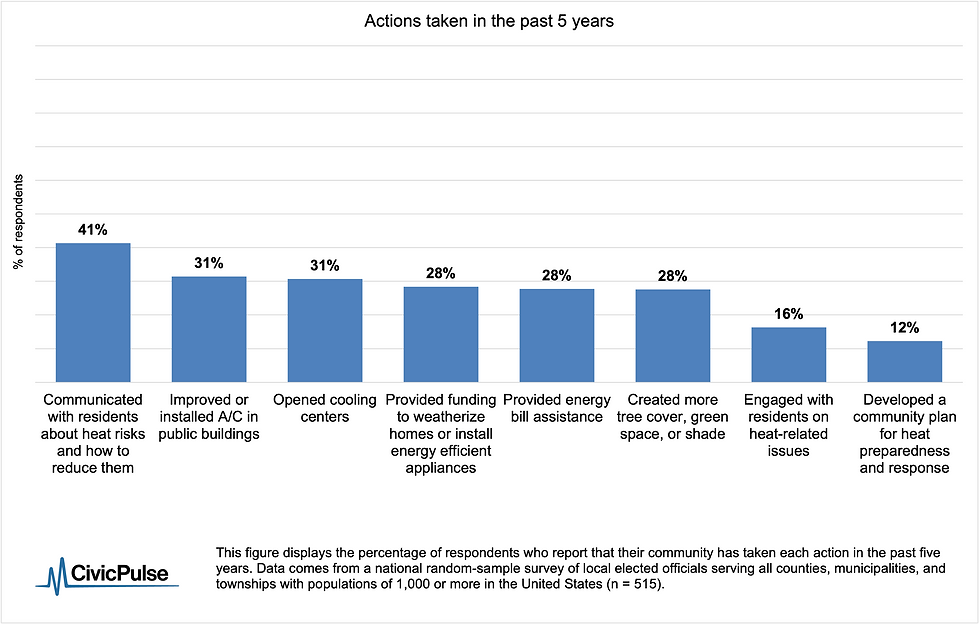 Local Health Department Issues Heat Advisory Due To Extreme Temperatures
May 13, 2025
Local Health Department Issues Heat Advisory Due To Extreme Temperatures
May 13, 2025 -
 Heat Advisory Issued For Paso Robles How Hot Will It Get
May 13, 2025
Heat Advisory Issued For Paso Robles How Hot Will It Get
May 13, 2025 -
 Sporne Iz Ave Marinike Tepi Shta Kazhe Natsionalni Savet Roma
May 13, 2025
Sporne Iz Ave Marinike Tepi Shta Kazhe Natsionalni Savet Roma
May 13, 2025 -
 Govor Mrzhnje Iz Ave Marinike Tepi I Reaktsi A Natsionalnog Saveta Roma
May 13, 2025
Govor Mrzhnje Iz Ave Marinike Tepi I Reaktsi A Natsionalnog Saveta Roma
May 13, 2025
