The 2025 Decline Of D-Wave Quantum (QBTS) Stock: An In-Depth Look

Table of Contents
Main Points: Assessing the Risks for D-Wave Quantum (QBTS)
2.1. Competitive Landscape and Technological Challenges
H3: Emerging Competitors and Increased Competition
The quantum computing sector is rapidly evolving, with numerous players vying for market dominance. D-Wave, a pioneer in adiabatic quantum computing, faces increasing pressure from competitors employing different approaches. This intensified competition poses a significant challenge to D-Wave's market share and future growth.
- IBM: Developing gate-based quantum computers with significantly higher qubit counts and improved coherence times.
- Google: Making strides in superconducting quantum computing, achieving "quantum supremacy" in specific tasks.
- IonQ: Focusing on trapped-ion technology, showcasing promising results in terms of scalability and error correction.
- Rigetti Computing: Another significant player in the gate-based quantum computing space, actively developing and deploying their systems.
These competitors are actively developing technologies that could potentially overshadow D-Wave's adiabatic quantum computing approach, which faces limitations in scalability and the ability to tackle a wider range of computational problems.
H3: Technological Limitations of Adiabatic Quantum Computing
D-Wave's adiabatic quantum computing (AQC) approach, while groundbreaking, possesses inherent limitations compared to gate-based and trapped-ion quantum computing methods. These limitations could hinder its ability to compete effectively in the long term.
- Scalability: Increasing the number of qubits in AQC systems presents significant challenges compared to other architectures.
- Error Correction: Implementing robust error correction mechanisms remains a major hurdle for AQC, impacting the accuracy and reliability of computations.
- Applicability: AQC's applicability to a broad range of real-world problems is currently more limited than that of universal gate-based quantum computers.
These technological limitations may lead to slower progress for D-Wave compared to competitors pushing the boundaries of more versatile quantum computing architectures.
2.2. Financial Performance and Market Valuation
H3: Analysis of D-Wave's Financial Statements
A thorough examination of D-Wave's financial statements reveals key insights into its financial health and sustainability. While specific figures fluctuate, a consistent pattern of significant operating losses and reliance on funding rounds is generally observed.
- Revenue Growth: Revenue growth has been relatively slow, indicating challenges in achieving widespread commercial adoption.
- Net Income: D-Wave has consistently reported negative net income, highlighting the significant financial investment required to develop and commercialize its technology.
- Debt Levels: D-Wave's financial position likely involves considerable debt, raising concerns about its long-term financial stability. (Note: Readers should consult current financial reports for precise details).
Visualizing these trends through charts and graphs provides a clear picture of D-Wave's financial performance.
H3: Overvalued Stock Price and Potential for Correction
The current QBTS stock price needs careful evaluation concerning the company's financial performance and future prospects. A high valuation multiple (P/E ratio, for instance), compared to industry averages, may suggest the stock is overvalued.
- Current Stock Price: A detailed analysis of the current QBTS stock price relative to its financial performance is essential.
- Valuation Multiples: Comparing key valuation metrics (P/E ratio, Price-to-Sales ratio) to industry averages helps determine if the stock is appropriately priced or potentially overvalued.
- Market Sentiment: Shifts in market sentiment towards quantum computing stocks could significantly impact the QBTS stock price.
2.3. Market Adoption and Practical Applications
H3: Limited Real-World Applications
While D-Wave has secured some applications in specific niches, the broader adoption of its technology faces limitations. Its current applications often demonstrate limited scalability and impact.
- Current Applications: Examples include applications in materials science, logistics optimization, and financial modeling, but their scope and practical impact are still developing.
- Deployment Comparisons: The number of successful real-world deployments of D-Wave systems needs to be compared with competitors' successes to assess market penetration.
H3: Challenges in Achieving Wider Market Adoption
Several factors hinder the wider adoption of D-Wave's technology. These challenges significantly impact the company's future growth trajectory.
- High Cost: The cost of acquiring and maintaining D-Wave's quantum systems remains a major barrier to entry for many potential customers.
- Complexity: Utilizing D-Wave's technology requires specialized expertise, creating a bottleneck for wider adoption.
- Skill Gap: A lack of skilled professionals who can effectively develop and deploy quantum algorithms further limits market adoption.
2.4. Risks and Uncertainties
H3: Geopolitical and Regulatory Risks
External factors can significantly impact D-Wave's business. Geopolitical events and regulatory changes pose potential risks.
- Trade Wars & Sanctions: International trade disputes or sanctions could disrupt supply chains or access to key markets.
- Government Regulations: Changes in government regulations regarding technology exports or data privacy could impact D-Wave's operations.
H3: Technological Disruptions and Unexpected Breakthroughs
The quantum computing field is characterized by rapid innovation and unexpected breakthroughs. This inherent uncertainty creates significant risks for all players, including D-Wave.
- Disruptive Technologies: Competitors could develop disruptive technologies that render D-Wave's technology obsolete.
- Unforeseen Advancements: Unexpected advancements in other areas of quantum computing could dramatically shift the competitive landscape.
Conclusion: Navigating the Potential Decline of D-Wave Quantum (QBTS) Stock in 2025
This analysis highlights several key factors that could contribute to a potential decline in D-Wave Quantum (QBTS) stock by 2025. The intense competition, technological limitations of AQC, financial challenges, limited market adoption, and significant inherent risks within the quantum computing industry all warrant careful consideration. While D-Wave's pioneering role in quantum computing is undeniable, its future success remains uncertain. While there's potential for upside, the risks are substantial. Before investing in QBTS or any quantum computing stock, conduct thorough due diligence, understand the inherent volatility of the market, and develop a responsible investment strategy. Remember, investing in D-Wave Quantum (QBTS) involves significant risk, and a decline in 2025 is a distinct possibility.

Featured Posts
-
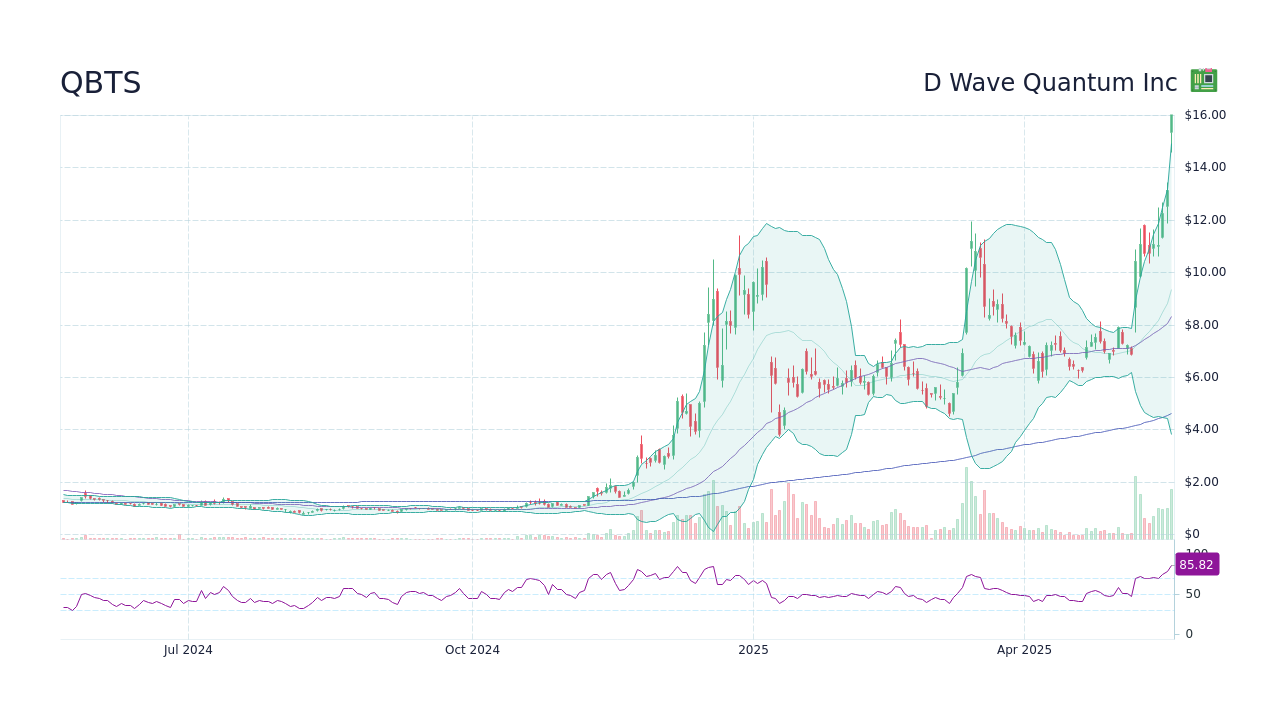 Investigating The Reasons Behind D Wave Quantum Qbts Stocks Friday Gain
May 20, 2025
Investigating The Reasons Behind D Wave Quantum Qbts Stocks Friday Gain
May 20, 2025 -
 I Krisi Stoys Sidirodromoys Analyontas Tin Xronia Kakodaimonia
May 20, 2025
I Krisi Stoys Sidirodromoys Analyontas Tin Xronia Kakodaimonia
May 20, 2025 -
 Decouvrir L Integrale Agatha Christie Une Exploration De Son Univers
May 20, 2025
Decouvrir L Integrale Agatha Christie Une Exploration De Son Univers
May 20, 2025 -
 Agatha Christie Writing Classes Launched By Bbc Using Ai
May 20, 2025
Agatha Christie Writing Classes Launched By Bbc Using Ai
May 20, 2025 -
 Investigation Launched Into Racial Slurs Targeting Angel Reese In Wnba
May 20, 2025
Investigation Launched Into Racial Slurs Targeting Angel Reese In Wnba
May 20, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Old North State Report Summary Of Events May 9 2025
May 20, 2025
Old North State Report Summary Of Events May 9 2025
May 20, 2025 -
 Billionaire Boy A Deep Dive Into Wealth And Privilege
May 20, 2025
Billionaire Boy A Deep Dive Into Wealth And Privilege
May 20, 2025 -
 Vyskum Home Office Vs Kancelaria Z Pohladu Manazerov
May 20, 2025
Vyskum Home Office Vs Kancelaria Z Pohladu Manazerov
May 20, 2025 -
 Key Developments From The Old North State Report May 9 2025
May 20, 2025
Key Developments From The Old North State Report May 9 2025
May 20, 2025 -
 Blog N Home Office Kancelaria Alebo Hybridny Pristup
May 20, 2025
Blog N Home Office Kancelaria Alebo Hybridny Pristup
May 20, 2025
