The Challenge Of Bringing Factory Jobs Back To The US: Workforce And Reality

Table of Contents
H2: The Skills Gap: A Major Hurdle in Reshoring
The US manufacturing sector faces a critical shortage of skilled workers, posing a major obstacle to successful reshoring. This skills gap significantly impacts the ability of companies to fill essential roles and ramp up production.
H3: Lack of Qualified Workers: Many factories require specialized skills in advanced manufacturing techniques, automation, and robotics – skills that are currently in short supply. The demand for highly trained professionals far outpaces the current supply.
- Needed Skills:
- CNC machining and programming
- Robotics operation and programming
- Advanced quality control and process improvement techniques
- Mechatronics and industrial automation systems
- Data analytics for manufacturing optimization
- Statistics: A recent report by [cite a relevant source, e.g., the Manufacturing Institute] indicates a projected shortage of [insert number] skilled manufacturing workers by [year]. This highlights the urgent need for targeted workforce development initiatives.
H3: Addressing the Skills Gap Through Workforce Development: Overcoming this skills gap requires a multi-pronged approach focusing on education and training. This includes investing in apprenticeships, vocational training programs, and expanding partnerships between industry and educational institutions.
- Successful Programs:
- [Example: Mention a specific successful apprenticeship program and its results]
- [Example: Discuss a community college initiative that successfully trains workers for specific manufacturing jobs]
- Government Initiatives: Federal and state governments can play a vital role through funding and incentives for workforce development programs. The [mention relevant government programs, e.g., the Department of Labor's apprenticeship programs] are crucial in this effort.
H2: Automation and its Impact on Reshoring Efforts
Automation is transforming the manufacturing landscape, presenting both challenges and opportunities for reshoring. While it enhances efficiency and productivity, it also changes the skill sets needed by the workforce.
H3: The Role of Automation in Modern Manufacturing: Automation technologies, including robotics, AI, and advanced sensors, are significantly altering manufacturing processes. This necessitates a shift towards workers with expertise in programming, maintaining, and troubleshooting these automated systems.
- Automated Processes:
- Automated assembly lines
- Robotic welding and painting
- Computer-controlled machining centers
- Automated quality inspection systems
- Benefits and Drawbacks: Automation can reduce labor costs and improve quality, but it can also lead to job displacement if not managed strategically.
H3: Balancing Automation with Human Workers: Successful reshoring strategies must integrate automation thoughtfully, leveraging its benefits while preserving opportunities for human workers. This requires reskilling and upskilling initiatives to equip workers for new roles.
- Successful Integration: [Example: Discuss a company that successfully integrated automation and human labor, highlighting its approach]
- Upskilling/Reskilling: Investing in training programs that equip workers with skills in areas such as robotics maintenance, data analysis, and programming is critical for a successful transition to a more automated manufacturing environment.
H2: The Cost Factor: Is Reshoring Economically Viable?
The economic feasibility of bringing factory jobs back to the US is a crucial consideration. While there's a strong desire to rebuild American manufacturing, comparing domestic and overseas production costs is complex.
H3: Comparing Domestic vs. Overseas Production Costs: Many factors contribute to the overall cost, including labor, transportation, raw materials, energy, and regulatory compliance. Simply comparing labor costs alone provides an incomplete picture.
- Cost Comparison Factors:
- Labor costs (wages, benefits, productivity)
- Transportation costs (shipping, logistics)
- Raw material costs and availability
- Energy costs and environmental regulations
- Taxes and tariffs
- Complexities: Accurate cost comparisons require considering the entire supply chain and all associated expenses.
H3: Government Incentives and Support for Reshoring: Government policies, tax breaks, and subsidies can play a significant role in making reshoring economically viable. These incentives can offset some of the higher costs associated with domestic production.
- Government Programs: [List examples of government programs supporting reshoring, e.g., tax credits for domestic manufacturing investments]
- Effectiveness: The effectiveness of these programs varies and requires ongoing evaluation and adjustment to ensure maximum impact.
3. Conclusion:
Bringing factory jobs back to the US presents significant challenges, including a critical skills gap, the transformative impact of automation, and the complexities of cost comparisons. Addressing these issues requires a collaborative effort involving workforce development initiatives, strategic automation implementation, and supportive government policies. Key takeaways include the need for comprehensive reskilling and upskilling programs, a focus on integrating automation effectively, and continued investment in government incentives to make reshoring a viable economic proposition.
To rebuilding American manufacturing and investing in US manufacturing jobs, we need to actively support workforce development programs, advocate for policies that create a competitive domestic manufacturing environment, and encourage companies to embrace strategic reshoring strategies. The long-term economic benefits for the US are significant, requiring a sustained commitment from all stakeholders.

Featured Posts
-
 Is The Trans Australia Running Record About To Fall
May 21, 2025
Is The Trans Australia Running Record About To Fall
May 21, 2025 -
 Bbc Antiques Roadshow American Couples Arrest In Britain
May 21, 2025
Bbc Antiques Roadshow American Couples Arrest In Britain
May 21, 2025 -
 Saskatchewan Political Panel Federal Leaders Visit Sparks Controversy
May 21, 2025
Saskatchewan Political Panel Federal Leaders Visit Sparks Controversy
May 21, 2025 -
 Funbox Opens First Permanent Location Indoor Bounce Park In Mesa Arizona
May 21, 2025
Funbox Opens First Permanent Location Indoor Bounce Park In Mesa Arizona
May 21, 2025 -
 Dexter Resurrection Brings Back Beloved Villains
May 21, 2025
Dexter Resurrection Brings Back Beloved Villains
May 21, 2025
Latest Posts
-
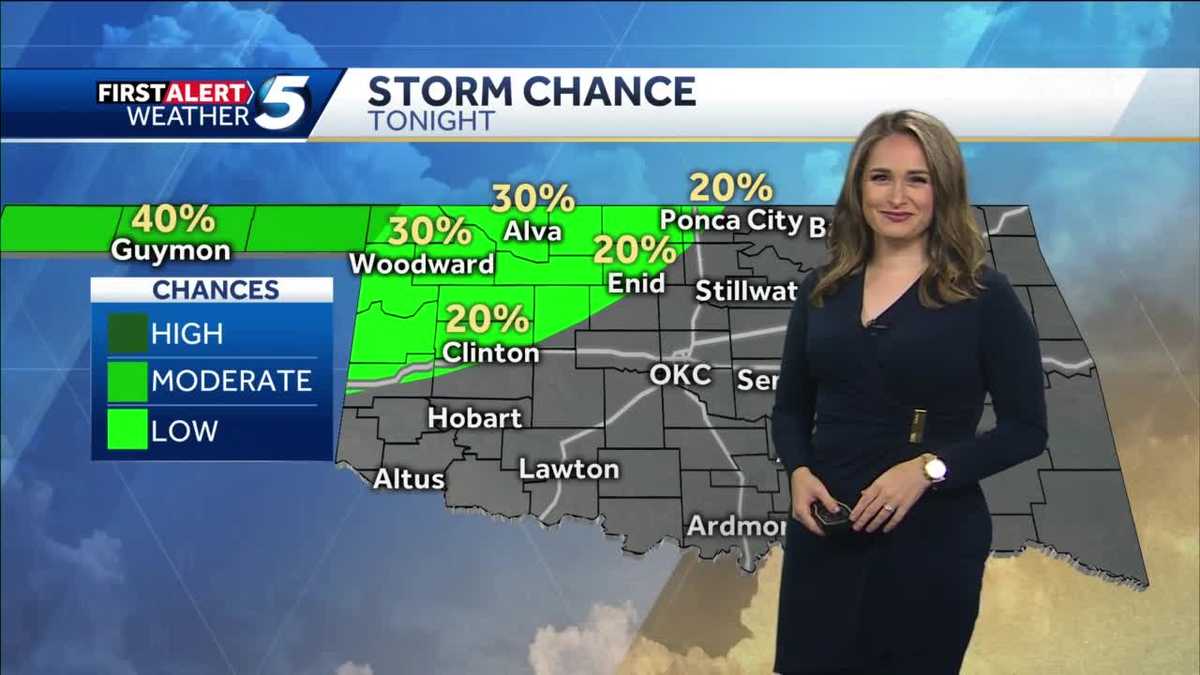 Monday Severe Weather Overnight Storm Chances And Impacts
May 21, 2025
Monday Severe Weather Overnight Storm Chances And Impacts
May 21, 2025 -
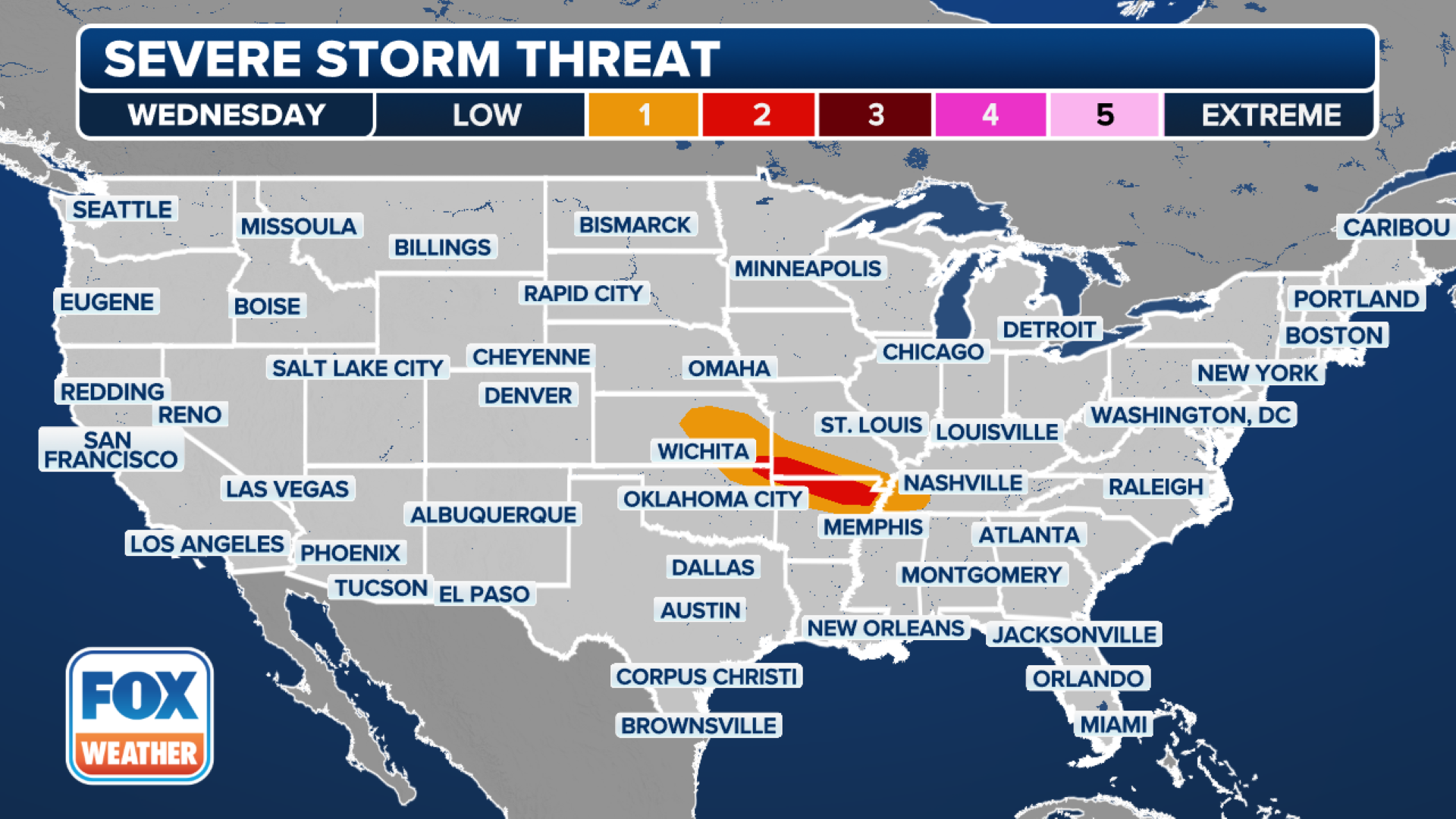 Overnight Storm Potential Severe Weather Risk Monday
May 21, 2025
Overnight Storm Potential Severe Weather Risk Monday
May 21, 2025 -
 Animal Welfare Investigation 49 Dogs Removed From Washington County Facility
May 21, 2025
Animal Welfare Investigation 49 Dogs Removed From Washington County Facility
May 21, 2025 -
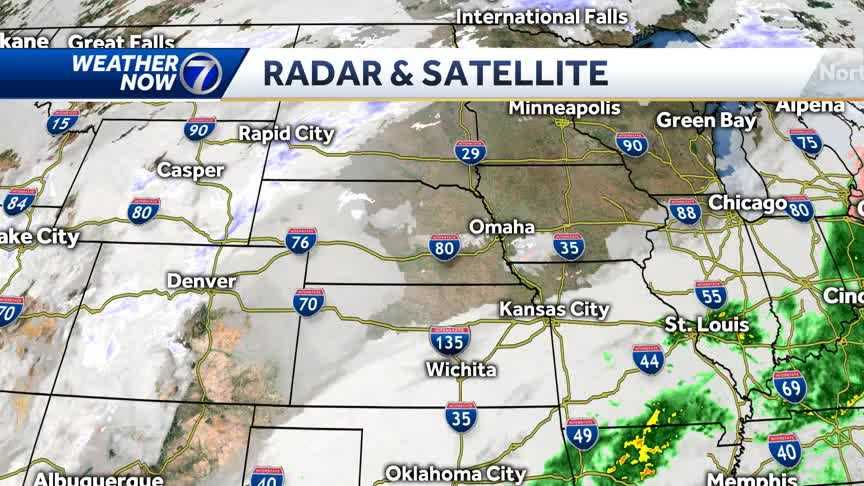 Wintry Mix Of Rain And Snow Impacts And Safety Precautions
May 21, 2025
Wintry Mix Of Rain And Snow Impacts And Safety Precautions
May 21, 2025 -
 Driving Safely During A Wintry Mix Of Rain And Snow
May 21, 2025
Driving Safely During A Wintry Mix Of Rain And Snow
May 21, 2025
