The Great Decoupling: A New Era Of Economic Fragmentation?
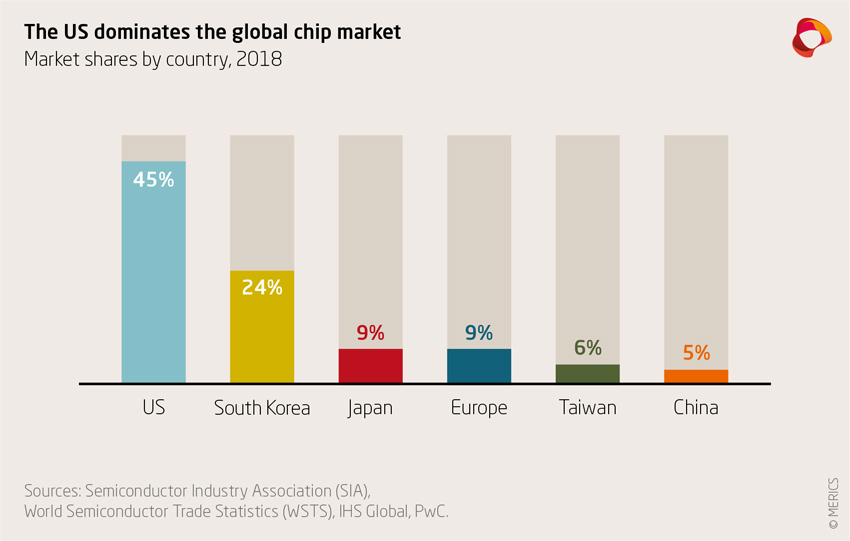
Table of Contents
Geopolitical Tensions and the Rise of Protectionism
The current global landscape is increasingly characterized by heightened geopolitical tensions and a resurgence of protectionist policies. This trend significantly contributes to the potential for a "Great Decoupling."
The US-China Trade War and its Ripple Effects
The US-China trade war, which began in 2018, serves as a prime example of the escalating tensions driving economic fragmentation. The imposition of tariffs on billions of dollars worth of goods disrupted global supply chains, leading to increased costs for businesses and consumers.
- Industries Affected: The technology sector, particularly semiconductors and telecommunications equipment, experienced significant disruptions. Manufacturing industries, reliant on complex global supply chains, also faced considerable challenges.
- Investment Patterns: Companies began diversifying their supply chains, reducing reliance on single sourcing from China. This led to a shift in foreign direct investment (FDI) towards countries deemed less risky, such as Vietnam, India, and Mexico.
- Technological Decoupling: The trade war accelerated the trend of technological decoupling, with both the US and China investing heavily in developing domestic technological capabilities to reduce reliance on each other.
The Growing Influence of Nationalism and Regional Blocs
Nationalism and the prioritization of domestic interests are contributing to the erosion of multilateral trade agreements and alliances. This shift is evident in the increasing popularity of regional trade agreements.
- Prioritizing Domestic Industries: Many countries are implementing policies aimed at bolstering their domestic industries, often at the expense of international competition. This includes subsidies, tariffs, and other protectionist measures.
- Rise of Regional Trade Agreements: The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), the largest free trade agreement in the world, exemplifies the shift towards regional economic blocs. Similar agreements are emerging in other regions.
- Weakening of Multilateral Organizations: The World Trade Organization (WTO) has struggled to effectively address escalating trade disputes, further contributing to the fragmentation of the global trading system.
Technological Decoupling: A Key Driver of Fragmentation
Technological decoupling, driven by national security concerns and data sovereignty issues, is another major factor contributing to the "Great Decoupling."
Data Security and National Security Concerns
Governments are increasingly prioritizing data security and national security, leading to stricter regulations on data localization and cross-border data flows.
- Data Localization Laws: Many countries are implementing laws requiring companies to store data within their borders, hindering cross-border data flows and impacting international collaboration.
- Impact on Cross-border Data Flows: Restrictions on data flows can limit the efficiency of global supply chains and hinder innovation by restricting access to data and expertise.
- Rise of National Champions in Tech: Governments are investing heavily in domestic tech companies, aiming to create national champions capable of competing on a global stage, reducing reliance on foreign technologies.
The Impact on Supply Chains and Innovation
Technological decoupling is leading to a significant reshaping of global supply chains and innovation ecosystems.
- Supply Chain Diversification: Companies are actively diversifying their supply chains to reduce reliance on single sources and mitigate geopolitical risks. This often involves "friend-shoring," relocating production to countries with closer political and economic ties.
- Rise of Friend-Shoring: This strategy prioritizes partnerships with countries that share similar values and security interests, often at the expense of lower production costs.
- Implications for Global Competitiveness: While diversification can enhance resilience, it can also lead to higher costs and potentially reduce overall global competitiveness.
Economic Consequences of the Great Decoupling
The potential consequences of a "Great Decoupling" are far-reaching and could significantly impact global economic growth and development.
Impact on Global Growth and Development
A fragmented global economy could lead to slower economic growth, particularly for developing countries that rely heavily on international trade and investment.
- Slower Growth: Reduced trade and investment flows can limit economic expansion and hinder the development of emerging economies.
- Increased Inequality: The decoupling could exacerbate existing inequalities, potentially widening the gap between developed and developing nations.
- Challenges for International Development Initiatives: International development efforts could be hampered by reduced cooperation and a decline in cross-border capital flows.
Shifting Investment Patterns and Market Volatility
A "Great Decoupling" could also lead to significant changes in global investment flows and increased market volatility.
- Investment Shifts: Companies may shift investments to countries perceived as politically and economically more stable and aligned with their interests.
- Potential for Capital Flight: Uncertainty surrounding geopolitical risks could lead to capital flight, destabilizing financial markets.
- Implications for Financial Markets: Increased market volatility could pose significant challenges for investors and policymakers.
Conclusion
The possibility of a "Great Decoupling" presents significant challenges to the global economy. The rising tide of geopolitical tensions, protectionist policies, and technological decoupling is creating a more fragmented and uncertain global landscape. Understanding the "Great Decoupling" is crucial for navigating the evolving global economic landscape. Further research into the impact on specific industries and regions is vital to mitigating potential risks and seizing opportunities in this new era of economic fragmentation. Proactive engagement with relevant organizations and initiatives dedicated to fostering international cooperation and mitigating the effects of decoupling is essential for shaping a more stable and prosperous future.

Featured Posts
-
 Match Dijon Concarneau Score Details Et Analyse De La Journee 28 De National 2
May 09, 2025
Match Dijon Concarneau Score Details Et Analyse De La Journee 28 De National 2
May 09, 2025 -
 Trump Announces New Trade Deal With Britain Details And Implications
May 09, 2025
Trump Announces New Trade Deal With Britain Details And Implications
May 09, 2025 -
 Mental Health Violence And The Media Deconstructing The Monster Myth
May 09, 2025
Mental Health Violence And The Media Deconstructing The Monster Myth
May 09, 2025 -
 French Minister Urges More Robust Eu Action Against Us Tariffs
May 09, 2025
French Minister Urges More Robust Eu Action Against Us Tariffs
May 09, 2025 -
 Champions League Prediction Rio Ferdinand Picks His Winner Before Arsenal Vs Psg
May 09, 2025
Champions League Prediction Rio Ferdinand Picks His Winner Before Arsenal Vs Psg
May 09, 2025
