The Great Decoupling's Impact On Industries: A Sector-by-Sector Analysis
Table of Contents
The term "Great Decoupling" refers to the ongoing process of economic decoupling between major global powers, particularly between the United States and China. This decoupling is characterized by a reduction in economic interdependence, a diversification of supply chains, and a rise in regionalization, meaning companies are increasingly focusing on sourcing and manufacturing within their own regions or in politically aligned countries, rather than relying on globalized supply chains. This shift is driven by factors including geopolitical risks, concerns over national security, and a desire to reduce reliance on specific countries for essential goods and services. The aim of this article is to provide a detailed analysis of how this economic decoupling is affecting various industrial sectors.
The Impact of the Great Decoupling on the Technology Sector
The technology sector is highly susceptible to the effects of The Great Decoupling. The intricate, globally interconnected nature of its supply chains makes it particularly vulnerable to disruptions caused by geopolitical shifts and trade restrictions.
Semiconductor Industry
The semiconductor industry is at the forefront of this disruption. Reduced reliance on specific countries, like Taiwan, for chip manufacturing necessitates a significant restructuring.
- Increased production in friendly nations: Countries are investing heavily in building their own domestic semiconductor production capabilities, reducing dependence on potential adversaries.
- Investment in domestic chip production: Governments are offering substantial subsidies and incentives to attract semiconductor manufacturers, leading to a resurgence of domestic production in several countries.
- Potential for higher prices: Increased production costs and reduced economies of scale could lead to higher prices for consumers and businesses.
- Impact on tech innovation: While diversification might reduce reliance on single sources, it could also potentially slow down the pace of innovation due to reduced collaboration and competition.
Software and Data
Data localization policies and cross-border data transfer restrictions are creating significant challenges for software companies.
- Cybersecurity concerns: Governments are increasingly prioritizing data security and are implementing stricter regulations to protect sensitive information.
- Impact on cloud computing: The ability to seamlessly store and process data across international borders is becoming increasingly complex.
- Implications for software development and collaboration: Restrictions on data sharing can hinder international collaboration in software development and innovation.
Telecommunications
The shift towards nationalization of 5G infrastructure is a key aspect of The Great Decoupling in the telecom sector.
- Increased security concerns: Countries are prioritizing the security of their 5G networks, often leading to the exclusion of specific vendors based on geopolitical considerations.
- Impact on international collaboration: The move towards nationalized infrastructure reduces opportunities for international collaboration and technology sharing.
- Potential for higher costs: The development and deployment of nationalized infrastructure can be more expensive compared to a globally collaborative approach.
The Great Decoupling and the Manufacturing Sector
The manufacturing sector is experiencing a significant reshaping of its global supply chains. The focus is shifting from cost-optimization to risk mitigation.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is undergoing a dramatic transformation as companies reassess their global supply chains.
- Reshoring: Automakers are relocating manufacturing facilities back to their home countries to reduce dependence on foreign suppliers and mitigate risks.
- Nearshoring: Companies are moving production to neighboring countries to shorten supply chains and reduce transportation costs.
- Higher transportation costs: Shorter, more regionalized supply chains may initially lead to higher transportation costs.
- Impact on vehicle prices: These shifts are likely to contribute to higher vehicle prices for consumers.
Textiles and Apparel
The textiles and apparel industry is witnessing a shift in production bases, with a focus on regional sourcing.
- Increased regional sourcing: Companies are increasingly sourcing materials and manufacturing closer to their target markets.
- Impact on developing economies: This shift can have significant consequences for developing economies that heavily rely on the textile and apparel industries.
- Changes in consumer prices: The changes in production locations and transportation costs will likely impact consumer prices.
Consumer Goods
The diversification of manufacturing locations for consumer goods is impacting product availability and prices.
- Longer lead times: Diversified supply chains inevitably result in longer lead times for products.
- Potential for shortages: Disruptions in any part of the diversified supply chain can easily lead to product shortages.
- Changes in consumer preferences: Consumers may need to adapt to changes in product availability and pricing.
The Great Decoupling's Effects on the Energy Sector
The energy sector is deeply affected by geopolitical shifts and the drive for energy independence.
Oil and Gas
The geopolitical implications of decoupling are profoundly impacting energy security and prices.
- Increased energy independence initiatives: Countries are investing heavily in domestic energy production to reduce reliance on foreign sources.
- Diversification of energy sources: The focus is shifting towards diversifying energy sources, reducing dependence on oil and gas.
- Potential for price volatility: Geopolitical instability and supply chain disruptions can lead to increased price volatility.
Renewable Energy
The Great Decoupling is impacting the growth of renewable energy technologies and international cooperation.
- Increased investments in domestic renewable energy: Countries are prioritizing the development of domestic renewable energy resources.
- Potential for slower innovation due to reduced international collaboration: Reduced collaboration might hinder innovation and the sharing of best practices.
Financial Services and the Great Decoupling
The financial services sector faces significant challenges and opportunities in the context of The Great Decoupling.
Cross-border Payments
International financial transactions are becoming more complex and expensive.
- Increased transaction costs: Cross-border payments are becoming more costly and time-consuming due to increased regulations and compliance requirements.
- Challenges for international trade: The increased complexity of cross-border payments poses challenges for international trade and investment.
- Opportunities for fintech companies: The increasing need for efficient and secure cross-border payment solutions creates opportunities for fintech companies.
Investment and Capital Flows
Decoupling is impacting foreign direct investment (FDI) and capital market integration.
- Reduced cross-border investment: Geopolitical uncertainties are leading to a decline in cross-border investment.
- Increased regional investment: Investment is shifting towards regional markets, reducing global capital market integration.
- Implications for global capital allocation: The shift in investment patterns has significant implications for global capital allocation and economic growth.
Conclusion: Navigating the Shifting Landscape of the Great Decoupling
The Great Decoupling is reshaping global industries, presenting both significant challenges and opportunities. The analysis across various sectors reveals a clear trend towards regionalization, diversification of supply chains, and a greater emphasis on national security. Understanding the specific impacts of The Great Decoupling on individual industries is crucial for businesses to adapt and thrive in this new economic environment. The implications for pricing, innovation, and international cooperation are substantial and require proactive strategic adjustments. To successfully navigate this evolving landscape, it's essential to conduct thorough research on the specific impacts of The Great Decoupling on your respective industry. Developing proactive strategies to manage risks and capitalize on opportunities presented by this significant global shift is no longer optional, but a necessity for long-term success. Understanding the Great Decoupling and its impact is key to shaping your future business strategy.

Featured Posts
-
 Daycare Vs Babysitter A Cost Comparison Following A 3 000 Babysitting Bill
May 09, 2025
Daycare Vs Babysitter A Cost Comparison Following A 3 000 Babysitting Bill
May 09, 2025 -
 Operation Sindoor Impact Kse 100 Trading Halted Amidst Market Panic
May 09, 2025
Operation Sindoor Impact Kse 100 Trading Halted Amidst Market Panic
May 09, 2025 -
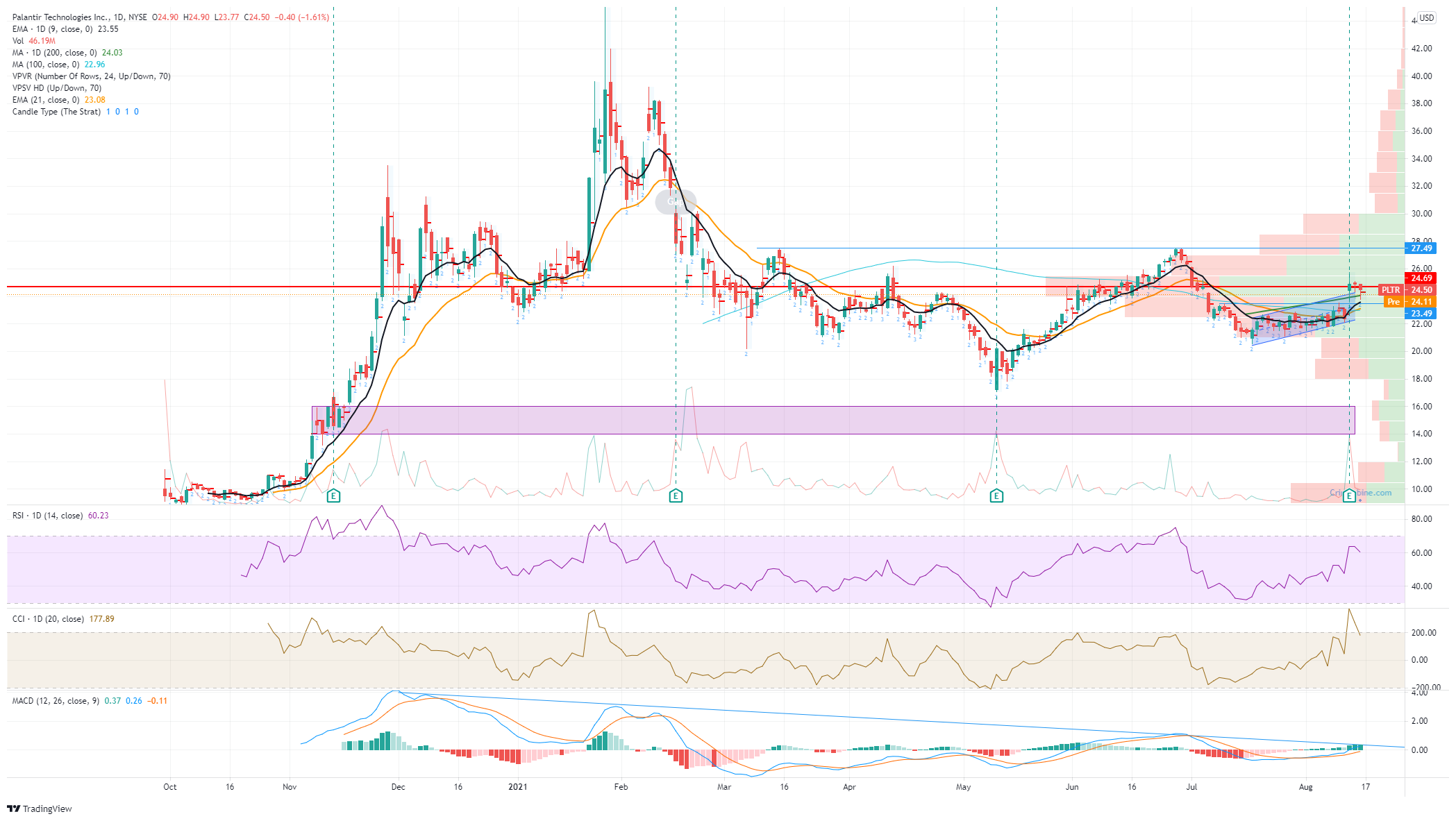 Should You Invest In Palantir Stock Before May 5th
May 09, 2025
Should You Invest In Palantir Stock Before May 5th
May 09, 2025 -
 Unexpected Twist Wynne Evans Career Path After Strictly Come Dancing
May 09, 2025
Unexpected Twist Wynne Evans Career Path After Strictly Come Dancing
May 09, 2025 -
 Kimbal Musk Profile Of Elons Brother And His Activism
May 09, 2025
Kimbal Musk Profile Of Elons Brother And His Activism
May 09, 2025
