The Impact Of Global Warming On Fungal Pathogens
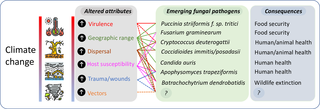
Table of Contents
Increased Geographic Range of Fungal Pathogens
Warming temperatures are allowing many fungal pathogens to thrive in previously unsuitable climates, resulting in a significant expansion of their geographic range. This expansion poses a substantial threat to both human and environmental health, as populations in newly affected areas may lack immunity or preparedness for these emerging diseases.
-
Examples of fungal pathogens expanding their range: Several species are demonstrating this phenomenon. Coccidioides, the fungus responsible for coccidioidomycosis (valley fever), is expanding its range in the southwestern United States due to increasing temperatures and drought conditions. Similarly, Histoplasma capsulatum, the cause of histoplasmosis, is being reported in areas previously considered too cold for its survival.
-
The role of temperature in fungal growth and reproduction: Temperature is a critical factor governing fungal growth and reproduction. Many fungal pathogens have optimal temperature ranges for growth; warmer temperatures outside these ranges can inhibit growth, but even slight increases can benefit growth rates, enabling faster spread and higher infection rates.
-
Studies showing correlations between warming temperatures and increased incidence of fungal infections: Numerous studies have demonstrated a clear correlation between rising temperatures and an increased incidence of fungal infections in new regions. These studies highlight the direct link between climate change and the expansion of fungal disease distribution. Further research is needed to fully understand the dynamics of this expansion across different fungal species and geographical locations. Related keywords: Fungal disease distribution, climate change fungal spread, geographic expansion of fungi.
Enhanced Virulence and Pathogenicity of Fungal Pathogens
Beyond geographic expansion, global warming also influences the virulence and pathogenicity of fungal pathogens. Warmer temperatures and increased humidity can act as catalysts, boosting the production of virulence factors and making infections more severe.
-
Discussion of specific virulence factors affected by temperature: Temperature significantly impacts the production of various virulence factors, including toxins, enzymes, and other molecules that contribute to fungal pathogenicity. For instance, higher temperatures can increase the production of mycotoxins, leading to more severe symptoms in infected individuals.
-
Examples of fungi exhibiting increased pathogenicity under warmer conditions: Many fungi demonstrate increased pathogenicity under warmer conditions. Studies have shown that some plant pathogens, under elevated temperatures, cause more extensive damage to crops. Similarly, certain human fungal pathogens exhibit increased virulence at higher temperatures, resulting in more severe and potentially fatal infections.
-
Impact on immunocompromised individuals and the potential for increased mortality rates: The enhanced virulence of fungal pathogens poses a particularly significant threat to immunocompromised individuals, who are already at increased risk of serious fungal infections. Climate change-driven increases in virulence could lead to higher mortality rates among vulnerable populations. Related keywords: Fungal virulence factors, climate change fungal virulence, increased pathogenicity.
Impact on Fungal-Plant Interactions and Food Security
Global warming significantly impacts plant diseases caused by fungal pathogens, resulting in substantial crop losses and threatening global food security. Increased temperatures and humidity create ideal conditions for the growth and spread of numerous plant pathogenic fungi.
-
Examples of fungal plant pathogens whose impacts are worsened by climate change: Numerous crop diseases caused by fungi, including various rusts and blights, are exacerbated by climate change. These diseases lead to significant reductions in crop yields and threaten food production worldwide.
-
Explanation of how temperature and humidity affect fungal infection of plants: High temperatures and humidity create optimal conditions for spore germination, fungal growth, and penetration of plant tissues. This increased infection rate directly translates to more significant crop losses.
-
Discussion of the economic and social consequences of crop failures due to fungal diseases: Crop failures due to fungal diseases have devastating economic and social consequences, leading to food shortages, price increases, and increased food insecurity, particularly in vulnerable communities. Related keywords: Fungal plant pathogens, climate change agriculture, food security fungal diseases.
Synergistic Effects with Other Environmental Factors
The effects of global warming on fungal pathogens are further exacerbated by synergistic interactions with other environmental stressors. Pollution, deforestation, and changes in land use can create conditions that favor fungal growth and spread, amplifying the impact of climate change.
-
Examples of synergistic effects between global warming and other factors on fungal growth: For example, deforestation can lead to increased humidity and temperature fluctuations, favoring fungal growth. Similarly, air pollution can weaken plant defenses, making them more susceptible to fungal infections.
-
Discussion of the potential for increased antibiotic resistance in fungi due to environmental changes: Environmental stressors, combined with the widespread use of antifungal agents, can contribute to the development and spread of antibiotic resistance in fungi, making infections increasingly difficult to treat.
-
Mention the importance of a holistic approach to managing the threat posed by fungal pathogens: Managing the threat of fungal pathogens requires a holistic approach that considers the complex interplay of climate change and other environmental factors. This necessitates integrated strategies combining climate change mitigation efforts with effective disease management practices. Related keywords: Environmental stress, fungal resistance, synergistic effects climate change.
Conclusion
Global warming is undeniably impacting the prevalence and severity of fungal pathogens, posing a growing threat to human and ecosystem health. The expansion of geographic ranges, increased virulence, and synergistic interactions with other environmental stressors highlight the urgent need for further research and proactive mitigation strategies. Understanding the complex interplay between global warming and fungal pathogens is crucial for developing effective interventions to combat this emerging threat. Further research into the effects of global warming on fungal pathogens is essential to develop strategies for prevention and treatment of fungal diseases. We must prioritize efforts to mitigate climate change and implement effective disease management strategies to protect against the escalating impact of these pathogens.

Featured Posts
-
 Best Places To Find Delicious Shrimp In The Hudson Valley
May 26, 2025
Best Places To Find Delicious Shrimp In The Hudson Valley
May 26, 2025 -
 Rekordnye 300 Podiumov Mercedes Rol Rassella I Dostizheniya Khemiltona
May 26, 2025
Rekordnye 300 Podiumov Mercedes Rol Rassella I Dostizheniya Khemiltona
May 26, 2025 -
 Giant Rubber Duck Brings Important Message To Myrtle Beach
May 26, 2025
Giant Rubber Duck Brings Important Message To Myrtle Beach
May 26, 2025 -
 Best Office Chair 2025 Our Expert Picks And Buyers Guide
May 26, 2025
Best Office Chair 2025 Our Expert Picks And Buyers Guide
May 26, 2025 -
 Has Armando Iannucci Lost His Creative Edge
May 26, 2025
Has Armando Iannucci Lost His Creative Edge
May 26, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Deficit De La Foire Au Jambon 2025 La Ville De Bayonne Face A Une Crise Financiere
May 31, 2025
Deficit De La Foire Au Jambon 2025 La Ville De Bayonne Face A Une Crise Financiere
May 31, 2025 -
 Foire Au Jambon Bayonne 2025 Le Maire S Interroge Sur Le Cout Exorbitant De L Organisation
May 31, 2025
Foire Au Jambon Bayonne 2025 Le Maire S Interroge Sur Le Cout Exorbitant De L Organisation
May 31, 2025 -
 Crepes Salados Para Merienda O Cena 8 Ideas Originales
May 31, 2025
Crepes Salados Para Merienda O Cena 8 Ideas Originales
May 31, 2025 -
 South Dagenham Crash Car On Its Side On Whalebone Lane
May 31, 2025
South Dagenham Crash Car On Its Side On Whalebone Lane
May 31, 2025 -
 8 Crepes Salados Recetas Sencillas Para Una Merienda O Cena Exquisita
May 31, 2025
8 Crepes Salados Recetas Sencillas Para Una Merienda O Cena Exquisita
May 31, 2025
