The Impact Of Wildfires: Unprecedented Global Forest Loss
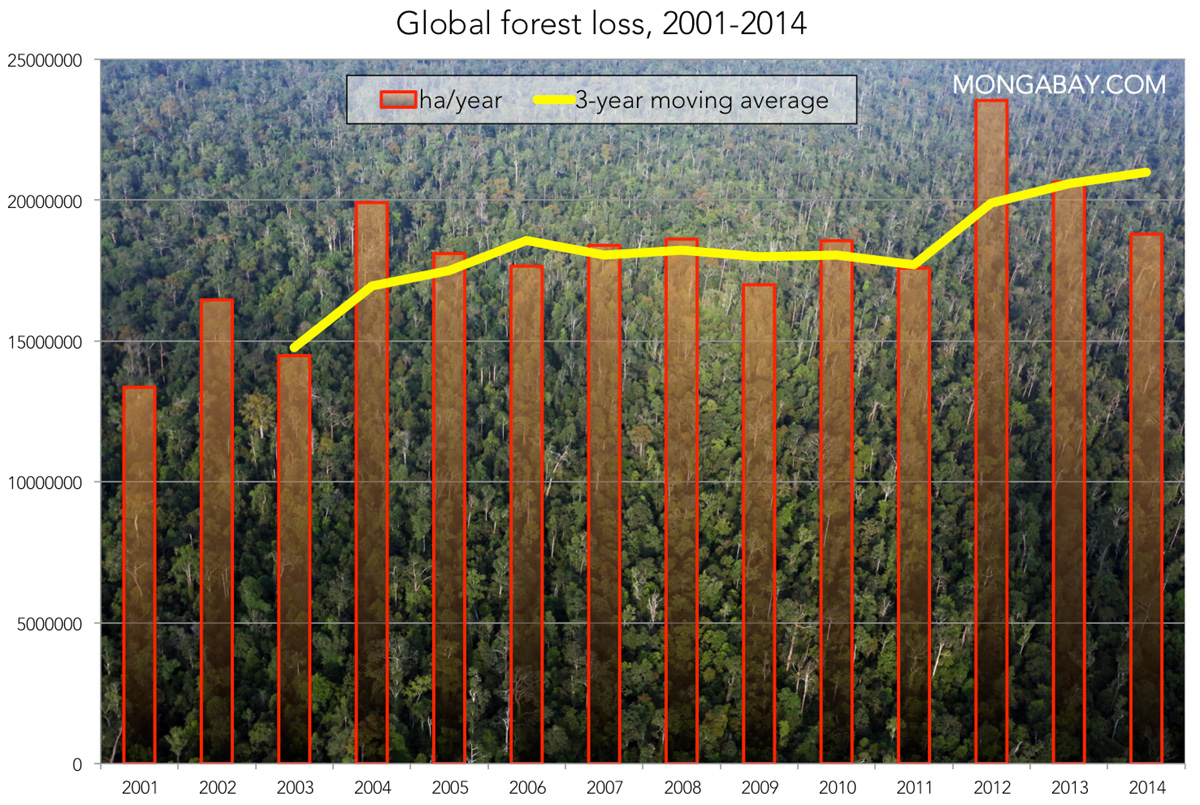
Table of Contents
Environmental Consequences of Wildfires and Global Forest Loss
The environmental consequences of wildfires and the associated global forest loss are far-reaching and deeply interconnected. The destruction extends beyond the immediate burn area, impacting ecosystems for years, even decades, to come.
Biodiversity Loss
Wildfires cause catastrophic biodiversity loss. The intense heat destroys habitats, leading to the displacement or extinction of countless plant and animal species.
- Examples of endangered species affected: Many endangered species, such as the California condor and the red-cockaded woodpecker, are particularly vulnerable to habitat loss from wildfires.
- Disruption of ecosystems: Wildfires disrupt delicate ecological balances, impacting food chains and altering the composition of plant communities. Regeneration can be slow and incomplete, leading to long-term ecosystem instability.
- Loss of habitat: The destruction of forests eliminates critical habitats for countless species, pushing them closer to extinction. This habitat destruction is a major driver of global forest loss.
Air and Water Pollution
Wildfires release massive amounts of smoke and particulate matter into the atmosphere, resulting in severe air pollution. Ash and other pollutants contaminate water sources, damaging aquatic ecosystems.
- Health impacts of air pollution: Wildfire smoke poses significant risks to human health, causing respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular problems, and other health issues.
- Water contamination effects on aquatic life: Ash and runoff from burned areas contaminate water bodies, harming aquatic life and making water sources unsafe for human consumption.
- Long-term environmental damage: The long-term effects of air and water pollution from wildfires can persist for many years, causing lasting damage to the environment.
Climate Change Impacts
Wildfires significantly contribute to climate change, creating a dangerous feedback loop. Burning forests release massive amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, accelerating global warming.
- Carbon emissions from burning biomass: Wildfires release vast quantities of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases, further contributing to the greenhouse effect.
- The impact on the carbon cycle: The destruction of forests disrupts the carbon cycle, reducing the planet's capacity to absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide.
- Increased global temperatures: The increased greenhouse gas emissions from wildfires contribute to rising global temperatures, creating a feedback loop that makes future wildfires more likely and more intense.
Soil Degradation
Wildfires severely degrade soil health, leading to erosion and reduced fertility. The loss of vegetation leaves soil exposed to the elements, accelerating the erosion process.
- Loss of topsoil: Wildfires can strip away topsoil, leaving behind barren land vulnerable to erosion.
- Reduced water retention: Burned soil loses its ability to retain water, leading to increased runoff and drought conditions.
- Increased vulnerability to future fires: Degraded soil is more susceptible to future wildfires, creating a vicious cycle of destruction.
Economic Impacts of Wildfires and Global Forest Loss
The economic consequences of wildfires and global forest loss are substantial and far-reaching, affecting various sectors and communities.
Damage to Property and Infrastructure
Wildfires cause extensive damage to property and infrastructure, leading to significant economic losses. The cost of rebuilding homes, businesses, and essential infrastructure is immense.
- Insurance claims: Insurance companies face massive payouts due to wildfire-related property damage.
- Government relief efforts: Governments often bear the burden of providing disaster relief and rebuilding infrastructure.
- Economic disruption in affected regions: Wildfires can disrupt economic activity in affected regions for extended periods, leading to job losses and reduced economic output.
Loss of Timber Resources
The destruction of forests through wildfires impacts the timber industry and related supply chains. The loss of timber resources leads to reduced production, job losses, and increased prices for wood products.
- Reduced timber production: Wildfires decimate timber resources, leading to a decline in timber production and reduced availability.
- Job losses in the forestry sector: The timber industry experiences job losses due to reduced production and disruption of operations.
- Impact on the wood products industry: The reduced availability of timber impacts the wood products industry, leading to price increases and supply chain disruptions.
Tourism and Recreation Impacts
Wildfires negatively impact tourism and recreation industries. The destruction of natural areas leads to the closure of parks and recreational areas, resulting in a loss of revenue and economic activity.
- Loss of revenue from tourism: The closure of parks and recreational areas due to wildfires results in significant losses of revenue for local communities.
- Closure of national parks and recreational areas: Wildfires can necessitate the closure of national parks and other recreational areas, impacting tourism and outdoor activities.
- Long-term impact on tourism: The long-term effects of wildfires on tourism can be substantial, particularly in areas that rely heavily on tourism revenue.
Societal Impacts of Wildfires and Global Forest Loss
Beyond the environmental and economic impacts, wildfires have profound societal consequences, impacting public health, communities, and social structures.
Public Health
Wildfires pose significant risks to public health. Wildfire smoke causes respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular problems, and other health issues. Displacement of populations due to wildfires creates additional challenges.
- Respiratory illnesses: Wildfire smoke contains numerous harmful pollutants that trigger respiratory illnesses, such as asthma and bronchitis.
- Cardiovascular problems: Exposure to wildfire smoke increases the risk of cardiovascular problems, including heart attacks and strokes.
- Mental health impacts: The stress and trauma associated with wildfires can have significant impacts on mental health.
- Displacement and relocation challenges: The displacement of populations due to wildfires puts a strain on social services and resources, creating challenges for those affected.
Displacement and Migration
Wildfires cause significant population displacement and migration. The destruction of homes and livelihoods forces people to relocate, putting a strain on communities and resources.
- Loss of homes and livelihoods: Wildfires often destroy homes and livelihoods, forcing people to seek shelter and rebuild their lives.
- Strain on social services: The influx of displaced populations puts a strain on social services and resources in receiving communities.
- Increased competition for resources: An influx of displaced populations can lead to increased competition for resources, such as housing, employment, and social services.
Conclusion
The unprecedented global forest loss caused by wildfires presents a serious threat to the environment, economy, and society. The environmental consequences include biodiversity loss, air and water pollution, climate change impacts, and soil degradation. Economically, wildfires cause damage to property, impact the timber and tourism industries, and disrupt economic activity. Societally, they pose serious public health risks and lead to population displacement and migration. The scale of global forest loss due to wildfires demands immediate action. Learn more about wildfire prevention and the impact of deforestation and join the fight to protect our forests. Support organizations working to combat deforestation, and advocate for policies that address climate change and protect our forests. Let's work together to mitigate the devastating effects of wildfires and prevent further global forest loss.

Featured Posts
-
 2025s Best Office Chairs Reviews And Comparisons
May 26, 2025
2025s Best Office Chairs Reviews And Comparisons
May 26, 2025 -
 Pogacars Tour Of Flanders Triumph A Masterclass In Solo Riding
May 26, 2025
Pogacars Tour Of Flanders Triumph A Masterclass In Solo Riding
May 26, 2025 -
 Flash Flood Watch Preparedness Tips For Hampshire And Worcester Residents
May 26, 2025
Flash Flood Watch Preparedness Tips For Hampshire And Worcester Residents
May 26, 2025 -
 Alex Rins Pecahkan Rekor Di Sprint Race Moto Gp Inggris Saksikan Di Trans7
May 26, 2025
Alex Rins Pecahkan Rekor Di Sprint Race Moto Gp Inggris Saksikan Di Trans7
May 26, 2025 -
 Transformation Des Anciens Locaux Rtbf Au Palais Des Congres De Liege
May 26, 2025
Transformation Des Anciens Locaux Rtbf Au Palais Des Congres De Liege
May 26, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Ipswich Town Player Performances Mc Kenna Shines Phillips And Cajuste Struggle
May 28, 2025
Ipswich Town Player Performances Mc Kenna Shines Phillips And Cajuste Struggle
May 28, 2025 -
 Mc Kenna Impresses Tuanzebe Positive Ipswich Towns Week In Review
May 28, 2025
Mc Kenna Impresses Tuanzebe Positive Ipswich Towns Week In Review
May 28, 2025 -
 Indiana Pacers Vs Chicago Bulls Game Time Tv Coverage And Streaming Details March 10
May 28, 2025
Indiana Pacers Vs Chicago Bulls Game Time Tv Coverage And Streaming Details March 10
May 28, 2025 -
 Pacers Vs Bulls March 10th How To Watch The Game Live
May 28, 2025
Pacers Vs Bulls March 10th How To Watch The Game Live
May 28, 2025 -
 Leeds United Eye Phillips Reunion Transfer Window Update
May 28, 2025
Leeds United Eye Phillips Reunion Transfer Window Update
May 28, 2025
