The New Workplace Reality: Are Workers Truly Replaceable?
Table of Contents
The Rise of Automation and AI in the Workplace
The integration of automation and AI is rapidly transforming industries worldwide. This technological shift is impacting job roles and requiring adaptations across the workforce.
Impact on Specific Industries
- Manufacturing: Robots and automated systems are increasingly prevalent on factory floors, handling repetitive tasks like assembly and packaging. This has led to job displacement in some areas, with estimates suggesting millions of manufacturing jobs have been affected globally.
- Customer Service: Chatbots and AI-powered virtual assistants are handling an increasing number of customer inquiries, leading to a reduction in the need for human customer service representatives in certain roles.
- Data Entry: Automation tools and machine learning algorithms are automating data entry tasks, significantly reducing the need for manual data input.
Keyword Integration: automation, AI, robotics, job displacement, automated systems, machine learning
The Changing Skillset Requirements
The rise of automation necessitates a shift in the skills demanded by employers. The "future-proof skills" are no longer solely technical; they increasingly include human-centric abilities.
- Critical thinking and problem-solving: The ability to analyze complex situations and devise effective solutions remains irreplaceable.
- Creativity and innovation: Generating new ideas and approaches is a uniquely human skill, crucial for adaptation and progress in a changing environment.
- Emotional intelligence: Understanding and managing emotions, both one's own and others', is essential in collaborative settings and human-centric roles.
- Adaptability and continuous learning: The ability to acquire new skills and adapt to technological advancements is crucial for navigating the evolving job market.
- Technical skills to manage and work alongside automation: Proficiency in programming, data analysis, and AI-related technologies is growing in demand.
Keyword Integration: future-proof skills, in-demand skills, skill gap, technological advancements
Irreplaceable Human Skills and Qualities
While automation excels at repetitive tasks, several human skills remain irreplaceable.
The Role of Creativity and Innovation
Many professions hinge on uniquely human abilities.
- Design: Architects, graphic designers, and product designers rely on creativity and aesthetic judgment, skills difficult for AI to replicate fully.
- Marketing and Advertising: Developing creative campaigns that resonate with target audiences requires an understanding of human psychology and emotional responses.
- Artistic Roles: Musicians, writers, and visual artists create original works that reflect human experience and imagination. AI can assist, but true artistic expression remains firmly in the human domain.
Keyword Integration: creativity, innovation, critical thinking, problem-solving, artistic expression
The Importance of Emotional Intelligence and Human Interaction
Numerous sectors rely heavily on human connection and empathy.
- Healthcare: Nurses, doctors, and therapists require emotional intelligence to build rapport with patients and provide sensitive care.
- Education: Teachers need empathy and interpersonal skills to connect with students and foster learning.
- Social Work: Social workers rely on emotional intelligence to understand and address the complex needs of vulnerable populations.
- Customer-facing Roles: Building trust and rapport with customers requires human connection and understanding, which AI struggles to replicate effectively.
Keyword Integration: emotional intelligence, human interaction, empathy, customer relations, human connection
Adaptability and Continuous Learning
The capacity to learn and adapt is a defining human trait.
- Lifelong learning: Embracing continuous learning is vital for staying relevant in a rapidly changing job market.
- Upskilling and reskilling initiatives: Actively seeking opportunities to develop new skills is crucial for career progression and adaptation.
- Adaptability: The willingness and ability to embrace change and learn new technologies are essential for success in the future of work.
Keyword Integration: lifelong learning, upskilling, reskilling, adaptability, career progression
The Future of Work: Collaboration Between Humans and Machines
The future of work is not about humans versus machines, but rather humans and machines working together.
Augmentation, Not Replacement
Technology's role is increasingly to augment human capabilities, not replace them.
- Human-machine collaboration: AI and automation can handle routine tasks, freeing human workers to focus on higher-level cognitive functions.
- Automation assistance: Automation tools can significantly increase efficiency and productivity, supporting human workers in their tasks.
- Productivity gains: By automating tedious tasks, technology allows human workers to be more efficient and productive.
Keyword Integration: human-machine collaboration, automation assistance, increased efficiency, productivity gains
The Evolving Job Market
Technological advancements are creating new job roles and transforming existing ones.
- Future job market: New roles in AI development, data science, and cybersecurity are emerging, requiring specialized skills.
- Emerging roles: Jobs requiring both technical expertise and strong interpersonal skills will be highly sought after.
- Job evolution: Many traditional roles are being redefined to incorporate technological tools and processes.
Keyword Integration: future job market, emerging roles, technological advancements, job evolution, future job trends
Conclusion: The Enduring Value of Human Workers
While automation and AI are undeniably transforming the workplace, this analysis demonstrates that human skills and qualities remain essential. Complete worker replacement is unlikely in many sectors. Adaptability and continuous learning are paramount in navigating this evolving landscape. Embrace the future of work and ensure you are not easily replaceable by actively developing in-demand skills and embracing lifelong learning. Are workers truly replaceable? The answer is nuanced, but human ingenuity will continue to be essential.

Featured Posts
-
 Hannover 96 Abstiegskampf Drohkulisse Und Fehlendes Derby Analyse Der Stimmung
May 13, 2025
Hannover 96 Abstiegskampf Drohkulisse Und Fehlendes Derby Analyse Der Stimmung
May 13, 2025 -
 Avengers Doomsday Could Ian Mc Kellens Casting Improve Scarlet Witch And Quicksilvers Origin Story
May 13, 2025
Avengers Doomsday Could Ian Mc Kellens Casting Improve Scarlet Witch And Quicksilvers Origin Story
May 13, 2025 -
 Ftc V Meta A Deep Dive Into The Antitrust Case
May 13, 2025
Ftc V Meta A Deep Dive Into The Antitrust Case
May 13, 2025 -
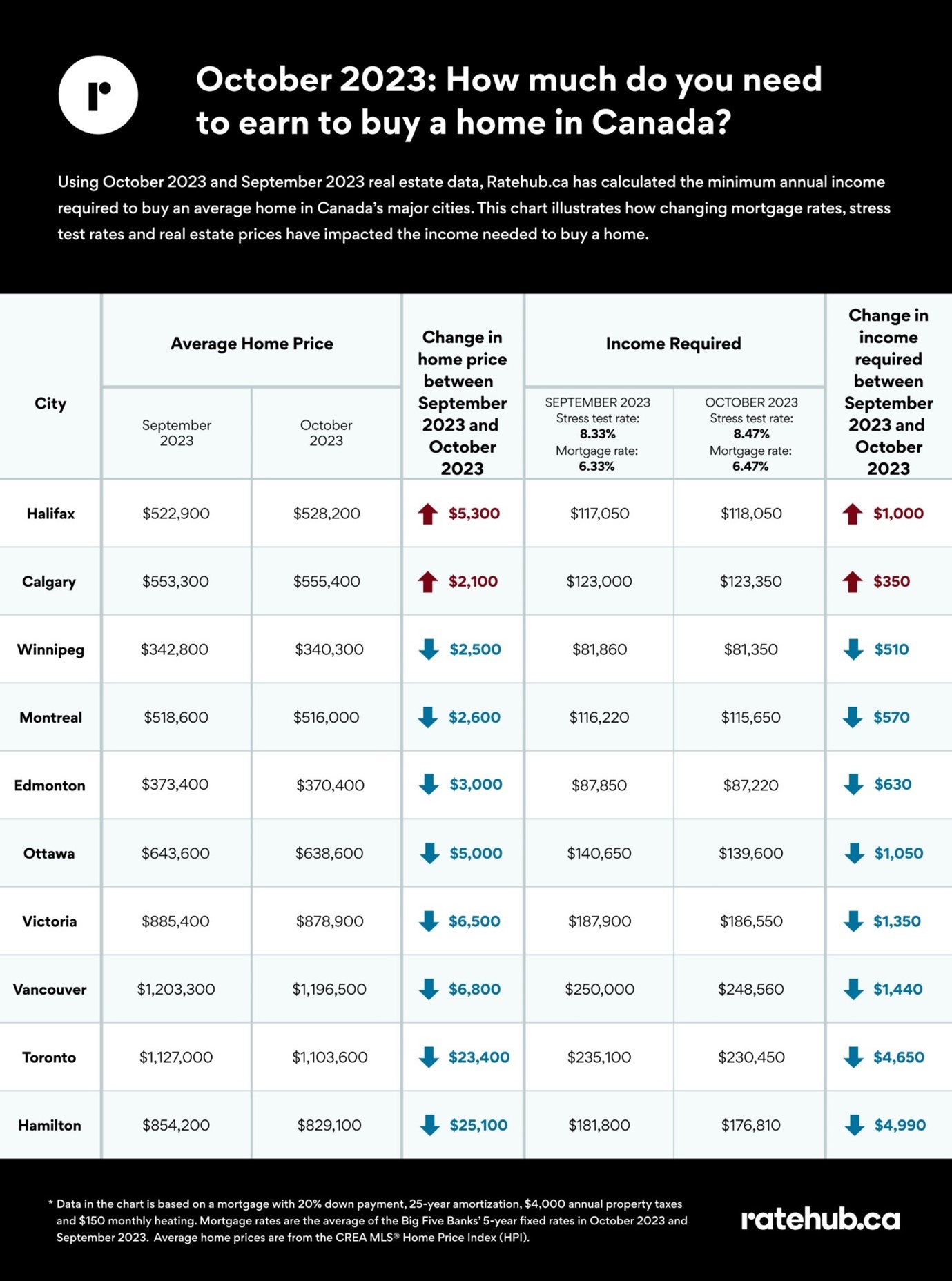 The Potential Of Low Mortgage Rates To Revitalize Canadas Housing Sector
May 13, 2025
The Potential Of Low Mortgage Rates To Revitalize Canadas Housing Sector
May 13, 2025 -
 Ali Larter Opens Up Why Her Relationship With Billy Bob Thornton Works
May 13, 2025
Ali Larter Opens Up Why Her Relationship With Billy Bob Thornton Works
May 13, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Recall Alert Walmarts Tortilla Chips And Jewelry Kits Recalled
May 14, 2025
Recall Alert Walmarts Tortilla Chips And Jewelry Kits Recalled
May 14, 2025 -
 Nationwide Recall Walmarts Action On Unsafe Baby Products
May 14, 2025
Nationwide Recall Walmarts Action On Unsafe Baby Products
May 14, 2025 -
 Consumer Alert Walmart Recalls Tortilla Chips And Jewelry Kits
May 14, 2025
Consumer Alert Walmart Recalls Tortilla Chips And Jewelry Kits
May 14, 2025 -
 Important Recall Notice Walmarts Tortilla Chips And Jewelry Kits
May 14, 2025
Important Recall Notice Walmarts Tortilla Chips And Jewelry Kits
May 14, 2025 -
 Walmart Recall Affects Baby Products Check Your Dresser
May 14, 2025
Walmart Recall Affects Baby Products Check Your Dresser
May 14, 2025
