The Ongoing Threat Of Measles: Factors Contributing To Persistence
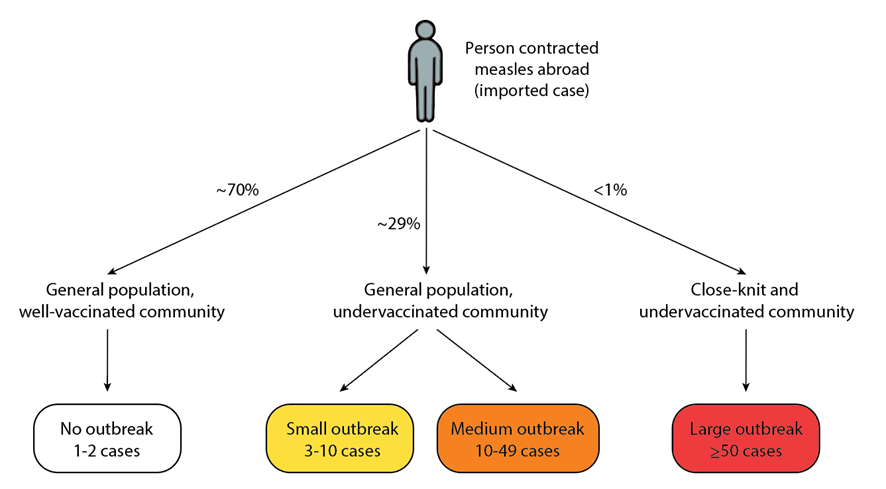
Table of Contents
Vaccine Hesitancy and Misinformation
The spread of misinformation surrounding vaccines is a major driver of measles persistence. This hesitancy, fueled by a distrust of vaccines, directly impacts vaccination rates and leaves populations vulnerable to outbreaks.
The Role of Social Media and Anti-vaccine Movements
The accessibility of unverified information, particularly on social media platforms, has amplified the spread of misinformation about vaccines. This includes:
- Increased accessibility to unverified information: Social media algorithms often prioritize engagement over accuracy, leading to the rapid dissemination of false claims.
- Spread of conspiracy theories and false claims about vaccine side effects: Anti-vaccine movements actively promote unsubstantiated narratives linking vaccines to autism and other health problems.
- Difficulty in combating misinformation effectively: The speed and reach of misinformation make it challenging for public health authorities to correct false narratives and build trust. The sheer volume of misinformation can overwhelm fact-checking efforts.
Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy through Public Health Campaigns
Effective communication is vital to counteract vaccine misinformation and restore public confidence. This involves:
- Targeted campaigns addressing specific concerns: Public health campaigns must tailor their messaging to address the specific anxieties and misconceptions within different communities.
- Utilizing credible sources and healthcare professionals: Messages should come from trusted sources like doctors, nurses, and established medical institutions, fostering credibility and building trust.
- Promoting transparent communication about vaccine safety and efficacy: Open communication about potential side effects (which are generally mild and temporary) alongside clear explanations of the benefits of vaccination is crucial. Transparency builds trust.
Gaps in Vaccination Coverage and Access
Uneven access to vaccines contributes significantly to measles persistence. This disparity in vaccination coverage leaves certain populations at higher risk.
Challenges in Reaching Remote and Underserved Populations
Geographic barriers and socioeconomic disparities limit vaccine access in many regions, resulting in pockets of low vaccination rates:
- Logistical challenges in vaccine delivery to remote areas: Reaching remote communities often requires specialized transportation and infrastructure, which can be costly and challenging.
- Limited access to healthcare facilities for marginalized communities: Poverty, lack of transportation, and discrimination can prevent individuals from accessing vaccination services.
- Insufficient resources for vaccination campaigns in developing countries: Developing nations often lack the financial and human resources to implement widespread vaccination campaigns effectively.
Importance of Universal Vaccination Programs
Sustained efforts to ensure high vaccination coverage globally are essential to curb measles persistence. This necessitates:
- Investing in vaccine supply chains and infrastructure: Robust cold chain infrastructure is essential to ensure vaccine stability and efficacy during transportation and storage.
- Implementing strategies for community engagement and outreach: Effective community engagement builds trust and encourages participation in vaccination programs.
- Collaboration between governments, international organizations, and NGOs: A coordinated global effort is required to overcome the challenges of achieving universal vaccination.
The Impact of Global Travel and Migration
Globalization facilitates the rapid international spread of measles, impacting even areas with high vaccination rates.
Ease of International Travel and Disease Spread
The ease of international travel increases the risk of measles importation into areas with high levels of immunity:
- Increased risk of importation of measles into areas with low immunity: Travelers infected with measles can unknowingly introduce the virus to susceptible populations.
- Challenges in tracking and containing outbreaks effectively: Rapid international travel makes it difficult to track and contain outbreaks before they spread widely.
- Importance of robust surveillance systems and travel advisories: Effective surveillance and travel advisories can help to prevent the introduction and spread of measles.
The Role of Immigration and Refugee Populations
Displaced populations are often at increased risk of measles due to limited access to healthcare:
- Need for targeted vaccination programs for refugee and migrant groups: These programs need to account for language barriers, cultural sensitivities, and logistical challenges.
- Addressing language and cultural barriers to access healthcare: Vaccination campaigns must be culturally sensitive and utilize appropriate language and communication strategies.
- Ensuring equitable access to healthcare for all populations: Access to healthcare should be a universal right, regardless of immigration status or socioeconomic background.
The Emergence of Measles Variants
The measles virus continuously evolves, creating the potential for vaccine-resistant strains, furthering measles persistence.
Evolution of the Measles Virus and Vaccine Escape Mutants
The ongoing evolution of the measles virus poses a significant challenge to global eradication efforts:
- Continuous monitoring of the virus's genetic makeup: Genomic surveillance is vital for identifying new variants and potential vaccine escape mutants.
- Developing strategies to address vaccine escape mutants: Research and development of new vaccines or vaccine strategies are needed to address the potential threat of resistant strains.
- Researching new vaccine approaches for broader protection: Continued research into novel vaccine approaches may be necessary to maintain high levels of population immunity.
Conclusion
The persistence of measles is a complex issue with multifaceted contributing factors. Addressing measles persistence requires a comprehensive strategy encompassing improved vaccination campaigns, effective communication to counter misinformation, increased access to healthcare, particularly for vulnerable populations, and robust global surveillance systems. Continued efforts to increase global measles vaccination coverage and address the social and logistical barriers to immunization are crucial for protecting communities worldwide. Only through concerted action and collaborative strategies can we hope to eliminate the ongoing threat of measles persistence and safeguard public health. Let's work together to achieve global measles eradication.

Featured Posts
-
 Broadcoms Proposed V Mware Price Hike At And T Reports A 1050 Jump
May 30, 2025
Broadcoms Proposed V Mware Price Hike At And T Reports A 1050 Jump
May 30, 2025 -
 Rolex Monte Carlo Masters 2025 Alcaraz And Musetti Final Showdown
May 30, 2025
Rolex Monte Carlo Masters 2025 Alcaraz And Musetti Final Showdown
May 30, 2025 -
 Reduced Excessive Heat Warnings Analyzing The Recent Trend
May 30, 2025
Reduced Excessive Heat Warnings Analyzing The Recent Trend
May 30, 2025 -
 The Polish Election Runoff Implications For The Future Of Maga Populism
May 30, 2025
The Polish Election Runoff Implications For The Future Of Maga Populism
May 30, 2025 -
 Bath And West Show Half Term Your Guide To Thrill Rides And Family Fun
May 30, 2025
Bath And West Show Half Term Your Guide To Thrill Rides And Family Fun
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Alcaraz Through To Barcelona Open Round Of 16 Following Ruud
May 31, 2025
Alcaraz Through To Barcelona Open Round Of 16 Following Ruud
May 31, 2025 -
 Racial Abuse Case Beautician Receives No Jail Time
May 31, 2025
Racial Abuse Case Beautician Receives No Jail Time
May 31, 2025 -
 Musks Dogecoin Support No Regrets Over Trump Administration Involvement
May 31, 2025
Musks Dogecoin Support No Regrets Over Trump Administration Involvement
May 31, 2025 -
 Elon Musks Cost Cutting 101 Million In Dei Spending And 8 Million On Transgender Mice Eliminated
May 31, 2025
Elon Musks Cost Cutting 101 Million In Dei Spending And 8 Million On Transgender Mice Eliminated
May 31, 2025 -
 Elon Musks Pressure Campaign Did Trumps Team Block An Open Ai Uae Deal
May 31, 2025
Elon Musks Pressure Campaign Did Trumps Team Block An Open Ai Uae Deal
May 31, 2025
