The Rising Tide Of Forest Loss: Wildfires And The Global Environmental Impact
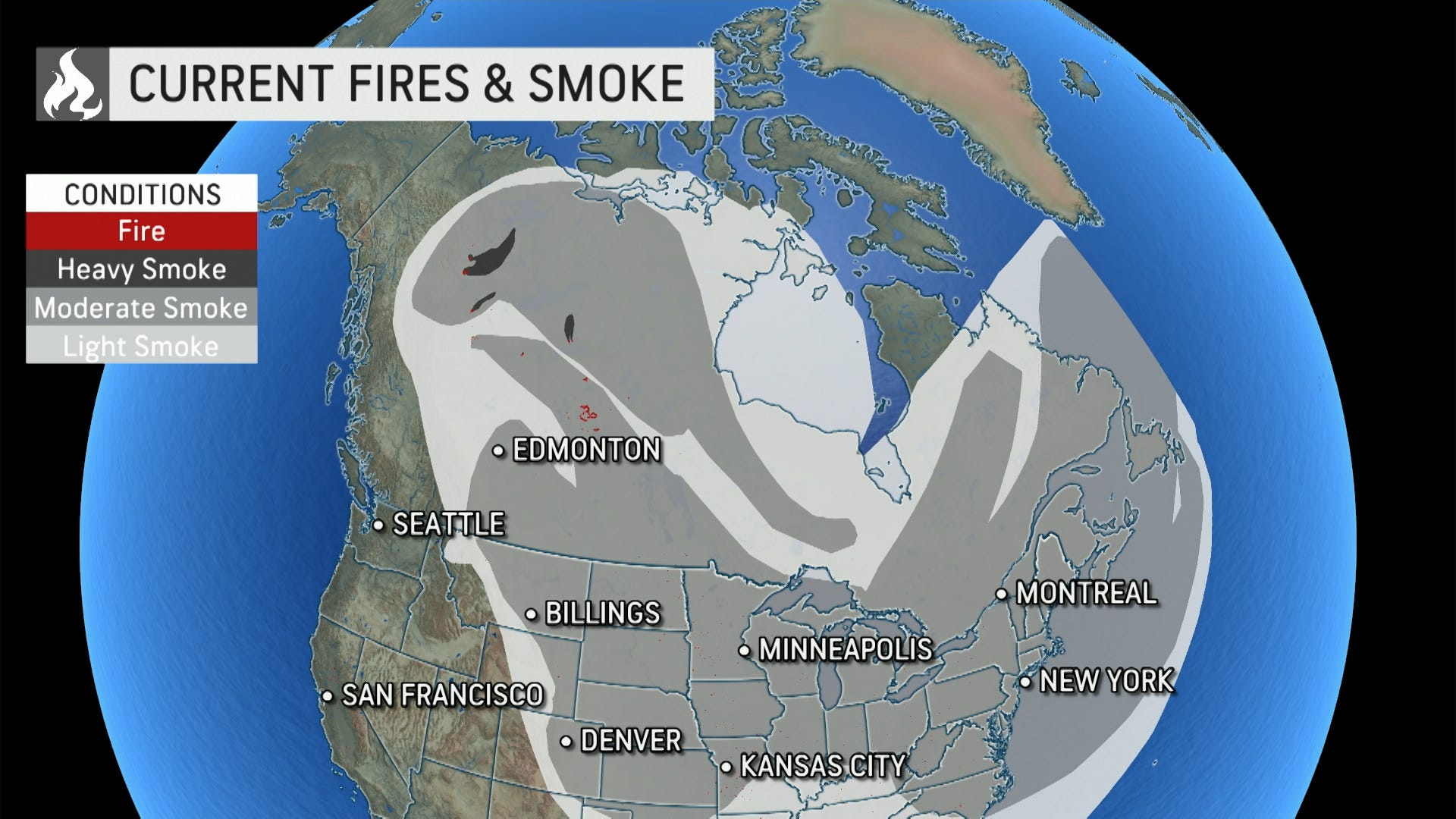
Table of Contents
The Increasing Frequency and Intensity of Wildfires
The dramatic increase in wildfire activity globally is undeniable. Larger, more intense, and longer-lasting fires are becoming the norm, leaving behind scarred landscapes and devastating consequences.
Climate Change as a Key Driver
Climate change is a primary driver of this alarming trend. Rising global temperatures lead to drier conditions, creating a tinderbox effect in forests worldwide. This increased aridity extends fire seasons, making forests more susceptible to ignition and rapid fire spread.
- Increased drought frequency: Longer and more severe droughts desiccate vegetation, turning forests into highly flammable fuel.
- Longer fire seasons: Warmer temperatures delay the onset of autumn rains, prolonging the period of high fire risk.
- Higher wind speeds: Climate change is linked to more intense and unpredictable weather patterns, including stronger winds that rapidly spread wildfires.
Data from the Global Forest Watch reveals a significant increase in global burned area over the past decades, highlighting the urgent need for action.
Human Activities Exacerbating the Problem
While climate change plays a significant role, human activities are significantly exacerbating the problem. Unsustainable practices and negligence are creating conditions that fuel larger and more destructive wildfires.
- Illegal logging: Removal of trees reduces forest density and creates more readily combustible fuel loads.
- Agricultural expansion: Clearing forests for agriculture and livestock grazing leaves behind dry, flammable underbrush.
- Urbanization encroaching on forests: Expanding human settlements increase the risk of human-caused ignitions near wildland-urban interfaces.
- Discarded cigarettes: A seemingly small act of negligence can have catastrophic consequences.
Regions like the Amazon rainforest, the boreal forests of Canada and Russia, and Australia's eucalyptus forests have experienced devastating wildfires in recent years, underscoring the global scale of this crisis.
The Environmental Consequences of Forest Loss
The consequences of widespread forest loss due to wildfires extend far beyond the immediate destruction. The ripple effects impact global ecosystems, climate stability, and human communities.
Biodiversity Loss
Wildfires decimate habitats, leading to a significant loss of biodiversity. The rapid destruction of ecosystems forces many plant and animal species into extinction or pushes them to the brink.
- Loss of plant and animal life: Countless species are lost in the immediate aftermath of wildfires, often before scientists even have a chance to understand their roles within their ecosystems.
- Disruption of ecological balance: The loss of key species creates cascading effects throughout the food web, with long-term consequences for the entire ecosystem's health.
Numerous endangered species, including the koala in Australia and various rainforest birds, are particularly vulnerable to habitat loss from wildfires.
Carbon Emissions and Climate Change
Forests act as vital carbon sinks, absorbing significant amounts of atmospheric carbon dioxide. Wildfires release this stored carbon back into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change.
- Increased greenhouse gas emissions: Burning forests releases massive amounts of CO2, methane, and other greenhouse gases, contributing significantly to global warming.
- Positive feedback loop exacerbating climate change: The increase in greenhouse gases leads to more intense warming, which in turn leads to more frequent and intense wildfires, creating a vicious cycle.
Studies show that wildfires contribute significantly to annual global carbon emissions, further highlighting their devastating impact on climate stability.
Soil Degradation and Water Cycle Disruption
Wildfires severely impact soil health and water resources. The intense heat destroys the organic matter in the soil, reducing its fertility and increasing the risk of erosion.
- Erosion: Loss of vegetation leaves the soil exposed to the elements, leading to significant topsoil loss.
- Loss of topsoil fertility: The destruction of organic matter reduces the soil's ability to support plant life, hindering forest regeneration.
- Altered water runoff patterns: The loss of vegetation alters the water cycle, leading to increased runoff and a greater risk of flooding.
Communities dependent on forest resources for clean water are particularly vulnerable to the impact of wildfires on water quality and availability.
Mitigation and Conservation Strategies
Combating the rising tide of forest loss requires a multifaceted approach, combining improved forest management practices, climate change mitigation, and enhanced community engagement.
Improved Forest Management Practices
Sustainable forestry practices are crucial in reducing the risk of wildfires. This includes careful planning and execution of controlled burns to reduce fuel loads and minimize the intensity of future fires.
- Preventative measures: Regular forest thinning, creation of firebreaks, and the removal of dead or diseased trees can significantly reduce the risk of large-scale wildfires.
- Early detection systems: Investing in advanced monitoring technologies, such as satellite imagery and sensor networks, allows for early detection and rapid response to wildfires.
Successful examples from countries with robust forest management programs demonstrate the effectiveness of these strategies.
Climate Change Mitigation
Addressing the root cause of increased wildfire frequency — climate change — is paramount. Global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions are crucial in creating a less fire-prone future.
- Transition to renewable energy: Shifting away from fossil fuels is critical in reducing carbon emissions and mitigating climate change.
- Carbon capture technologies: Developing and deploying technologies that capture and store CO2 from the atmosphere can help reduce the concentration of greenhouse gases.
- International cooperation: International agreements and collaborative efforts are necessary to address the global challenge of climate change.
Individual actions, such as reducing carbon footprints and advocating for sustainable policies, also play a vital role.
Community Engagement and Education
Raising public awareness and engaging local communities in fire prevention is essential. Education programs can empower individuals to make informed decisions and participate in wildfire mitigation efforts.
- Education campaigns: Public awareness campaigns can educate people about the risks of wildfires and the importance of responsible behavior in fire-prone areas.
- Fire safety guidelines: Clear guidelines and regulations can help prevent human-caused ignitions.
- Early warning systems: Effective warning systems, combined with community evacuation plans, can save lives and minimize property damage.
Indigenous communities, with their vast knowledge of traditional land management practices, play a vital role in developing and implementing effective fire prevention strategies.
Conclusion
The rising tide of forest loss due to wildfires presents a significant threat to global environmental stability. The interconnectedness of climate change, unsustainable practices, and devastating wildfires underscores the urgency of comprehensive action. We must implement improved forest management techniques, aggressively mitigate climate change, and foster strong community engagement. The consequences of inaction are too severe to ignore. By understanding the challenges and embracing proactive solutions, we can collectively work towards a future where our forests thrive. Learn more about protecting our forests and join the fight against forest loss today!

Featured Posts
-
 Abn Amro Financiert Innovatief Digitaal Platform Transferz Details Van De Investering
May 22, 2025
Abn Amro Financiert Innovatief Digitaal Platform Transferz Details Van De Investering
May 22, 2025 -
 Councillors Wifes Jail Sentence For Hotel Fire Tweet Appeal Awaits
May 22, 2025
Councillors Wifes Jail Sentence For Hotel Fire Tweet Appeal Awaits
May 22, 2025 -
 Chi Sprostit Vidmova Ukrayini U Vstupi Do Nato Plani Rosiyi Schodo Podalshoyi Agresiyi
May 22, 2025
Chi Sprostit Vidmova Ukrayini U Vstupi Do Nato Plani Rosiyi Schodo Podalshoyi Agresiyi
May 22, 2025 -
 Ea Fc 24 Fut Birthday Top Tier Cards And Team Building Guide
May 22, 2025
Ea Fc 24 Fut Birthday Top Tier Cards And Team Building Guide
May 22, 2025 -
 Wealth Transfer And Succession Planning Challenges And Strategies For High Net Worth Families
May 22, 2025
Wealth Transfer And Succession Planning Challenges And Strategies For High Net Worth Families
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Nato Ta Ukrayina Riziki Vidmovi Vid Chlenstva Za Otsinkoyu Yevrokomisiyi
May 22, 2025
Nato Ta Ukrayina Riziki Vidmovi Vid Chlenstva Za Otsinkoyu Yevrokomisiyi
May 22, 2025 -
 Tuerkiye Ve Italya Nin Ortak Nato Goerevi Planin Ayrintilari
May 22, 2025
Tuerkiye Ve Italya Nin Ortak Nato Goerevi Planin Ayrintilari
May 22, 2025 -
 Kaliningrad Pod Ugrozoy Patrushev O Planakh Nato I Reaktsii Rossii
May 22, 2025
Kaliningrad Pod Ugrozoy Patrushev O Planakh Nato I Reaktsii Rossii
May 22, 2025 -
 Chi Zagrozhuye Ukrayini Vidmova Vid Nato Analiz Yevrokomisara
May 22, 2025
Chi Zagrozhuye Ukrayini Vidmova Vid Nato Analiz Yevrokomisara
May 22, 2025 -
 Zayavlenie Patrusheva Nato Planiruet Zakhvatit Kaliningrad Analiz Situatsii
May 22, 2025
Zayavlenie Patrusheva Nato Planiruet Zakhvatit Kaliningrad Analiz Situatsii
May 22, 2025
