The Rosy Apple Aphid: A Major Threat To Apple Harvests This Year
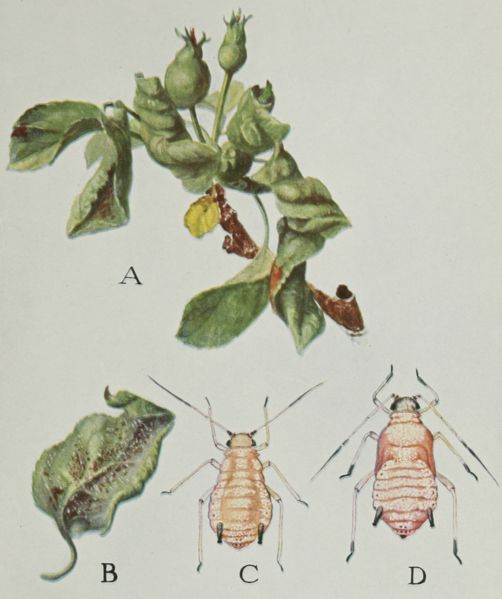
Table of Contents
Identifying the Rosy Apple Aphid Infestation
Early detection is key to effective rosy apple aphid control. Recognizing the signs of an infestation is the first step in protecting your apple trees.
Recognizing the Signs:
A rosy apple aphid infestation manifests in several ways:
- Leaf curling and distortion: Aphids feed on the sap of young leaves, causing them to curl, distort, and develop a reddish or purplish hue. This curling provides the aphids with protection from predators and pesticides.
- Presence of aphids on leaves and shoots: Close inspection of young leaves and shoots will reveal clusters of small, pinkish-gray aphids. These aphids are often found on the undersides of leaves.
- Honeydew excretion leading to sooty mold growth: Aphids excrete a sticky substance called honeydew. This honeydew provides a breeding ground for sooty mold, a black, unsightly fungus that can further damage the leaves and reduce photosynthesis.
- Stunting of new growth and reduced fruit size: Severe infestations can lead to stunted growth of new shoots and significantly smaller, misshapen fruit. This directly impacts the yield and quality of your apple harvest.
[Insert images/illustrations here showing characteristic rosy apple aphid damage, leaf curling, honeydew, and sooty mold.]
Life Cycle and Spread:
Understanding the rosy apple aphid's life cycle is essential for effective control. The lifecycle involves eggs, nymphs, and adult aphids.
- Overwintering: Rosy apple aphids overwinter as eggs laid on the bark of apple trees, typically in crevices and around buds.
- Spring Emergence: In spring, these eggs hatch into nymphs, which begin feeding and rapidly reproducing.
- Rapid Reproduction: Rosy apple aphids reproduce asexually throughout the growing season, leading to exponential population growth.
- Spread: Aphids spread primarily through wind currents and by the movement of infested planting material. They can also be carried by birds or other insects.
- Secondary Infestations: The high reproductive rate increases the potential for secondary infestations to spread quickly throughout the orchard.
The Impact of Rosy Apple Aphid on Apple Production
The rosy apple aphid's impact extends beyond just cosmetic damage; it significantly affects both the quantity and quality of your apple harvest.
Reduced Yield and Fruit Quality:
- Smaller, misshapen fruit: Aphid feeding directly impacts fruit development, resulting in smaller, misshapen apples with reduced market value.
- Reduced sugar content: The sap loss caused by aphid feeding can lead to a decrease in the sugar content of the apples, impacting their flavor and overall quality.
- Economic consequences: Reduced yield and fruit quality translate directly into lower profits for apple growers. Studies have shown significant yield losses of up to 50% in severely infested orchards. [Insert data or statistics on potential yield losses here, citing sources.]
Long-Term Effects on Apple Trees:
The damage caused by rosy apple aphids is not limited to a single season.
- Weakened trees: Infested trees become weaker and more vulnerable to other diseases and pests, further compromising their health and productivity.
- Tree dieback: In severe cases, persistent heavy infestations can lead to tree dieback, resulting in the loss of entire trees.
- Impact on orchard health: The cumulative effect of repeated infestations weakens the overall health and longevity of the orchard, significantly affecting long-term yields.
Effective Control Measures for Rosy Apple Aphid
Effective rosy apple aphid control requires a multi-pronged approach that utilizes integrated pest management (IPM) strategies.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Strategies:
IPM emphasizes a holistic approach, combining various methods to minimize pest populations while preserving the environment and orchard health.
- Monitoring: Regular monitoring of aphid populations is crucial for early detection and timely intervention.
- Biological control: Introducing natural predators like ladybugs, lacewings, and syrphid flies can significantly reduce aphid numbers.
- Cultural control: Practices like proper pruning, sanitation (removing infested leaves and branches), and maintaining orchard hygiene help prevent aphid buildup.
- Chemical control: Chemical pesticides should be used only as a last resort and only after careful consideration. Choose products specifically targeted at aphids, follow label instructions precisely, and consider the impact on beneficial insects.
Natural Predators and Beneficial Insects:
Encouraging natural predators is a crucial component of IPM.
- Attracting beneficial insects: Planting flowering plants that attract beneficial insects, such as wildflowers and herbs, can help increase their populations in your orchard.
- Protecting beneficial insects: Avoid using broad-spectrum insecticides that could harm beneficial insects along with aphids.
- Examples of natural predators: Ladybugs, lacewings, hoverflies (syrphid flies), and parasitic wasps are all effective natural predators of aphids.
Conclusion
The rosy apple aphid poses a serious threat to apple harvests this year. Understanding its life cycle, recognizing the signs of infestation, and implementing effective control measures—particularly through integrated pest management strategies—are vital for protecting apple orchards and ensuring a successful harvest. Don't let the rosy apple aphid ruin your yield; take proactive steps to protect your apple trees today. Learn more about effective rosy apple aphid control methods and protect your apple harvest. Consult with local agricultural extension services for region-specific advice and recommendations for managing this significant apple pest.

Featured Posts
-
 Conoce A Los Aspirantes A Diputados De Nueva Corriente Plataforma Y Propuestas
May 19, 2025
Conoce A Los Aspirantes A Diputados De Nueva Corriente Plataforma Y Propuestas
May 19, 2025 -
 Gilbert Burns Ko D By Morales At Ufc Vegas 106 Fight Result And Analysis
May 19, 2025
Gilbert Burns Ko D By Morales At Ufc Vegas 106 Fight Result And Analysis
May 19, 2025 -
 Syntrivi Enatenisis Proliptika Metra Kai Lyseis
May 19, 2025
Syntrivi Enatenisis Proliptika Metra Kai Lyseis
May 19, 2025 -
 Uber One Kenya Enjoy Exclusive Deals And Free Rides
May 19, 2025
Uber One Kenya Enjoy Exclusive Deals And Free Rides
May 19, 2025 -
 Iran Issues Death Sentences In Connection With Mosque Attacks
May 19, 2025
Iran Issues Death Sentences In Connection With Mosque Attacks
May 19, 2025
