U.S. Federal Reserve Holds Steady: Inflation And Economic Pressures
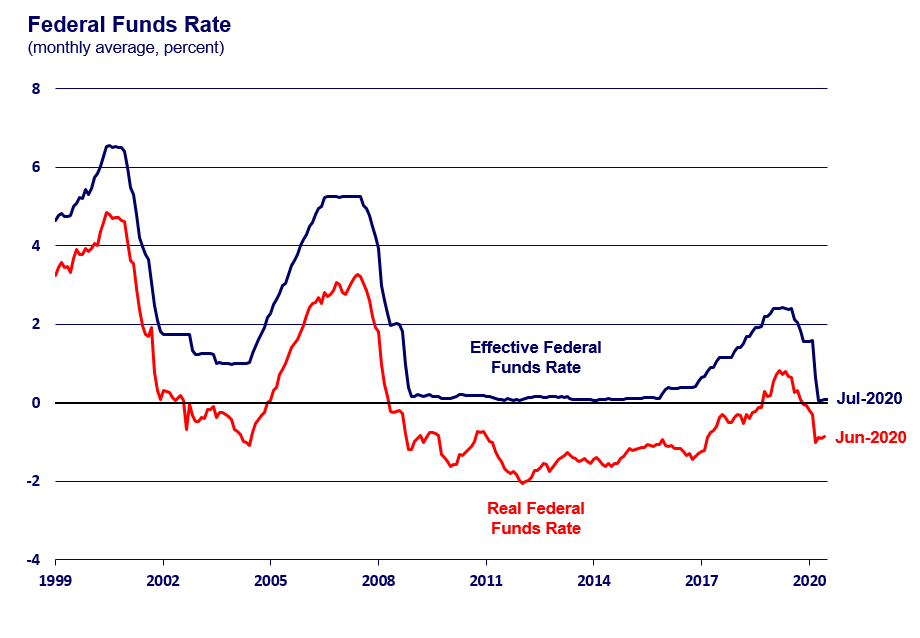
Table of Contents
Inflationary Pressures Remain a Concern
Persistent inflation remains a primary concern for the Federal Reserve, forcing a delicate balancing act between controlling price increases and maintaining economic stability.
Persistent Inflation
The current inflation rate continues to deviate from the Fed's target of 2%. While recent data shows some moderation, inflationary pressures persist.
- CPI data: The Consumer Price Index (CPI) still reflects elevated prices across various goods and services.
- Core inflation: Even excluding volatile food and energy prices, core inflation remains stubbornly high, indicating underlying inflationary pressures within the economy.
- Impact of supply chain issues: Lingering supply chain disruptions continue to contribute to higher costs for businesses and consumers.
- Energy prices: Fluctuations in energy prices, particularly oil and gas, significantly impact overall inflation and complicate the Fed's policy decisions.
The persistence of inflation stems from a confluence of factors, including robust consumer demand, supply chain bottlenecks, and geopolitical instability. Understanding these root causes is crucial for predicting future inflationary trends and informing the Fed's monetary policy response.
Impact of Inflation on Consumers and Businesses
High inflation significantly impacts both consumers and businesses. Increased prices erode purchasing power, affecting household spending and consumer confidence.
- Decreased consumer confidence: As prices rise, consumers feel less secure about their financial well-being, leading to reduced spending.
- Rising borrowing costs: Higher interest rates, a tool the Fed uses to combat inflation, increase borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, potentially dampening investment and spending.
- Impact on investment decisions: Businesses face increased uncertainty when making investment decisions due to unpredictable inflation and potential economic slowdowns.
The ripple effects of inflation are felt across various sectors, from decreased consumer spending on discretionary items to reduced business investment and potential job losses. The Fed's challenge lies in mitigating these negative impacts while addressing underlying inflationary pressures.
Economic Growth Slowdown and Uncertainty
Alongside inflation concerns, the Fed is grappling with a potential economic slowdown and significant uncertainty.
GDP Growth and Forecasts
Recent GDP growth figures have shown mixed results, fueling concerns about a potential recession.
- Real GDP growth: While some quarters have shown positive growth, the pace has slowed considerably compared to previous years.
- Potential recession scenarios: Economists are divided on the probability and severity of a potential recession, with varying forecasts depending on the Fed's policy actions and other economic indicators.
- Impact of monetary policy: The Fed's monetary policy directly impacts economic growth. Higher interest rates, while aiming to curb inflation, can also slow down economic expansion.
Balancing economic growth with inflation control presents a significant challenge for the Fed. Maintaining economic expansion without exacerbating inflation requires a carefully calibrated approach.
Labor Market Dynamics
The labor market provides crucial insights into the overall health of the economy and its influence on inflation.
- Unemployment rate: The unemployment rate remains relatively low, indicating a tight labor market.
- Job creation: While job creation persists, the pace may be slowing, reflecting the broader economic slowdown.
- Wage inflation: Strong wage growth can contribute to inflationary pressures, as businesses pass increased labor costs onto consumers.
- Labor shortages: Many sectors are experiencing labor shortages, potentially contributing to upward pressure on wages.
The Fed closely monitors labor market dynamics to assess the inflationary impact of wage growth and potential bottlenecks. A tight labor market can fuel wage-price spirals, complicating the Fed's task of controlling inflation.
The Federal Reserve's Monetary Policy Strategy
The Fed's decision to hold U.S. Federal Reserve interest rates steady reflects a cautious and data-dependent approach.
Justification for Holding Rates Steady
The Fed's reasoning for maintaining current interest rates involves several key factors:
- Risk assessment: The Fed is carefully assessing the risks associated with further rate hikes, weighing the potential for slowing economic growth against the need to curb inflation.
- Inflation expectations: The Fed is monitoring inflation expectations to gauge whether current policies are effectively anchoring inflation expectations to its 2% target.
- Data dependency: The Fed emphasizes its commitment to a data-dependent approach, meaning that future policy decisions will hinge on incoming economic data and their implications.
- Potential for future rate hikes or cuts: The possibility of future rate hikes or cuts remains open, depending on the evolution of economic indicators and inflation trends.
The Fed’s communication strategy is designed to promote transparency and manage market expectations. Clear communication helps to avoid sharp market reactions to policy shifts.
Future Outlook for Interest Rates
Predicting the future path of U.S. Federal Reserve interest rates involves considering various scenarios:
- Possible scenarios: Future adjustments might involve further rate hikes, rate cuts, or maintaining current levels, depending on evolving economic conditions.
- Geopolitical events: Geopolitical instability and unforeseen global events can significantly impact economic growth and inflation, influencing the Fed's policy decisions.
The future direction of interest rates will depend heavily on incoming economic data, the evolution of inflation, and evolving geopolitical factors. Continuous monitoring is crucial for understanding potential shifts.
Conclusion
The U.S. Federal Reserve's decision to hold interest rates steady reflects a carefully considered response to persistent inflation and economic uncertainty. The Fed's strategy prioritizes balancing the need to curb inflation with the risks of hindering economic growth. The coming months will be crucial for observing how the current policy impacts inflation and economic growth, guiding future adjustments to U.S. Federal Reserve interest rates. Understanding the Fed's actions and their potential impact is essential for both businesses and individuals making informed financial decisions. Stay informed about the latest developments regarding U.S. Federal Reserve interest rates by closely following reputable financial news sources and analyzing key economic indicators.

Featured Posts
-
 Harry Styles On That Awful Snl Impression His Honest Reaction
May 09, 2025
Harry Styles On That Awful Snl Impression His Honest Reaction
May 09, 2025 -
 A First Look Inside The Transformed Queen Elizabeth 2 Cruise Ship
May 09, 2025
A First Look Inside The Transformed Queen Elizabeth 2 Cruise Ship
May 09, 2025 -
 Stiven King Mask I Tramp Prikhilniki Putina Ta Zradniki Ameriki
May 09, 2025
Stiven King Mask I Tramp Prikhilniki Putina Ta Zradniki Ameriki
May 09, 2025 -
 Ryujinx Shuts Down The Impact Of Nintendos Contact On Emulator Development
May 09, 2025
Ryujinx Shuts Down The Impact Of Nintendos Contact On Emulator Development
May 09, 2025 -
 Jan 6th Hearing Star Cassidy Hutchinson Announces Fall Memoir Release
May 09, 2025
Jan 6th Hearing Star Cassidy Hutchinson Announces Fall Memoir Release
May 09, 2025
