Understanding Stock Market Valuations: BofA's Insight For Investors
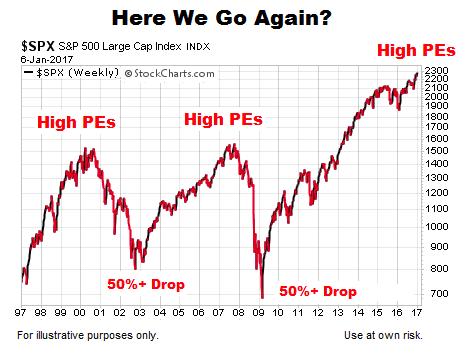
Table of Contents
Key Valuation Metrics Explained
Understanding how to value a company is crucial for any investor. Several key metrics can help determine if a stock is undervalued or overvalued. Let's delve into some of the most important ones:
Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E Ratio)
The Price-to-Earnings Ratio, or P/E ratio, is a fundamental valuation metric that compares a company's stock price to its earnings per share (EPS). It's calculated by dividing the market value per share by the earnings per share.
- High P/E ratios: Suggest investors expect higher growth in the future. A high P/E ratio often indicates that investors are willing to pay a premium for the company's expected future earnings. This is common with high-growth technology companies.
- Low P/E ratios: Might indicate undervalued stocks or potential risks. A low P/E ratio could suggest that the market has a negative outlook on the company's future earnings. However, it could also be a genuine undervaluation opportunity.
- Industry Benchmarks: Understanding industry benchmarks is crucial for accurate comparison. Comparing the P/E ratio of a company to its competitors within the same industry provides a more meaningful context. A high P/E ratio within a low-growth industry might be a red flag, while the same ratio in a high-growth sector might be justified.
Price-to-Book Ratio (P/B Ratio)
The Price-to-Book Ratio compares a company's market capitalization to its book value of equity. The book value is essentially the net asset value of a company, calculated as total assets minus total liabilities.
- Asset-Heavy Companies: The P/B ratio is particularly useful for valuing asset-heavy companies like banks or real estate firms, where the book value represents a significant portion of the company's overall value.
- Undervaluation or Problems?: Low P/B ratios may signal undervaluation, but could also indicate underlying problems. A low P/B ratio might suggest that the market is not confident in the company's ability to generate future earnings.
- Industry Comparison: Similar to P/E ratios, comparing P/B ratios within the same industry sector is essential for a fair evaluation. A low P/B ratio compared to peers could signify an undervaluation, while a high ratio might indicate overvaluation.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis is a more sophisticated and complex method. It projects a company's future cash flows and discounts them back to their present value, providing an estimate of the company's intrinsic value.
- Forecasting Challenges: DCF analysis requires forecasting future performance, which can be challenging and subjective. The accuracy of the valuation relies heavily on the accuracy of the projected cash flows.
- Time Value of Money: DCF analysis offers a more comprehensive valuation, considering the time value of money. A dollar received today is worth more than a dollar received in the future due to its potential earning capacity.
- BofA's Use of DCF: BofA analysts often utilize DCF models in their stock recommendations, incorporating their expertise and market insights to create more robust projections.
BofA's Approach to Stock Market Valuation
Bank of America's approach to stock market valuation is multifaceted and incorporates various factors beyond simple financial ratios.
Sector-Specific Analysis
BofA's research incorporates in-depth analysis of individual sectors, recognizing that different industries have unique valuation considerations.
- Industry-Specific Trends: Technology stocks, for example, might be valued differently than consumer staples, reflecting the vastly different growth trajectories and risk profiles of these sectors.
- Specialized Insights: BofA's sector specialists provide valuable insights into industry-specific trends, competitive dynamics, and regulatory changes that can significantly impact valuations.
Qualitative Factors
Beyond quantitative metrics, BofA considers qualitative factors that influence a company's value:
- Management Quality: Strong management teams, known for their strategic vision and execution capabilities, contribute to higher valuations.
- Competitive Landscape: Competitive pressures can impact future profitability and hence valuation. A company operating in a highly competitive market might have lower valuations than a company with a stronger competitive advantage.
- Regulatory Environment: Regulatory changes can significantly affect company performance and valuation. New regulations can create opportunities or impose restrictions, impacting future earnings.
Macroeconomic Considerations
BofA's valuation incorporates macroeconomic factors:
- Interest Rates: Rising interest rates generally impact valuations negatively, especially for companies with high debt levels.
- Inflation: Inflation can affect both revenue and expenses, impacting a company's profitability and, consequently, its valuation.
- Economic Growth: Economic growth forecasts are important for projecting future cash flows and overall market sentiment.
Practical Application for Investors
Understanding these valuation methods and incorporating BofA's insights translates to better investment decisions.
Diversification
Don't rely on a single valuation metric; use multiple approaches (P/E, P/B, DCF) to get a comprehensive picture of a company's worth. A diversified approach reduces reliance on any single indicator and mitigates risk.
Long-Term Perspective
Stock market valuations fluctuate; focus on long-term value creation rather than short-term gains. Market volatility is a natural occurrence, and a long-term perspective is crucial for weathering market downturns and achieving optimal returns.
Staying Informed
Regularly review BofA's research reports and other financial news to stay updated on market trends and valuation changes. Continuous learning and staying informed are vital for making sound investment choices in the dynamic world of stock markets.
Conclusion
Understanding stock market valuations is crucial for successful investing. By utilizing key metrics like P/E and P/B ratios, incorporating sophisticated methods such as DCF analysis, and considering BofA's insights on sector-specific analysis and macroeconomic factors, investors can make more informed decisions. Remember to diversify your portfolio, take a long-term perspective, and stay informed about market trends. Mastering stock market valuations, with the help of resources like BofA's research, can significantly enhance your investment strategy. Start improving your understanding of stock market valuations today!

Featured Posts
-
 Is It A Brotherhood Or A Rivalry Anton Mena On Vinicius Jr And Mbappe At Real Madrid
May 29, 2025
Is It A Brotherhood Or A Rivalry Anton Mena On Vinicius Jr And Mbappe At Real Madrid
May 29, 2025 -
 Elon Musks Space X Upcoming Starship Launch Date And Engine Test Details From Texas
May 29, 2025
Elon Musks Space X Upcoming Starship Launch Date And Engine Test Details From Texas
May 29, 2025 -
 Morgan Wallen 2025 Tour A Guide To Buying Tickets At The Best Prices
May 29, 2025
Morgan Wallen 2025 Tour A Guide To Buying Tickets At The Best Prices
May 29, 2025 -
 Man Doodgeschoten In Venlo Schietpartij
May 29, 2025
Man Doodgeschoten In Venlo Schietpartij
May 29, 2025 -
 Mark Pellingtons Lone Wolf A Conspiracy Thriller Concludes Production
May 29, 2025
Mark Pellingtons Lone Wolf A Conspiracy Thriller Concludes Production
May 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Good Life Defining And Achieving Your Personal Vision
May 31, 2025
The Good Life Defining And Achieving Your Personal Vision
May 31, 2025 -
 Designing The Good Life A Practical Guide
May 31, 2025
Designing The Good Life A Practical Guide
May 31, 2025 -
 Finding Your Good Life Practical Steps For Happiness And Fulfillment
May 31, 2025
Finding Your Good Life Practical Steps For Happiness And Fulfillment
May 31, 2025 -
 The Good Life Practical Tips For A More Fulfilling Existence
May 31, 2025
The Good Life Practical Tips For A More Fulfilling Existence
May 31, 2025 -
 Practical Steps To A Good Life Simple Strategies For Wellbeing
May 31, 2025
Practical Steps To A Good Life Simple Strategies For Wellbeing
May 31, 2025
