US Debt Ceiling: August Deadline Looms, Treasury Warns

Table of Contents
Understanding the US Debt Ceiling
The US debt ceiling, also known as the federal debt limit, is a statutory limit on the total amount of money the US government can borrow to meet its existing legal obligations. It's not a limit on spending; rather, it's a limit on the government's ability to finance its already-authorized spending. This limit is set by Congress and has been adjusted numerous times throughout history. The purpose, ostensibly, is to control government borrowing and spending. However, its frequent use and the political battles surrounding it have led to several near-defaults.
- Definition of the debt ceiling: A legal limit on the total amount of debt the US Treasury can hold.
- Historical instances of debt ceiling crises: The US has faced several debt ceiling crises in the past, leading to market volatility and uncertainty. These past crises have often been resolved at the last minute, increasing the risk of future defaults.
- The process of raising or suspending the debt ceiling: Congress must pass legislation to raise or suspend the debt ceiling. This requires a majority vote in both the House of Representatives and the Senate.
- The role of Congress and the Treasury Department: Congress sets the debt ceiling, while the Treasury Department manages the government's borrowing and debt.
The August Deadline and Potential Consequences
The Treasury Department's warnings about the August deadline are serious. They predict the possibility of the US defaulting on its debt obligations if the debt ceiling isn't raised or suspended before then. A US default would have catastrophic consequences, both domestically and internationally.
- Specific date of the projected deadline: While the exact date fluctuates depending on revenue and spending, August is currently cited as the critical timeframe where the Treasury Department’s extraordinary measures may be exhausted.
- Potential scenarios if the debt ceiling is not raised: A failure to raise the debt ceiling could result in the US government being unable to pay its bills, including Social Security benefits, military salaries, and interest on its debt.
- Impact on US credit rating: A default would severely damage the US's credit rating, leading to higher borrowing costs for the government and potentially triggering a global financial crisis.
- Potential market reactions and investor confidence: Global markets would likely react negatively to a US default, causing significant market volatility and potentially a global recession.
- Consequences for government programs and services: Essential government programs and services could be severely impacted or even shut down.
Political Wrangling and Potential Solutions
The political debate surrounding the debt ceiling is highly partisan. Republicans generally advocate for spending cuts and reduced government spending as a condition for raising the debt ceiling, while Democrats typically argue for raising the debt ceiling without conditions. Finding a bipartisan compromise appears increasingly difficult, adding to the urgency of the situation.
- Positions of Democrats and Republicans on the debt ceiling: Democrats generally favor raising the debt ceiling without attaching conditions, while Republicans often push for spending cuts in exchange.
- Potential compromise proposals: Negotiations may involve a combination of spending cuts and revenue increases, though reaching an agreement remains a significant challenge.
- Role of the White House and Congressional leadership: The White House and Congressional leadership are central in mediating the negotiations and finding a solution that can pass both chambers of Congress.
- Public opinion on the debt ceiling debate: Public opinion is divided, with varying levels of concern and understanding about the implications of a potential default.
The Role of Treasury's Extraordinary Measures
To buy time until Congress acts, the Treasury Department employs extraordinary measures – accounting maneuvers to temporarily manage cash flow. These measures, however, are not a long-term solution and have limitations.
- Explanation of the various extraordinary measures: These measures might include delaying certain payments or prioritizing certain obligations over others.
- Timeframe within which these measures can be effective: The effectiveness of these measures is limited, providing only a short-term buffer.
- Limits to these measures and the potential for exhaustion: Once these measures are exhausted, the US government may face a default on its obligations.
Conclusion
The August deadline for the US debt ceiling presents a critical juncture for the nation's economy and political stability. Failure to address this issue could trigger a catastrophic financial crisis, damaging the US's reputation and severely impacting its citizens and the global economy. The ongoing political wrangling underscores the urgent need for bipartisan compromise and a responsible solution to prevent a potential default. This is not simply a political debate; it's a matter of national and global economic security.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the ongoing US debt ceiling debate. Contact your elected officials and urge them to prioritize finding a responsible solution to avoid a devastating default. Understanding the implications of the US debt ceiling crisis is crucial for every citizen. Learn more and participate in shaping the future of US fiscal policy.

Featured Posts
-
 Trumps Legacy The Transgender Communitys Perspective
May 10, 2025
Trumps Legacy The Transgender Communitys Perspective
May 10, 2025 -
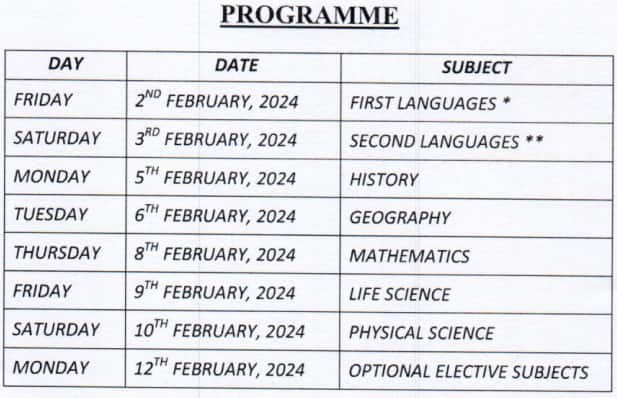 Madhyamik 2025 Merit List Date Time And Official Website
May 10, 2025
Madhyamik 2025 Merit List Date Time And Official Website
May 10, 2025 -
 Frantsiya I Polsha Makron I Tusk Podpishut Vazhniy Dogovor
May 10, 2025
Frantsiya I Polsha Makron I Tusk Podpishut Vazhniy Dogovor
May 10, 2025 -
 Tracking Elon Musks Net Worth Changes The Trump Presidencys Initial 100 Days
May 10, 2025
Tracking Elon Musks Net Worth Changes The Trump Presidencys Initial 100 Days
May 10, 2025 -
 Macron Confirms France And Poland To Sign Friendship Treaty
May 10, 2025
Macron Confirms France And Poland To Sign Friendship Treaty
May 10, 2025
