Wyoming Otter Management: A Pivotal Moment For Conservation

Table of Contents
The Current State of Otter Populations in Wyoming
Understanding the current state of otter populations is paramount for effective Wyoming otter management. While precise numbers are challenging to obtain, estimates suggest a fluctuating population distributed unevenly across the state. Otter presence is generally higher along major rivers and waterways with suitable habitat, but significant declines have been observed in certain areas. This uneven distribution underscores the need for targeted conservation strategies within specific regions.
Key threats jeopardizing Wyoming otter populations include:
- Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: Development, agricultural expansion, and dam construction significantly reduce available habitat, isolating otter populations and hindering gene flow.
- Water Pollution: Runoff from agricultural lands, industrial discharge, and other sources contaminate waterways, impacting water quality and harming otters directly through ingestion or skin contact. This is a serious concern for Wyoming otter management.
- Disease: Outbreaks of diseases like canine distemper virus can devastate local otter populations.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: Entanglements in fishing gear and road mortality contribute to otter mortality.
Specific data regarding population numbers and geographic distribution is currently limited due to the challenges of monitoring elusive wildlife. However, ongoing research and monitoring efforts are crucial for informing future Wyoming otter management plans. Areas like the Snake River and Green River basins are known to support relatively healthy populations, while other regions show evidence of decline. Understanding these variations is key to targeted conservation efforts.
Effective Conservation Strategies for Wyoming Otters
Effective Wyoming otter management requires a multi-pronged approach incorporating several key strategies:
Habitat Restoration and Protection
Protecting and restoring crucial otter habitats is fundamental. This involves:
- Riparian Zone Restoration: Re-establishing and protecting the vegetation along riverbanks provides crucial habitat and food sources for otters.
- Wetland Conservation: Protecting and restoring wetlands increases biodiversity and provides essential habitat.
- Land Acquisition and Conservation Easements: Protecting critical habitat through land acquisition or easements prevents further habitat loss and fragmentation.
- Collaboration with Landowners: Engaging landowners in conservation efforts is vital for successful habitat protection on private lands. This can involve offering incentives for implementing conservation practices or providing technical assistance.
Pollution Control and Water Quality Improvement
Reducing pollution is vital for protecting otters and their ecosystems. Strategies include:
- Stricter Regulations on Industrial Discharge: Implementing and enforcing stricter regulations on industrial wastewater discharge reduces the amount of harmful pollutants entering waterways.
- Best Management Practices for Agriculture: Promoting and implementing best management practices in agriculture minimizes agricultural runoff and reduces pollutant loading in rivers and streams.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about the importance of water quality and the impact of pollution on wildlife.
Disease Management and Monitoring
Monitoring otter health and disease prevalence is crucial:
- Disease Surveillance: Implementing effective disease surveillance programs allows for early detection and management of outbreaks.
- Veterinary Care: Providing veterinary care for injured or sick otters can help to improve survival rates.
- Research on Disease Transmission: Further research on the transmission of diseases among otters is needed to develop effective mitigation strategies.
The Role of Public Awareness and Community Engagement in Wyoming Otter Management
Public education and community involvement are essential for successful Wyoming otter management. Strategies include:
- Educational Programs and Outreach: Developing and implementing educational programs and outreach initiatives to raise public awareness about otters and their conservation needs.
- Citizen Science Projects: Engaging the public in citizen science projects such as otter monitoring can gather valuable data and increase public engagement.
- Collaboration with Local Communities: Working with local communities and stakeholders to foster a sense of ownership and responsibility for otter conservation.
Securing the Future of Wyoming Otter Management
The future of Wyoming’s otters hinges on effective management and community engagement. Addressing habitat loss, pollution, and disease requires a collaborative effort between government agencies, conservation organizations, and the public. By implementing the strategies discussed above, we can work towards a sustainable future for Wyoming’s otter populations. Learn more about how you can contribute to Wyoming otter conservation today! Contact the Wyoming Game and Fish Department and other relevant conservation organizations for more information and opportunities to get involved. [Insert links to relevant organizations here].

Featured Posts
-
 From Anfield To Hout Bay Klopps Influence On A South African Club
May 22, 2025
From Anfield To Hout Bay Klopps Influence On A South African Club
May 22, 2025 -
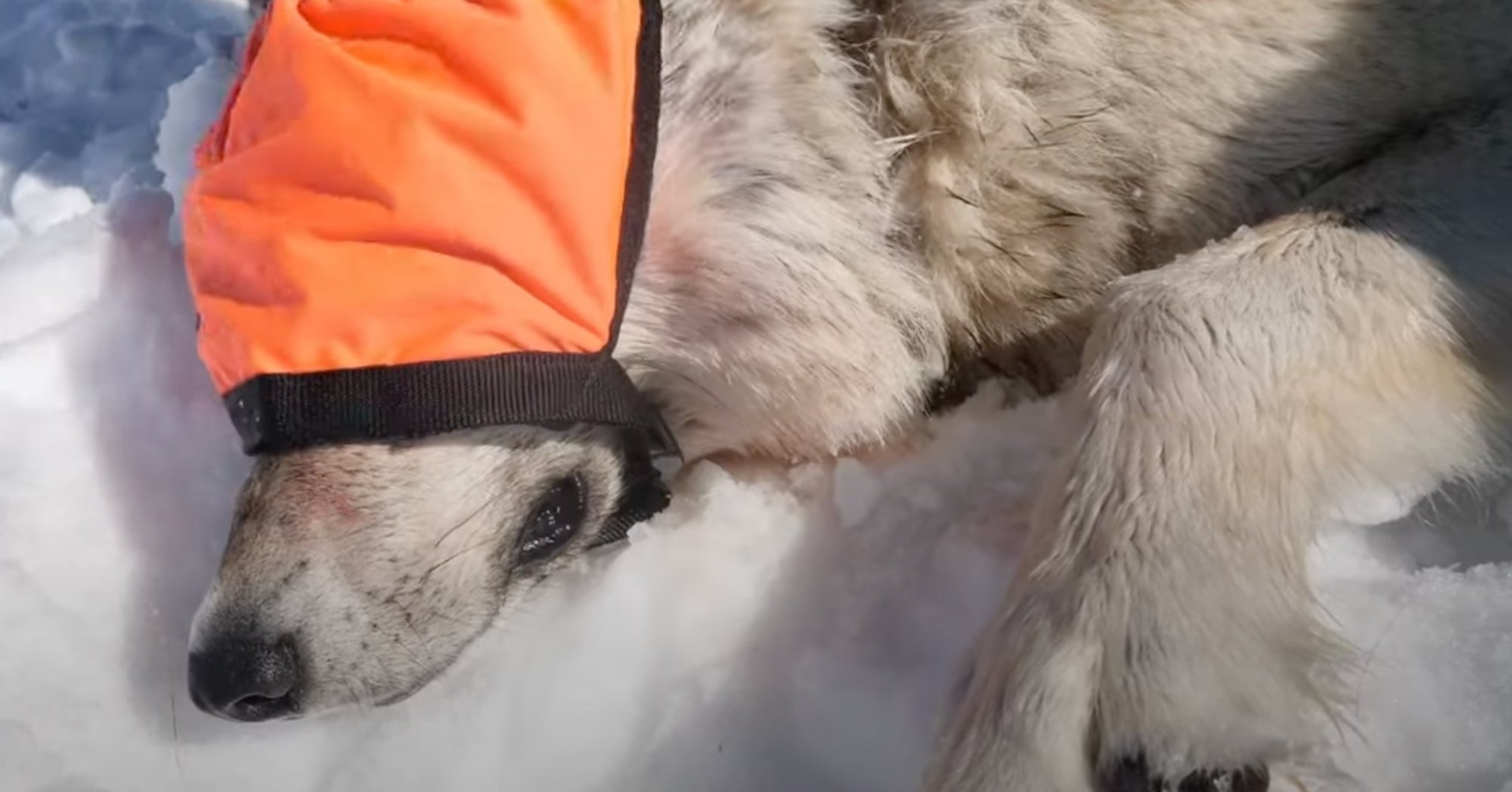 Second Gray Wolf From Colorado Reintroduction Program Dies In Wyoming
May 22, 2025
Second Gray Wolf From Colorado Reintroduction Program Dies In Wyoming
May 22, 2025 -
 Abn Amro Rapport Te Grote Afhankelijkheid Van Goedkope Arbeidsmigranten In De Voedingsindustrie
May 22, 2025
Abn Amro Rapport Te Grote Afhankelijkheid Van Goedkope Arbeidsmigranten In De Voedingsindustrie
May 22, 2025 -
 Adam Ramey Of Dropout Kings Passes Away At 31 A Tragic Loss
May 22, 2025
Adam Ramey Of Dropout Kings Passes Away At 31 A Tragic Loss
May 22, 2025 -
 Digital Detox For Families Your Guide To A Screen Free Week
May 22, 2025
Digital Detox For Families Your Guide To A Screen Free Week
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
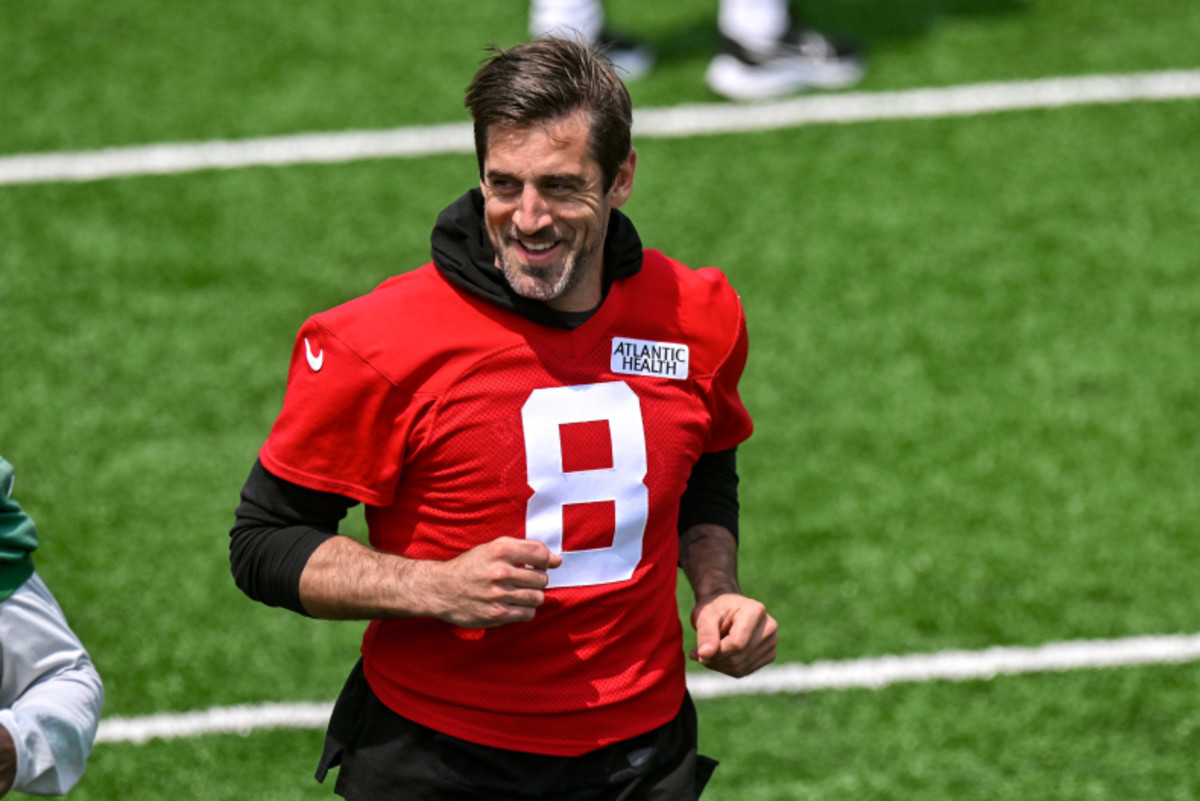 Aaron Rodgers At Steelers Training Camp Speculation And Analysis
May 22, 2025
Aaron Rodgers At Steelers Training Camp Speculation And Analysis
May 22, 2025 -
 Steelers Fans Face Potential Ireland Matchup Disappointment
May 22, 2025
Steelers Fans Face Potential Ireland Matchup Disappointment
May 22, 2025 -
 Aaron Rodgers Visits Steelers Training Facility What Does It Mean
May 22, 2025
Aaron Rodgers Visits Steelers Training Facility What Does It Mean
May 22, 2025 -
 Analyzing A Potential Steelers Trade For An Nfc Quarterback
May 22, 2025
Analyzing A Potential Steelers Trade For An Nfc Quarterback
May 22, 2025 -
 Unlikely Trade Steelers Consider Nfc Quarterback Acquisition
May 22, 2025
Unlikely Trade Steelers Consider Nfc Quarterback Acquisition
May 22, 2025
