AI Thinking: More Hype Than Substance? A Critical Analysis

Table of Contents
The Current State of AI: Narrow vs. General Intelligence
The field of AI is broadly divided into two categories: narrow AI (ANI) and general AI (AGI). ANI, also known as weak AI, refers to AI systems designed to perform specific tasks. These systems excel within their defined parameters, often demonstrating impressive capabilities in areas like image recognition, natural language processing, and game playing. Examples include AI-powered medical diagnosis tools, spam filters, and self-driving car systems. However, it's crucial to understand that ANI's expertise is entirely task-specific. These systems lack the general understanding and adaptability that characterize human intelligence.
ANI excels at specific tasks but lacks general understanding.
AGI, on the other hand, represents artificial general intelligence—a hypothetical AI possessing human-level cognitive abilities. This includes the capacity for reasoning, problem-solving, learning, and adapting across a wide range of tasks and environments. AGI remains firmly in the realm of theoretical possibility; we are far from creating truly general-purpose AI. Current AI relies heavily on vast datasets and immense computational power, limiting its adaptability and flexibility beyond its programmed domain.
AGI remains a theoretical concept, far from realization.
Current AI is heavily reliant on vast datasets and computational power.
Exaggerated Claims and Misconceptions in AI Marketing
The marketing of AI technologies often oversells their capabilities, contributing to the hype surrounding "AI thinking." Companies frequently use the term "AI" to describe systems that employ sophisticated algorithms but fall far short of genuine intelligence. This misleading representation fosters unrealistic expectations. For example, a system that can accurately predict customer preferences based on past purchases is often labeled as possessing "AI thinking," even though its capabilities are limited to statistical analysis and pattern recognition.
Anthropomorphizing AI leads to unrealistic expectations.
Marketing often conflates sophisticated algorithms with true intelligence.
Ethical considerations are often overlooked in the rush to commercialize AI.
Furthermore, the anthropomorphism of AI—attributing human-like qualities to machines—contributes to the misconception of AI consciousness and sentience. This leads to unrealistic fears and hopes about AI's potential impact on society. The ethical implications of AI development and deployment are often overshadowed by the pursuit of commercial success. Responsible AI development necessitates careful consideration of potential biases and unintended consequences.
The Reality of AI Thinking: Pattern Recognition and Statistical Analysis
In reality, current AI excels primarily at pattern recognition and statistical analysis. Machine learning models identify patterns in vast datasets, enabling them to make predictions and classifications. However, this proficiency does not equate to true "thinking." AI algorithms learn from data, identifying correlations and making inferences based on statistical probabilities. They lack genuine understanding or the ability to reason in the way humans do.
AI systems are highly dependent on the quality and bias of training data.
AI struggles with tasks requiring common sense reasoning and contextual understanding.
AI decisions are often opaque and difficult to interpret.
Consider the limitations of AI in handling ambiguous situations or unexpected inputs. Unlike humans, who can leverage common sense and contextual understanding to navigate uncertainty, AI often struggles in such scenarios. This highlights the fundamental difference between sophisticated algorithms and genuine intelligence. The decisions made by AI systems are often opaque, making it challenging to understand the rationale behind their conclusions.
The Future of AI Thinking: Potential and Challenges
Despite its current limitations, the future of AI holds significant potential. Advancements in explainable AI (XAI) aim to increase the transparency of AI algorithms, making their decision-making processes more understandable and accountable. This is crucial for building trust and ensuring responsible AI development. However, achieving AGI presents immense challenges.
Increased transparency in AI algorithms is crucial for trust and accountability.
Addressing biases in AI systems is essential for fairness and equity.
Collaboration between researchers, policymakers, and the public is vital for responsible AI.
Technical limitations, ethical concerns, and the sheer complexity of replicating human-level intelligence pose significant hurdles. The development of AGI necessitates careful consideration of ethical implications and potential societal impacts. Responsible AI development requires collaboration between researchers, policymakers, and the public to ensure that AI technologies are used ethically and for the benefit of humanity. Addressing biases embedded within AI systems is crucial for fairness and equity.
Conclusion: Separating Fact from Fiction in AI Thinking
In conclusion, while current AI systems demonstrate impressive capabilities in specific domains, the notion of "AI thinking" often represents an oversimplification and, in many cases, misleading marketing. Current AI excels at pattern recognition and statistical analysis, but it lacks the general intelligence, reasoning abilities, and contextual understanding of humans. Approaching claims about AI thinking with a healthy dose of skepticism is essential. The future of AI holds both immense potential and considerable challenges, demanding careful consideration of ethical implications and responsible development. We must engage in informed discussions about the future of artificial intelligence, promoting further research and critical analysis of AI thinking and its implications. Let's move beyond the hype and focus on building AI systems that are both powerful and beneficial to humanity.

Featured Posts
-
 Nyt Spelling Bee Solutions April 3rd 2025 Complete Guide
Apr 29, 2025
Nyt Spelling Bee Solutions April 3rd 2025 Complete Guide
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Why Older Viewers Are Choosing You Tube For Entertainment
Apr 29, 2025
Why Older Viewers Are Choosing You Tube For Entertainment
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Avanzamenti Nella Parita Sul Posto Di Lavoro Una Realta In Continua Evoluzione
Apr 29, 2025
Avanzamenti Nella Parita Sul Posto Di Lavoro Una Realta In Continua Evoluzione
Apr 29, 2025 -
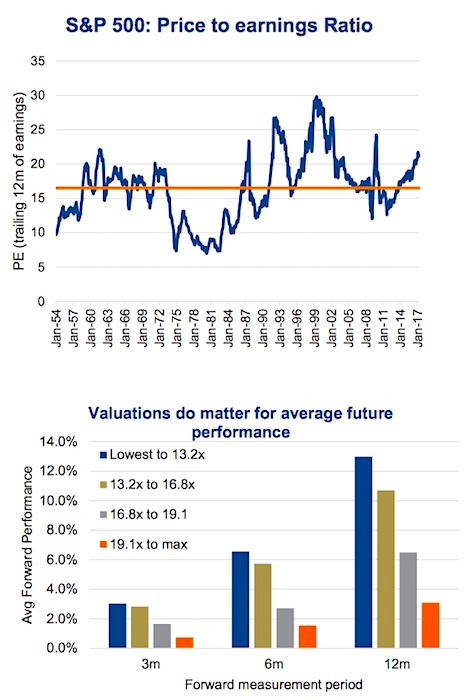 Understanding High Stock Market Valuations A Bof A Analysis
Apr 29, 2025
Understanding High Stock Market Valuations A Bof A Analysis
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Winning Names For Minnesota Snow Plows Announced
Apr 29, 2025
Winning Names For Minnesota Snow Plows Announced
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Uncovering Alex Winters Early Work Pre Freaked Mtv Sketches
May 12, 2025
Uncovering Alex Winters Early Work Pre Freaked Mtv Sketches
May 12, 2025 -
 The End Of An Era Thomas Muellers Farewell Match At Allianz Arena
May 12, 2025
The End Of An Era Thomas Muellers Farewell Match At Allianz Arena
May 12, 2025 -
 The Forgotten Mtv Comedy Shows Alex Winter Created Before Freaked
May 12, 2025
The Forgotten Mtv Comedy Shows Alex Winter Created Before Freaked
May 12, 2025 -
 25 Years At Allianz Arena Thomas Muellers Emotional Goodbye
May 12, 2025
25 Years At Allianz Arena Thomas Muellers Emotional Goodbye
May 12, 2025 -
 Bayern Munich Legend Thomas Mueller A Poignant Farewell After 25 Years
May 12, 2025
Bayern Munich Legend Thomas Mueller A Poignant Farewell After 25 Years
May 12, 2025
