Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) And Rising Sea Levels In The US
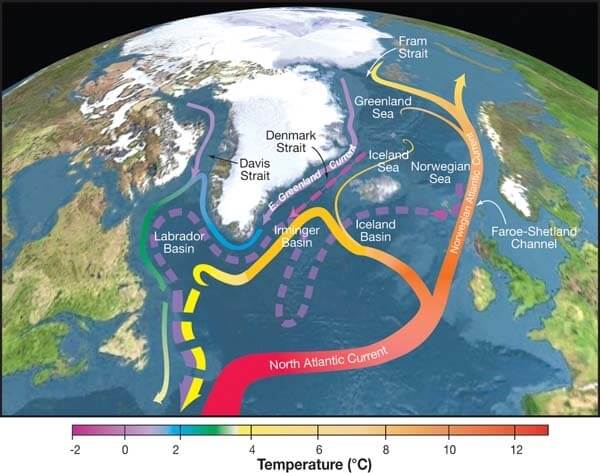
Table of Contents
Understanding the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC)
The Mechanics of AMOC
The AMOC is a complex system of interconnected ocean currents acting like a massive conveyor belt, transporting warm water from the tropics northward along the US East Coast via the Gulf Stream and North Atlantic Current. As this warm water reaches higher latitudes, it cools, becomes denser, and sinks to the ocean floor. This cold, deep water then flows southward, completing the circulation loop. [Insert diagram of AMOC here]. This process is essential for regulating global heat distribution and influencing weather patterns worldwide.
AMOC's Influence on Global Climate
AMOC exerts a significant influence on global climate, particularly in the North Atlantic region and consequently on the climate of the US. The warm Gulf Stream current, a key component of AMOC, keeps temperatures along the US East Coast significantly milder than other regions at similar latitudes. Disruptions to this vital current system can trigger significant climate shifts with far-reaching implications.
- AMOC acts as a giant conveyor belt of heat. It transports vast amounts of heat from the tropics towards the poles, influencing regional and global temperatures.
- Disruption to AMOC can lead to significant climate shifts. A weakening AMOC can alter weather patterns, leading to colder temperatures in some regions and increased storminess in others.
- The Gulf Stream's influence on US East Coast temperatures. The Gulf Stream moderates temperatures along the East Coast, making it considerably warmer than other areas at similar latitudes.
- Connection between AMOC and regional weather patterns (e.g., hurricanes). Changes in AMOC strength may influence the intensity and frequency of hurricanes affecting the US.
The Link Between AMOC and Rising Sea Levels in the US
Weakening AMOC and its Consequences
A weakening AMOC is directly linked to rising sea levels along the US East Coast. Several mechanisms contribute to this effect. Firstly, a slowdown in the northward flow of warm water leads to less heat being transported away from the tropics, resulting in thermal expansion of seawater and a rise in sea level. Secondly, changes in ocean currents can alter the distribution of water mass, further impacting sea levels regionally.
Regional Impacts of Sea Level Rise on the US
The consequences of sea level rise driven by AMOC changes are severe and geographically disparate. Coastal areas of the US, particularly Florida, the Mid-Atlantic states, and other low-lying regions, are particularly vulnerable.
- Increased coastal flooding and erosion. Higher sea levels exacerbate the impact of storm surges and high tides, leading to more frequent and severe coastal flooding and erosion.
- Saltwater intrusion into freshwater aquifers. Rising sea levels contaminate freshwater sources, impacting drinking water supplies and agriculture.
- Displacement of coastal communities. Rising waters threaten to displace populations living in vulnerable coastal areas.
- Damage to infrastructure (roads, bridges, buildings). Coastal infrastructure is vulnerable to damage from increased flooding and erosion.
- Economic impacts on tourism and fishing industries. Sea level rise threatens coastal economies reliant on tourism and fishing.
Scientific Evidence and Future Projections
Current Research on AMOC
Scientists are actively monitoring AMOC using a variety of methods, including satellite observations, oceanographic buoys, and sophisticated climate models. Numerous studies have indicated a potential weakening of AMOC, although the extent and precise causes are still under investigation. [Cite relevant scientific studies and reports here].
Predicting Future Sea Level Rise
Predicting future sea level rise is complex, with uncertainties arising from the intricate interactions between AMOC, climate change, and other factors. However, climate models project a continued rise in sea levels along the US coast, with a significant contribution potentially attributed to AMOC weakening.
- Analysis of historical AMOC data. Historical data reveals long-term trends and variations in AMOC strength.
- Climate models used for future projections. Advanced climate models simulate the complex interactions within the climate system to project future sea level changes.
- Potential scenarios for AMOC weakening and associated sea level rise. Different scenarios are modeled, ranging from moderate to severe weakening of AMOC, each resulting in different projections of sea level rise.
- The role of human activities in accelerating AMOC changes. Human-induced climate change, primarily through greenhouse gas emissions, is considered a significant driver of AMOC changes.
Conclusion
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) plays a vital role in regulating global climate and sea levels. Scientific evidence suggests a potential weakening of AMOC, which is projected to contribute significantly to rising sea levels along the US coastline. This poses a substantial threat to coastal communities, infrastructure, and the US economy. The consequences, including increased flooding, erosion, and displacement of populations, are far-reaching and require urgent attention. Addressing climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions is crucial to mitigating the potential for further AMOC disruption and the resulting sea-level rise. We must actively pursue research, invest in resilient infrastructure, and implement effective adaptation strategies to safeguard our vulnerable coastal areas. Learn more about the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) and its impact, and support initiatives focused on climate change mitigation to protect the US coastline from the devastating effects of rising sea levels.

Featured Posts
-
 Trumps Offer Trip To China For Meeting With Xi Jinping
May 18, 2025
Trumps Offer Trip To China For Meeting With Xi Jinping
May 18, 2025 -
 Ubers Self Driving Gamble Etf Investment Opportunities
May 18, 2025
Ubers Self Driving Gamble Etf Investment Opportunities
May 18, 2025 -
 The Blake Lively Dispute Selena Gomez Delivers A Wake Up Call To Taylor Swift
May 18, 2025
The Blake Lively Dispute Selena Gomez Delivers A Wake Up Call To Taylor Swift
May 18, 2025 -
 Ftcs Monopoly Case Against Meta A Shift In Strategy
May 18, 2025
Ftcs Monopoly Case Against Meta A Shift In Strategy
May 18, 2025 -
 Ufc Vegas 106 Morales Earns Second Straight Performance Bonus
May 18, 2025
Ufc Vegas 106 Morales Earns Second Straight Performance Bonus
May 18, 2025
