Bank Of Canada Faces Tough Choices Amid Rising Core Inflation
Table of Contents
The Persistent Problem of Core Inflation
Core inflation, a measure of inflation that excludes volatile components like food and energy, remains a persistent concern for the Bank of Canada. Understanding core inflation is crucial to grasping the central bank's current predicament. While headline inflation may fluctuate, persistent core inflation signals underlying inflationary pressures within the Canadian economy. This indicates that price increases are becoming embedded in the system, making them harder to control.
- Definition of core inflation and its components: Core inflation measures the price changes of goods and services excluding those most susceptible to short-term fluctuations. Different methodologies exist, but common exclusions include food and energy prices.
- Current core inflation rate in Canada and its trajectory: As of [insert most recent data], Canada's core inflation rate stands at [insert current rate]%, [insert information regarding upward or downward trend]. This figure is [higher/lower] than the Bank of Canada's target of 2%.
- Reasons for the persistence of core inflation: The persistence of core inflation is multifaceted. Factors include strong wage pressures as employees seek to keep pace with rising living costs, ongoing supply chain disruptions leading to higher production costs, and robust consumer demand contributing to demand-pull inflation.
- Comparison to other developed nations' inflation rates: Compared to other G7 nations, Canada's core inflation rate is [insert comparison – higher, lower, similar] indicating [insert analysis of the comparison, e.g., relatively strong/weak performance compared to peers].
The Bank of Canada's Current Monetary Policy Strategy
The Bank of Canada's current monetary policy strategy centers on managing inflation through interest rate hikes and quantitative tightening. The goal is to cool down the economy and reduce inflationary pressures without triggering a significant economic downturn.
- Summary of recent interest rate changes: The Bank of Canada has [summarize recent interest rate changes, e.g., increased the policy interest rate by X basis points in Y meetings].
- Explanation of the Bank of Canada's inflation target: The Bank of Canada aims to maintain inflation at an average of 2% over the medium term. This target serves as a benchmark for monetary policy decisions.
- Discussion of the potential impact of quantitative tightening: Quantitative tightening involves reducing the Bank of Canada's balance sheet by allowing government bonds to mature without immediate reinvestment. This reduces the money supply, further dampening inflationary pressures.
- Analysis of the effectiveness of current monetary policy: The effectiveness of the current policy is still under evaluation. While interest rate hikes have shown some signs of slowing economic growth, their impact on core inflation remains to be fully seen. Lag effects in monetary policy mean that the full impact may not be apparent for several months.
The Risks of Aggressive Interest Rate Hikes
While interest rate hikes are a necessary tool to combat inflation, aggressive increases carry significant risks, primarily the potential for a recession. The impact on the Canadian economy needs careful consideration.
- Impact of higher interest rates on consumer spending and business investment: Higher borrowing costs lead to reduced consumer spending and business investment, slowing economic activity. This is particularly impactful on sectors sensitive to interest rate changes, such as housing.
- Potential for increased unemployment: A slowing economy can lead to job losses as businesses cut back on hiring and investment. This contributes to a potential rise in unemployment.
- Risk of a housing market correction: Higher interest rates significantly impact the housing market, potentially triggering a correction characterized by falling prices and reduced sales activity.
- Analysis of the potential severity of a recession: The severity of a potential recession depends on several factors, including the pace of interest rate increases, the resilience of the Canadian economy, and the global economic climate. A prolonged period of high interest rates would increase the likelihood of a deeper recession.
Alternative Approaches and Potential Outcomes
The Bank of Canada is not limited to aggressive interest rate hikes. Alternative approaches and a combination of monetary and fiscal policies should be considered.
- Potential for a pause or slowdown in interest rate hikes: A pause or slowdown in interest rate increases could allow the economy to absorb the impact of previous hikes and assess their effectiveness. This approach risks higher inflation remaining persistent.
- Role of fiscal policy in mitigating inflationary pressures: Fiscal policy, through government spending and taxation, can play a supplementary role in managing inflation. Targeted measures could alleviate inflationary pressures without significantly hindering economic growth.
- Discussion of supply-side solutions to address inflation: Addressing supply-side bottlenecks through infrastructure investments or trade policy adjustments could enhance productivity and alleviate inflationary pressures from supply shortages.
- Analysis of the potential long-term economic consequences of different policy choices: Different policy choices have varied long-term consequences for the Canadian economy. A balance must be struck between controlling inflation and supporting sustainable economic growth and employment.
Conclusion
The Bank of Canada faces a complex challenge in balancing inflation control with sustained economic growth. The persistence of core inflation necessitates decisive action, but aggressive interest rate hikes carry the significant risk of triggering a recession. Alternative approaches and a careful assessment of the long-term economic consequences are essential. The Bank of Canada's decisions regarding rising core inflation will significantly impact the Canadian economy. Stay informed about the evolving economic situation and the central bank's response to effectively navigate these challenging times. Follow our updates on the Bank of Canada and its ongoing efforts to manage rising core inflation.

Featured Posts
-
 Partial Collapse Of 600 Year Old Chinese Tower Impact On Tourism And Preservation
May 22, 2025
Partial Collapse Of 600 Year Old Chinese Tower Impact On Tourism And Preservation
May 22, 2025 -
 Overcoming The Love Monster A Path To Healing And Growth
May 22, 2025
Overcoming The Love Monster A Path To Healing And Growth
May 22, 2025 -
 Solved The 21 Year Old Peppa Pig Enigma
May 22, 2025
Solved The 21 Year Old Peppa Pig Enigma
May 22, 2025 -
 Liverpool And Liga Inggris 2024 2025 Siapa Pelatih Yang Akan Membawa Mereka Juara
May 22, 2025
Liverpool And Liga Inggris 2024 2025 Siapa Pelatih Yang Akan Membawa Mereka Juara
May 22, 2025 -
 Festival Le Bouillon Clisson Programmation Et Engagement
May 22, 2025
Festival Le Bouillon Clisson Programmation Et Engagement
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Mid Hudson Valley Gas Prices A Sharp Increase
May 22, 2025
Mid Hudson Valley Gas Prices A Sharp Increase
May 22, 2025 -
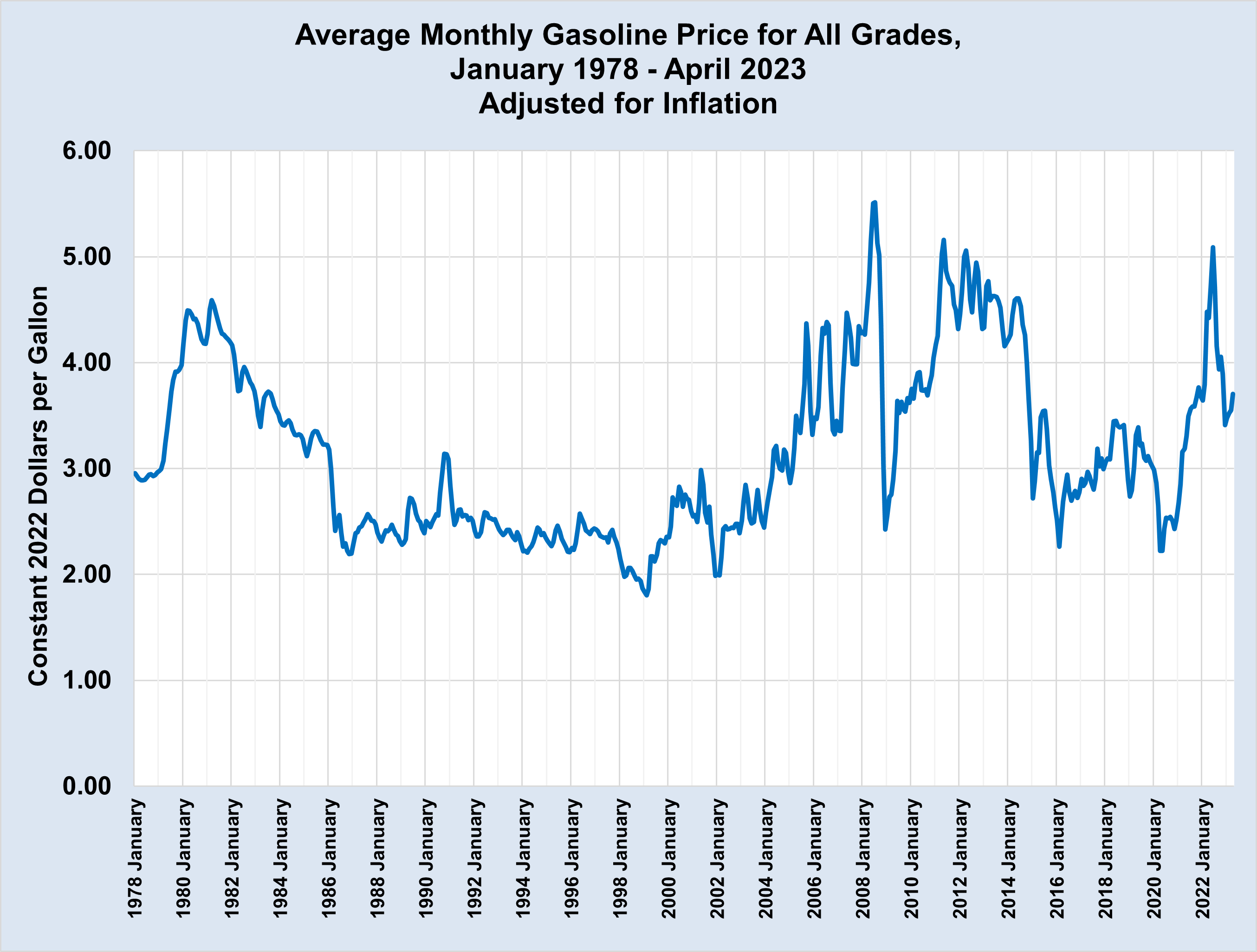 Average Gas Price Increase Up Nearly 20 Cents A Gallon
May 22, 2025
Average Gas Price Increase Up Nearly 20 Cents A Gallon
May 22, 2025 -
 Gasoline Prices Surge In Mid Hudson Valley
May 22, 2025
Gasoline Prices Surge In Mid Hudson Valley
May 22, 2025 -
 National Average Gas Price Jumps Almost 20 Cents
May 22, 2025
National Average Gas Price Jumps Almost 20 Cents
May 22, 2025 -
 Major Blaze Consumes 600 Foot Chicken Barn In Pennsylvania
May 22, 2025
Major Blaze Consumes 600 Foot Chicken Barn In Pennsylvania
May 22, 2025
