BRB's Acquisition Of Banco Master: A Public-Private Fusion In Brazil's Banking Sector

Table of Contents
Understanding the Players: BRB and Banco Master
BRB (Banco de Brasília), a publicly-owned bank, boasts a long history serving the Federal District and surrounding areas. Its extensive branch network and strong public sector backing provide a solid foundation for growth and stability. Before the acquisition, BRB held a significant market share within its region, primarily focusing on traditional banking services.
Banco Master, on the other hand, operated as a privately-owned bank with a more niche market focus. Known for its strong digital presence and innovative approach to financial technology, Banco Master catered to a different customer segment than BRB. The contrast between the two banks is striking:
- BRB: Strong public sector backing, extensive branch network in Brasília, traditional banking focus, established customer base.
- Banco Master: Private ownership, strong digital presence, niche market focus, innovative fintech offerings, younger customer demographic.
This difference in strengths and operational styles presented both opportunities and challenges for a successful merger. The combination of BRB’s established infrastructure and Banco Master’s tech-driven approach promises a unique banking experience.
Details of the Acquisition: Terms and Conditions
While specific financial details of the BRB acquisition of Banco Master may not be fully public, the process itself is noteworthy. It is understood that the acquisition involved regulatory approvals from the relevant Brazilian authorities, including the Central Bank of Brazil (Banco Central do Brasil). The process likely involved due diligence, negotiations, and a final agreement on the acquisition price and terms. Further investigation is required to obtain detailed information on the acquisition timeline and the involvement of any competing bidders.
Key acquisition details (once publicly available) will include:
- Acquisition price: The total amount paid by BRB for Banco Master's assets and liabilities.
- Timeline of the acquisition process: The duration from initial negotiations to final closure.
- Regulatory bodies involved: A list of all Brazilian regulatory agencies that approved the transaction.
- Integration plan: How BRB plans to integrate Banco Master’s operations, systems, and customer base.
The success of this banking consolidation strategy will heavily depend on a well-executed integration plan.
Implications for the Brazilian Banking Sector
The BRB acquisition of Banco Master has several implications for the Brazilian banking sector. The merger will undoubtedly increase BRB's market share, particularly in areas where Banco Master had a strong presence. This increased market share could lead to greater competition, potentially benefiting consumers through:
- Increased access to financial services: Expansion into new markets and customer segments.
- Improved service offerings: Combining the strengths of both banks could result in enhanced products and services.
- Potentially lower fees: Economies of scale from the merger might lead to reduced costs for consumers.
However, some risks are associated with this consolidation:
- Concerns about reduced competition: A dominant player in the market could potentially lead to less choice and innovation.
- Potential job losses: Overlapping roles and functions might result in redundancies.
The long-term effects on the Brazilian banking landscape depend on several factors, including the integration process, regulatory oversight, and the competitive response from other banks. The potential for changes in interest rates and banking fees is also a significant consideration.
The Public-Private Partnership Model
The BRB-Banco Master fusion is a prime example of a public-private partnership (PPP) in Brazil’s banking sector. This model combines the resources and expertise of a public entity (BRB) with the innovation and market focus of a private entity (Banco Master). The advantages of this model include leveraging public sector stability with private sector efficiency, potentially leading to a more resilient and dynamic banking system. However, challenges might include differing goals and management styles between public and private partners, and potential conflicts of interest. Careful analysis of successful and unsuccessful PPP models in the Brazilian and global banking sectors can provide valuable insights into the long-term success of this particular merger.
Conclusion
The BRB acquisition of Banco Master represents a significant development in Brazil’s banking sector. This public-private partnership has the potential to reshape the market landscape, impacting competition, consumer access, and the overall economic climate. While the long-term effects remain to be seen, this merger offers valuable insights into the evolving dynamics of the Brazilian financial industry. Further analysis is needed to fully understand the long-term implications of this substantial public-private fusion in Brazil's banking industry. Stay informed about the evolving landscape and the ongoing impact of the BRB and Banco Master merger. Learn more about the implications of this key acquisition and its effects on the Brazilian economy.

Featured Posts
-
 2 Fall On Amsterdam Stock Exchange Following Trumps Tariff Announcement
May 24, 2025
2 Fall On Amsterdam Stock Exchange Following Trumps Tariff Announcement
May 24, 2025 -
 Annie Kilners Posts Following Kyle Walkers Night Out Allegations Of Poisoning
May 24, 2025
Annie Kilners Posts Following Kyle Walkers Night Out Allegations Of Poisoning
May 24, 2025 -
 Ferrari 296 Speciale Potencia Hibrida De 880 Cv Revelada
May 24, 2025
Ferrari 296 Speciale Potencia Hibrida De 880 Cv Revelada
May 24, 2025 -
 The 10 Fastest Ferrari Production Cars Lap Times
May 24, 2025
The 10 Fastest Ferrari Production Cars Lap Times
May 24, 2025 -
 Joy Crookes Carmen A Deep Dive Into The New Single
May 24, 2025
Joy Crookes Carmen A Deep Dive Into The New Single
May 24, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Apple Stock Outlook Post Q2 Earnings Report
May 24, 2025
Apple Stock Outlook Post Q2 Earnings Report
May 24, 2025 -
 Strengthening Ties Bangladeshs European Partnerships For Economic Growth
May 24, 2025
Strengthening Ties Bangladeshs European Partnerships For Economic Growth
May 24, 2025 -
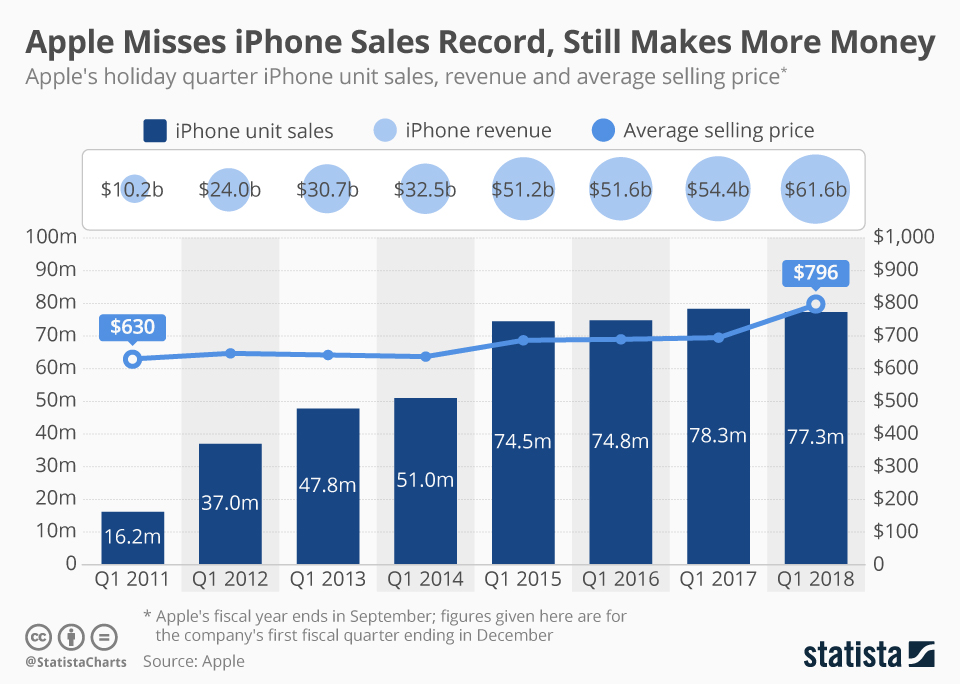 Apple Stock Q2 Earnings I Phone Sales And Revenue Growth
May 24, 2025
Apple Stock Q2 Earnings I Phone Sales And Revenue Growth
May 24, 2025 -
 Apple Stock Performance Exceeding Q2 Expectations
May 24, 2025
Apple Stock Performance Exceeding Q2 Expectations
May 24, 2025 -
 Apple Stock Soars I Phone Sales Drive Strong Q2 Results
May 24, 2025
Apple Stock Soars I Phone Sales Drive Strong Q2 Results
May 24, 2025
