Canadian Economists Predict Deeper Recession Despite Tariff Reductions
Table of Contents
Factors Contributing to the Predicted Deeper Recession
Several interconnected factors contribute to the increasingly pessimistic outlook for the Canadian economy, suggesting a deeper recession than previously forecast.
Persistent Inflation
Stubbornly high inflation rates continue to plague the Canadian economy, significantly impacting consumer spending and business investment.
- Rising interest rates: The Bank of Canada's efforts to curb inflation through interest rate hikes have increased borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, dampening investment and spending.
- Decreased consumer confidence: High inflation erodes purchasing power, leading to decreased consumer confidence and reduced spending on non-essential goods and services. Statistics Canada's consumer confidence index reflects this trend.
- Supply chain disruptions: Lingering supply chain issues contribute to inflationary pressures, further hindering economic growth.
The current inflation rate in Canada, as reported by Statistics Canada, remains significantly above the Bank of Canada's target, indicating persistent inflationary pressures. This prolonged period of high inflation is unprecedented in recent Canadian economic history, demanding a closer look at its sustained impact.
Global Economic Slowdown
The Canadian economy is deeply intertwined with the global economy. A slowdown in major trading partners, coupled with geopolitical instability, significantly impacts Canada's economic performance.
- Slowdown in major trading partners: Recessions or slowdowns in the US and European Union, key trading partners for Canada, directly impact Canadian exports and economic growth.
- Geopolitical instability: The ongoing war in Ukraine, along with other geopolitical uncertainties, creates volatility in global markets, affecting commodity prices and investor confidence.
- Energy price volatility: Fluctuations in global energy prices, particularly oil and natural gas, significantly impact Canada's energy sector and overall economic stability.
The interconnectedness of the global economy means that a slowdown in one region can quickly ripple through others, making Canada vulnerable to external economic shocks.
Housing Market Correction
The ongoing correction in the Canadian housing market presents another significant headwind for the economy. Declining house prices and reduced construction activity have ripple effects throughout the economy.
- Decreased housing prices: Falling house prices reduce household wealth, leading to decreased consumer spending and potentially impacting the financial health of some households.
- Reduced construction activity: The slowdown in the housing market translates into reduced construction activity, impacting employment in the construction sector and related industries.
- Impact on consumer wealth: The decline in housing values diminishes the net worth of many Canadians, impacting their willingness to spend and invest.
This correction, after years of rapid price appreciation, is a significant factor contributing to the predicted deeper recession.
Limited Impact of Tariff Reductions
While the recent implementation of tariff reductions was intended to stimulate the economy, their impact is likely to be limited in offsetting the other negative economic forces at play.
Insufficient Stimulus
The magnitude of the tariff cuts may be insufficient to counteract the significant economic headwinds facing Canada.
- Magnitude of tariff cuts: The scale of tariff reductions might be too small to significantly boost consumer spending or business investment.
- Timing of implementation: The timing of the tariff reductions might not coincide with the economic downturn, limiting their effectiveness.
- Competing economic pressures: Other negative economic forces, such as inflation and global slowdown, overshadow the positive effects of tariff reductions.
Data comparing the scale of tariff reductions to the overall size of the Canadian economy is necessary to properly assess their impact.
Consumer and Business Sentiment
Low consumer and business confidence can negate any positive effects stemming from tariff reductions.
- Surveys of consumer and business confidence: Surveys consistently show low levels of consumer and business confidence, indicating a lack of optimism about future economic prospects.
- Impact on investment decisions: Low confidence discourages businesses from investing and expanding, limiting job creation and economic growth.
Without a significant boost in confidence, the positive effects of tariff reductions are likely to be muted.
Other Economic Headwinds
Additional economic challenges further amplify the negative outlook and limit the effectiveness of tariff reductions.
- Labor shortages: Persistent labor shortages constrain business growth and productivity, hindering economic expansion.
- Rising energy costs: Higher energy costs increase production costs for businesses and reduce household disposable income, dampening economic activity.
- Geopolitical risks: Ongoing geopolitical uncertainties add to the overall economic uncertainty, further reducing investment and growth.
These combined challenges create a challenging economic environment, making the task of stimulating growth significantly more difficult.
Potential Consequences for Canadian Businesses and Consumers
The predicted deeper recession carries significant consequences for Canadian businesses and consumers.
Increased Unemployment
An economic slowdown often leads to job losses and rising unemployment rates.
- Impact on specific sectors: Sectors most vulnerable to economic downturns, such as manufacturing and construction, may experience disproportionately high job losses.
- Regional variations in unemployment: Unemployment rates may vary across different regions of Canada, depending on their economic structure and resilience.
The correlation between economic slowdowns and job losses is well-established, and this recession is likely to be no exception.
Reduced Consumer Spending
Economic uncertainty tends to lead to reduced consumer spending, potentially exacerbating the recession.
- Impact on retail sales: A decline in consumer spending directly impacts retail sales, potentially leading to business closures and further job losses.
- Consumer debt levels: High consumer debt levels may further constrain spending as households prioritize debt repayment.
Decreased consumer spending creates a vicious cycle, further slowing down economic activity.
Government Response
The Canadian government may implement fiscal and monetary policies to mitigate the recession's impact.
- Fiscal policy measures: The government might increase spending or reduce taxes to stimulate economic activity.
- Monetary policy adjustments: The Bank of Canada might adjust interest rates further to balance inflation and economic growth.
The effectiveness of government intervention will depend on the severity of the recession and the government's ability to implement timely and appropriate policies.
Conclusion: Understanding the Depth of the Predicted Recession in Canada
In summary, leading Canadian economists predict a deeper recession than initially anticipated, despite recent tariff reductions. Significant factors contributing to this pessimistic outlook include persistent inflation, a global economic slowdown, a housing market correction, and the limited impact of tariff reductions. These factors combined suggest a more challenging economic climate than previously foreseen. The potential consequences for Canadian businesses and consumers include increased unemployment and reduced consumer spending, highlighting the need for both governmental and personal preparation.
Stay informed about the evolving economic situation in Canada and prepare for the potential challenges ahead. Understanding the complexities of the Canadian economic recession predictions is crucial for making informed decisions regarding your personal finances and business strategies. Staying informed about the Canadian recession, economic forecast Canada, and the overall Canadian economic outlook is essential during these uncertain times.

Featured Posts
-
 La Carte Blanche L Heritage Intellectuel De Marc Fiorentino
Apr 23, 2025
La Carte Blanche L Heritage Intellectuel De Marc Fiorentino
Apr 23, 2025 -
 Calendario Laboral 16 5 Millones De Espanoles Disfrutaran De Puente El 21 De Abril
Apr 23, 2025
Calendario Laboral 16 5 Millones De Espanoles Disfrutaran De Puente El 21 De Abril
Apr 23, 2025 -
 Analysis Detroit Tigers 5 1 Defeat And Second Series Loss To Brewers
Apr 23, 2025
Analysis Detroit Tigers 5 1 Defeat And Second Series Loss To Brewers
Apr 23, 2025 -
 Ankara Iftar Ve Sahur Saatleri 10 Mart 2025 Pazartesi
Apr 23, 2025
Ankara Iftar Ve Sahur Saatleri 10 Mart 2025 Pazartesi
Apr 23, 2025 -
 Trgovine Otvorene Na Uskrs I Uskrsni Ponedjeljak Gdje Kupiti Sto Vam Treba
Apr 23, 2025
Trgovine Otvorene Na Uskrs I Uskrsni Ponedjeljak Gdje Kupiti Sto Vam Treba
Apr 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Elizabeth Line Strike Dates Planned Action And Route Impacts In February And March
May 10, 2025
Elizabeth Line Strike Dates Planned Action And Route Impacts In February And March
May 10, 2025 -
 Stock Market News Sensex Nifty Record Significant Gains Sector Specific Updates
May 10, 2025
Stock Market News Sensex Nifty Record Significant Gains Sector Specific Updates
May 10, 2025 -
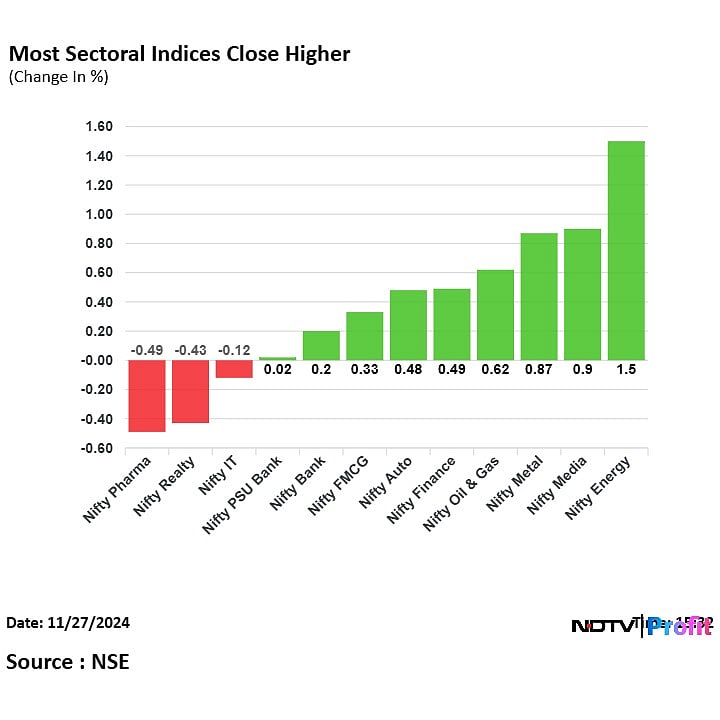 Indian Stock Market Update Sensex Nifty Rally Adani Ports Eternal Performance
May 10, 2025
Indian Stock Market Update Sensex Nifty Rally Adani Ports Eternal Performance
May 10, 2025 -
 Stock Market Today Sensex And Nifty Surge Adani Ports Gains Eternal Declines
May 10, 2025
Stock Market Today Sensex And Nifty Surge Adani Ports Gains Eternal Declines
May 10, 2025 -
 Is It Too Late To Invest In Palantir Stock Before The Predicted 40 Rise In 2025
May 10, 2025
Is It Too Late To Invest In Palantir Stock Before The Predicted 40 Rise In 2025
May 10, 2025
